Abstract
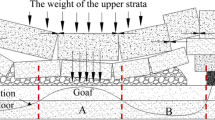
To research the failure characteristic of coal seam floor with a certain dip angle and the monitoring and prediction of water inrush. Taking the coal mining face in Xinhong 3#Mine as the study object, a water inrush model of water floor under pressure of six different angles in coal layers was established. Using FLAC3D numerical simulation as a method of making a comprehensive comparative study about the depth and range of the mining failure depth of different angle in coal layers. The study results showed that the damage from of the floor in deep area after mining was quite different from the one in the shallow area. The plastic failure depth of floor increases with the increase of working face width, the vertical stress of the bottom plate of the working face is increasing gradually; the plastic failure depth of floor increased to the maximum and then decreased with the increase of coal seam dip angle. It will reach the maximum failure depth at 30°, and is easy to occur shear failure. The maximum failure depth is up to 28.77 m, which is very close to field monitoring result, it can provide the basis for preventing water inrush of mine caused by deep mining floor.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao SG, Yao QL, Wang FH et al (2010) Analysis of water inrush risk from coal seam floor over a confined water body. J Min Saf Eng 27(3):346–350
Guo WJ, Zhao JH, Yin LM et al (2017) Study on fault water inrush mechanism and nonlinear seepage-stress coupling. J Shandong Univ Sci Technol 6:1–7
Jiang YD, Lu YK, Zhao YX et al (2011) Similar simulation test for breakage law of working face floor in coal mining above aquifer. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 30(08):1571–1578
Jin DW (2002) Research status and outlook of water outburst from seam floor in China coal mines. Coal Sci Technol 30(6):1–4
Li KK, Wang CX (1997) The technique measuring the stress of rock mass used in the study of the mechanism of the water-inrush from coal floo. Coal Geol Explor 3:33–36
Li CP, Li JJ, Li ZX et al (2013) Establishment of spatiotemporal dynamic model for water inrush spreading processes in underground mining operations. Saf Sci 55:45–52
Liu WT, Liu SL (2015) Mechanical analysis and numerical simulation on the mining failure depth of floor. Min Res Dev 2:46–55
Liu WT, Mu DR, Xie XX (2012) Sensitivity analysis of the main factors controlling floor failure depth and a risk evaluation of floor water inrush for an inclined coal seam. Mine Water Environ 4:1–13
Liu WT, Mu DR, Yang L et al (2017) Calculation method and main factor sensitivity analysis of inclined coal floor damage depth. J China Coal Soc 42(4):849–859
Ma FH, Sun L, Li D (2011) Numerical simulation analysis of covering rock strata as mining steep-inclined coal seam under fault movement. T Nonferr Metal Soc 21(3):S556–S561
Meng XX, Liu WT, Mu DR (2018a) Influence analysis of mining’s effect on failure characteristics of a coal seam floor with faults: a numerical simulation case study in the Zhaolou coal mine. Mine Water Environ 29:1–9
Meng XX, Liu WT, Meng T (2018b) Experimental investigation of thermal cracking and permeability evolution of granite with varying initial damage under high temperature and triaxial compression. Adv Mater Sci Eng 19:1–9
Qian MG, Miu XX, Xu JL (1996) Theoretical study of key stratum in ground control. J China Coal Soc 3:2–7
Shi LQ (2009) Summary of research on mechanism of water-inrush from seam floor. J Shandong Univ Sci Technol 28(3):17–23
Shi LQ, Han J (2005) Theory and practice of dividing coal mining area floor into four-zone. J China Univ Min Techno 1:19–26
Shi LQ, Xu DJ, Qiu M et al (2013) Improved on the formula about the depth of damaged floor in working area. J China Coal Soc 38(S2):299–303
Sun J (2014) Failure characteristics of floor “three-zone” along the inclined direction of coal seam. J Min Saf Eng 31(01):115–121
Sun J, Wang LG, Tang FR et al (2011) Microseismic monitoring failure characteristics of inclined coal seam floor. Rock Soil Mechanics 32(5):1589–1595
Wang ZY, Liu HQ (1989) Research on mechanism of water-inrush from coal seam floor. Research on mechanism of water-inrush from coal seam floor 1:36–39
Wei JC, Li BY (2000) Security evaluation of coal mining above the confined aquifers. Coal Geol Explor 28(04):57–59
Xing ZG, Li BY (1980) Preliminary discussion on water inrush mechanism in coal seam floor. Coal Geol Explor 2:51–56
Xu ZM, Sun YJ, Gong SY et al (2012) Monitoring and numerical simulation of formation of water inrush pathway caused by coal mining above confined water with high pressure. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 31(8):1698–1704
Zeng YF, Wu Q, Liu SQ et al (2016) Vulnerability assessment of water bursting from ordovician limestone into coal mines of China. Environ Earth Sci 75(22):1431
Zhang JC, Liu TQ (1990) On depth of fissured zone in seam floor resulted from coal extraction and its distribution characteristics. J China Coal Soc 2:46–55
Zhang R, Jiang ZQ, Yu ZR (2013) Comprehensive testing and numerical analysis on the failure characteristics of mining coal seam floor. J Min Saf Eng 30(04):531–537
Zhang R, Jiang ZQ, Zhou HY et al (2014) Groundwater outbursts from faults above a confined aquifer in the coal mining. Nat Hazards 71(3):1861–1872
Zhang SC, Guo WJ, Sun WB et al (2015) Formation and evolution process of floor water-inrush channel under high water pressure. J Shandong Univ Sci Technol 2:25–29
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural science Foundation of China (Grant 51274135), the National High Technology Research and Development Program (863 Program) of China (Grant 2015AA016404-4), and the State Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant 2017YFC0804108).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Du, Y., Liu, Y. et al. Failure Characteristics of Floor Mining-Induced Damage Under Deep Different Dip Angles of Coal Seam. Geotech Geol Eng 37, 985–994 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-018-0666-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-018-0666-9