Abstract
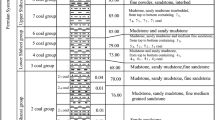
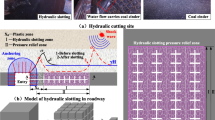
The Dengfeng coalfield belongs to the typical “three soft” coal seam and has a high gas content ranging from 10 to 13 m3/t, and the coal seam gas content reaches a maximum 13.69 m3/t. Because of its coal seam occurrence, no protective layer can be mined. The conventional regional pre-pumping measures have several problems. For example, the construction of a pre-pumping borehole is difficult, and it easily causes a coal and gas outburst. The low permeability and rheological characteristics of the coal seam lead to the collapse of the borehole and seriously affects the drainage effect. The influence radius of the drainage borehole is small, which results in a larger quantity of new drilling boreholes and significantly increases the operational cost. Compared to the conventional regional pre-pumping measures, floor roadway hydraulic flushing rapid outburst technology can effectively overcomes these issues. Hydraulic flushing uses water to flush the borehole, and the newly formed fractures and the release of free gas greatly reduce the elastic potential and gas expansion energy of coal and rock, which thus significantly improve the permeability of the coal and improve the coal seam degasification efficiency for outburst risk control. In this paper, a hydraulic punching method is utilized for coal seam stimulation in the Machi mine. Reasonable technical parameters of hydraulic punching were obtained: the water pressure of punching and breaking coal is 8–15 MPa, and the equivalent diameter of the hydraulic punching nozzle should be < 7.47 mm. After the implementation of the hydraulic punching measures, the gas extraction capacity of the coal around the borehole is greatly improved. For 90 days gas extraction after stimulation, the gas content of the 11,061 lane decreased from 8.42–12.12 m3/t to 3.09–5.75 m3/t, relieving pressure and increasing permeability of “three soft” coal and simultaneously eliminating the outburst danger of the coal seam.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguado MBD, Nicieza CG (2007) Control and prevention of gas outbursts in coal mines, Riosa-Olloniego coalfield, Spain. Int J Coal Geol 69(4):253–266
AЛcйниκοB AA et al (1981) Cut and discharge chute with water gun in the coal seam with prominent danger. Bai Shanshu translation, Yang Qizhong proof. Coal and gas outburst prevention and control technology translation anthology, Coal Industry Press, Beijing, pp 265–267
Chen XJ, Cheng YP (2015) Influence of the injected water on gas outburst disasters in coal mine. Nat Hazards 76:1093–1109
Chen QL, Zhang TG, Zhang JG (1999) Investigation of gas drainage and utilization technology in mine of Commonwealth of Independent States. Safety in Coal Mines 6:14–17 (In Chinese)
Cheng W, Nie W, Zhou G, Xue J (2012) Research and practice on fluctuation water injection technology at low permeability coal seam. Saf Sci 50(4):851–856
Huang B, Liu C, Fu J, Guan H (2011) Hydraulic fracturing after water pressure control blasting for increased fracturing. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 48(6):976–983
Kong X, Wang E, Liu X, Li N, Chen L, Feng J, Kong B, Li D, Liu Q (2016) Coupled analysis about multi-factors to the effective influence radius of hydraulic flushing: application of response surface methodology. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 32:538–548
Li B, Liu MJ, Liu YW (2011) Research on pressure relief scope of hydraulic flushing bore hole. Procedia Eng 26:382–387
Li QG, Lin BQ, Zhai C (2015) A new technique for preventing and controlling coal and gas outburst hazard with pulse hydraulic fracturing: a case study in Yuwu coal mine, China. Nat Hazards 75:2931–2946
Lin BQ, Li ZW, Zhai C, Bi Q (2011) Pressure relief and permeability-increasing technology based on high pressure pulsating hydraulic fracturing. J Min Saf Eng 28:452–455
Liu MJ, Kong LA, Hao FC, Xin XP, Wei GY, Liu YW (2005) Application of hydraulic flushing technology in severe outburst coal. J China Coal Soc 30(4):451–454
Liu Y, Xia BW, Liu XT (2015) A novel method of orienting hydraulic fractures in coal mines and its mechanism of intensified conduction. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 27:190–199
Morales H (1992) Characteristic analysis on hydraulic crush in Australia BoEn coal-field. In: Symposium on coalbed methane research and development in Australia
Mrak G (1992) Characteristic test of hydraulic crush on nordic coal seam. In: Symposium on coalbed methane research and development in Australia
Mu CM, Han J (2015) Mechanical characteristics of high pressure water jets impacting on coal. Explos Shk Waves 35(3):442–448
Mu CM, Wu YY (2013) Crushing strength of the coal against high pressure water penetration. Chin J Appl Mech 30(3):451–456
Wang ZF, Li ZQ (2004) Study on outburst prevention mechanism of hydraulic extrusion. Saf Coal Mines 35(12):1–4 (in Chinese)
Wang YF, He XQ, Wang EY, Li YZ (2014) Research progress and development tendency of the hydraulic technology for increasing the permeability of coal seams. J China Coal Soc 39(10):1945–1955 (In Chinese)
Xu YP (2007) The key technical research of eliminating coal and gas outburst rapidly of hydraulic extrusion. M.Sc. Thesis, Jiaozuo, Henan Polytechnic University
Xu LH, Jiang CL (2017) Initial desorption characterization of methane and carbon dioxide in coal and its influence on coal and gas outburst risk. Fuel 203:700–706
Xu YP, Qiu YG (2008) Experimental study on rapid outburst prevention measures by hydraulic extrusion. Coal Eng 10:44–46 (in Chinese)
Xu YP, Wang ZF (2011) The development of the coal and gas outburst prediction positional sampler. Procedia Eng 26:1495–1501
Xu YP, Wang ZF, Guo HG (2011) Experimental study of the raw coal desorption method on the corresponding relation between coal seam gas pressure and content. Procedia Eng 26:2422–2427
Yuan L (2016) Control of coal and gas outbursts in Huainan mines in China: a review. J Rock Mech Geotechn Eng 8:559–567
Yuan L, Lin BQ, Yang W (2015) Research progress and development direction of gas control with mine hydraulic technology in China coal mine. Coal Sci Technol 43(1):45–49 (In Chinese)
Zhou HX, Cheng YP, Liu HY, Guo PK, Wang LG (2011) Permeability and fluidity improvement mechanism of crossing borehole group in outburst coal seam. J Min Saf Eng 28(4):618–622
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial support from the Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51874122 and 51704100), Key Scientific Research Projects Plan of Henan Higher Education Institutions (19A440008), Key Laboratory of Gas and Fire Control for Coal Mines (China University of Mining and Technology), Program for Innovative Research Team of Henan Polytechnic University, Foundation and advanced Technology Research Project of Henan Province, (162300410038).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Wang, L. Technical Parameters of Hydraulic Punching in a Typical Coal Seam and an Investigation of Outburst Prevention Effect: A Case Study in the Machi Mine, China. Geotech Geol Eng 38, 1971–1986 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-019-01142-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-019-01142-2