Abstract
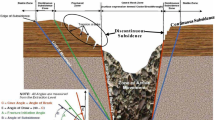
Impoundments of tailings and active surface subsidence zones induced by ore mining were the major environmental problems. The aim of this study was to investigate the technical feasibility of impoundment of tailings using active surface subsidence zones. The self-designed scaled physical model was conducted to investigate the movement laws of tailings under different heights of granular media and tailings, and then drawing ore in these experiments was performed to simulate the mining process. The experimental results showed that the isolated extraction zone and stoping sequence had a primary influence on the doping process of tailings. Besides, when the height of granular media was more than that of the isolated movement zone, the uniform mode of drawing ore could be decreased the amounts of tailings drawn from drawpoints. Meanwhile, the doping process was not impacted by continuously emission of tailings to active surface subsidence zones. Thus, the field test was employed in the Dabeishan Iron Mine and the mining schemes were put forward based on the experimental data. The results showed that the recovery ratio and dilution ratio were 80.9% and 24.3% respectively, and that the scheme established in this paper could be used in practice.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Adiansyah JS, Rosano M, Vink S et al (2015) A framework for a sustainable approach to mine tailings management: disposal strategies. J Clean Prod 108:1050–1062
Araya N, Kraslawski A, Cisternas LA (2020) Towards mine tailings valorization: recovery of critical materials from Chilean mine tailings. J Clean Prod 263:121555
Bock S, Prusek S (2015) Numerical study of pressure on dams in a backfilled mining shaft based on PFC3D code. Comput Geotech 66:230–244
Castro R, Trueman R, Halim A (2017) A study of isolated draw zones in block caving mines by means of a large 3D physical model. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 44(6):860–870
Ding HX, Chen S, Chang S et al (2020) Prediction of surface subsidence extension due to underground caving: a case study of hemushan iron mine in China. Math Probl Eng 815:1–10
Edraki M, Baumgartl T, Manlapig E et al (2014) Designing mine tailings for better environmental, social and economic outcomes: a review of alternative approaches. J Clean Prod 84:411–420
He RX, Ren FY, Tan BH et al (2019) Distribution law of granular lateral pressure in caved ore-rock with limited width. J Northeast Univ Nat Sci 40(3):108–112 (in Chinese)
Hou YP, Liu C, Ding PC et al (2018) Study on solidification effect of heavy metal by tailings cementation and discharging. Adv Eng Sci 50(5):235–242 (in Chinese)
Kiventera J, Piekkari K, Isteri V et al (2019) Solidification/stabilization of gold mine tailings using calcium sulfoaluminate-belite cement. J Clean Prod 2019(239):1–8
Klebercz O, Mayes WM, Anton ÁD et al (2012) Ecotoxicity of fluvial sediments downstream of the ajka red mud spill, hungary. Environ Monit 14(8):2063–2071
Li LC, Tang CA, Zhao XD et al (2014) Block caving-induced strata movement and associated surface subsidence: a numerical study based on a demonstration model. Bull Eng Geol Env 73(4):1165–1182
Li GH, Ren FY, Ding HX et al (2021) A dynamic intersecting arrangement model based on isolated draw zones for stope structure optimization during sublevel caving mining. Math Probl Eng 2021:1
Liu Y (2020) Study of prediction and control method for surface subsidence range by mining influence in the dabeishan iron mine. Northeastern University, Shenyang (in Chinese)
Liu HJ, Peng PA, Wang LG (2015) Comprehensive evaluation and simulation for large-scale mining using natural caving method. J Central South Univ 46(2):617–624
Liu Y, Ren FY, He RX et al (2018) Prediction of surface subsidence range based on the critical medium column’s theory using ore drawing. J Northeast Univ Nat Sci 39(3):416–420 (in Chinese)
Ma J (2012) Investigation on backfilling body movement law of the subsided area and backfilling measures of Jin Shan Dian iron mine. Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan (in Chinese)
Moodley I, Sheridan CM, Kappelmeyer U et al (2018) Environmentally sustainable acid mine drainage remediation: research developments with a focus on wasteby-products. Miner Eng 126:207
Ren FY, Zhang DJ, Cao JL et al (2018a) Study on the rock mass caving and surface subsidence mechanism based on an in situ geological investigation and numerical analysis. Math Probl Eng 2018:1
Ren FY, Liu Y, Cao JL et al (2018b) Discussion on the mining by districts in Dabeishan iron mine. Metal Mine 505(7):45–49 (in Chinese)
Ren FY, Liu Y, He RX et al (2020) Experimental study of tailings’ moving laws in collapse pit induced by drawing ore. J Northeast Univ Nat Sci 41(6):858–862 (in Chinese)
Rocha D, Braga M, Rodrigues CT (2019) Geophysical methods for br tailings dam research and monitoring in the mineral complex of Tapira-Minas Gerais, brazil. Revista Brasileira De Geofísica 37:275
Rusdinar Y, Raki M, Baumgartl T et al (2013) Long term performance of hydrogeochemical riverine mine tailings deposition at freeport Indonesia. Mine Water Environ 32(1):56–70
Schoenberger E (2016) Environmentally sustainable mining: the case of tailings storage facilities. Resour Policy 49:119–128
Torres E, Lozano A, Macias F et al (2018) Passive elimination of sulfate and metals from acid mine drainage using combined limestone and barium carbonate systems. J Clean Prod 182:114–123
Vyazmensky A, Stead D, Elmo D et al (2010) Numerical analysis of block caving-induced instability in large open pit slopes: a finite element/discrete element approach. Rock Mech Rock Eng 43(1):21–39
Zhang Q, Zhang JX, Zhao X et al (2014) Industrial tests of waste rock direct backfilling underground in fully mechanized coal mining face. Environ Eng Manag 13:1291–1297
Zhang JX, Qiang Z, Sun Q et al (2015) Surface subsidence control theory and application to backfill coal mining technology. Environ Earth Sci 74(2):1439–1448
Zhang XF, Tao GQ, Zhu ZH (2018) Laboratory study of the influence of dip and ore width on gravity flow during longitudinal sublevel caving. J Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 103:179–185
Zhu G, Wu X, Ge J, Liu F et al (2020) Influence of mining activities on groundwater hydrochemistry and heavy metal migration using a self-organizing map (SOM). J Clean Prod 257:120664
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51534003), the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2016YFC0801601), Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia (No. 2021LHBS05004). Autonomous Region. The authors would also like to acknowledge the reviewers for their professional comments and constructive suggestions regarding improvements of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Zhou, Y., He, R. et al. The Critical Factors and Preventive Measures of Impoundment of Tailings Using Active Surface Subsidence Zones. Geotech Geol Eng 41, 271–282 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-022-02278-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-022-02278-4