Abstract
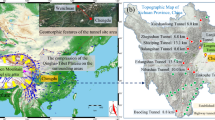
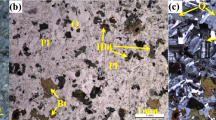
Spalling has been recognized as a stress-induced brittle fracture adjacent to the underground openings when tunneling or mining deeply in a hard massive rock mass. Using a database consisting of 29 spalling cases of gneissic granite during the excavation of Qirehataer tunnels, a comprehensive evaluation of rock mass spalling strength, spalling failure depth and the influence of excavation damaged zone (EDZ) and the cross-section shapes is performed and presented. Relationships between the spalling failure depth and the rock mass damage index for D-shape and Horse-shoe shape cross-sections of non-circular tunnels with and without consideration of EDZ are analyzed and discussed. The study found that EDZ has a significant influence on the maximum tangential stress adjacent to the boundary of tunnels that the EDZ has a trend to result in a deeper failure depth than not taking the EDZ into account. The influence degree of EDZ on spalling failure depth could be 1.85 and 2.18 times higher than that without considering EDZ, for the D-shape and Horse-shoe shape tunnels, respectively. Through comparisons with the analysis based on in-situ geophysical testing data, it is found Martin and Christiansson’s method may have a trend to overestimate the spalling failure depth, the overestimation ratio of influence degree may be up to 1.35, and the overestimation becomes more significant with the increase of the rock mass damage index. Based on the analysis and comparisons with different shapes of tunnel cross-sections, it is also found that the D-shape geometry of tunnels has the advantage of avoiding spalling failure over than Horseshoe-shape in the hard and brittle rock mass.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated or used during the study appear in the submitted article. More detailed data are available upon request.
References
Cai M, Kaiser PK, Tasaka Y, Maejima T, Morioka H, Minami M (2014) Generalized crack initiation and crack damage stress thresholds of brittle rock masses near underground excavations. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 41(5):833–847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2004.02.001
Diederichs MS (2007) Mechanistic interpretation and practical application of damage and spalling prediction criteria for deep tunneling. Can Geotech J 44(9):1082–1116
Dimmock PS, Mair RJ (2008) Effect of building stiffness on tunneling-induced ground movement. J Tunnel Undergr Space Technol 23:438–450
Dowding CH, Andersson C (1986) Potential for rock bursting and slabbing in deep caverns. Eng Geol 22(3):265–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(86)92629-x
Eberhardt E, Stead D, Stimpson B, Read RS (1998) Identifying crack initiation and propagation thresholds in brittle rock. Can Geotech J 35(2):222–233. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-35-2-222
Ghaffari M, Mahdevari S (2022) The effect of tunnel geometry and geomechanical parameters of host rock on tunnel displacement profile. Geotech Geol Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-022-02063-3
Gong QM, Yin LJ, Wu SY, Zhao J, Zhao Y (2012) Rock burst and slabbing failure and its influence on TBM excavation at headrace tunnels in Jinping II hydropower station. Eng Geol 124:98–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2011.10.007
Hajiabdolmajid V, Kaiser P (2003) Brittleness of rock and stability assessment in hard rock tunneling. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 18(1):35–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0886-7798(02)00100-1
Hajiabdolmajid V, Kaiser P, Martin CD (2003) Mobilized strength components in a brittle failure of rock. Geotéchnique 53(3):327–336
Hoek E, Brown ET (1980) Underground excavations in rock. Institution of Mining and Metallurgy, London
Hudson JA, Bäckström A, Rutqvist J, Jing L, Backers T, Chijimatsu M, Christiansson R, Feng XT, Kobayashi A, Koyama T, Lee HS, Neretnieks I, Pan PZ, Rinne M, Shen BT (2009) Characterizing and modeling the excavation damaged zone in crystalline rock in the context of radioactive waste disposal. Environ Geol 57(6):1275–1297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1554-z
Lei Q, Latham JP, Xiang JS, Tsang CF (2017) Role of natural fractures in damage evolution around the tunnel. Eng Geol 231:110–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.10.013
Li SJ, Feng XT, Li ZH, Chen BR, Zhang CQ, Zhou H (2012) In situ monitoring of rockburst nucleation and evolution in the deeply buried tunnels of Jinping II hydropower station. Eng Geol 137–138:85–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.03.010
Li XB, Tao M, Wu CQ, Du K, Wu QH (2017) Spalling strength rock different static pre-confining pressures. Int J Impact Eng 99:69–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2016.10.001
Li X, Li XF, Zhang QB, Zhao J (2018) A numerical study of spalling and related rockburst under dynamic disturbance using a particle-based numerical manifold method (PNMM). Tunn Undergr Space Technol 81:438–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2018.08.026
Ma K, Tang CA, Wang LX, Tang DH, Zhuang DY, Zhang QB, Zhao J (2016) Stability analysis of underground oil storage caverns by an integrated numerical and micro-seismic monitoring approach. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 54:81–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2016.01.024
Maleki M, Sereshteh H, Mousivand M, Bayat M (2011) An equivalent beam model for the analysis of tunnel-building interaction. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 26(4):524–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2011.02.006
Marinos V, Carter TG (2018) Maintaining geological reality in application of GSI for the design of engineering structures in rock. Eng Geol 239:282–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.03.022
Martin CD, Christiansson R (2009) Estimating the potential for spalling around a deep nuclear waste repository in crystalline rock. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 46(2):219–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2008.03.001
Martin CD, Kaiser PK, McCreath DR (1999) Hoek-Brown parameters for predicting the depth of brittle failure around tunnels. Can Geotech J 36(1):136–151. https://doi.org/10.1139/t98-072
Martin CD (1993) The strength of massive lac du bonnet granite around underground openings. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Manitoba
Nicksiar M, Martin CD (2013) Crack initiation stress in low porosity crystalline and sedimentary rocks. Eng Geol 154:64–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.12.007
Perras MA, Diederichs MS (2016) Predicting excavation damage zone depths in brittle rocks. J Rock Mech Geotec Eng 8(1):60–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2015.11.004
Pickhavar JA, Burd HJ, Houlsby GT (2010) An equivalent beam method to model masonry building in 3D finite element analysis. J Comput Geotech 88:1049–1063
Rocscience (2018) User’s guide for Phase2-2D finite element program for calculating stresses and estimating support around underground excavations. Toronto, Canada
Sassa K (1988) Suggested methods for seismic testing within and between boreholes. Int J Rock Mech Mining Sci Geo Abstr 25(6):449–472
Sellers EJ, Klerck P (2000) Modeling of the effect of discontinuities on the extent of the fracture zone surrounding deep tunnels. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 15(4):463–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0886-7798(01)00015-3
Shan Z, Yan P (2010) Management of rock bursts during the excavation of the deep tunnels in Jinping II Hydropower Station. Bull Eng Geol Environ 69(3):353–363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-010-0266-2
Shen B, Barton N (2018) Rock fracturing mechanisms around underground openings. Geomech Eng 16(1):35–47. https://doi.org/10.12989/gae.2018.16.1.035
Stacey TR (1981) A simple extension strain criterion for fracture of brittle rock. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 18:469–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(81)90511-8
Zhao X, Cai M (2010) Considerations of rock dilation on modeling failure and deformation of hard rocks—a case study of the mine-by test tunnel in Canada. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 2(4):338–349. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1235.2010.00338
Zhao GB, Wang DY, Gao B, Wang SJ (2017) Modifying rockburst criteria based on observations in a division tunnel. Eng Geol 216:153–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.11.014
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Bei Fang Investigation, Design & Research Co. ltd, China for allowing us to use the data collected during the design, research and construction of the project. This study was also partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No: 51709156). We also express our thanks to Dr. Chao Hu at the China Renewable Energy Engineering Institute, for their insightful discussions.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No: 51709156).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Material preparation and data collection were performed by GZ when he worked for Bei Fang Investigation, Design & Research Co. Ltd, China. The conception was discussed between DW and GZ, DW, LS and GZ performed analyses for this paper, the project was guided by Sijing Wang and he made comments on conception. The first draft of the manuscript was written by GZ and modified by DW and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, G., Wang, D., Shi, L. et al. Influences of EDZ and Cross-Section Shapes on Spalling Failure Depth of Non-circular Tunnels in Gneissic Granite. Geotech Geol Eng 41, 91–105 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-022-02264-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-022-02264-w