Abstract
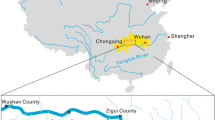
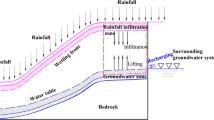
Water is one of the leading factors in the sliding geological disasters of rock slope, and the harm of fissure water to slope rock mass more and more becomes one of the hotspot research problems in transportation infrastructure construction in mountainous area. Based on the current research status quo of effect of fissure water on rock mass, the interaction mechanisms of water and rock in stratified rock slope were analyzed by related theories such as rock mass mechanics, fluid mechanics and soil mechanics including softening dissolution, scour hole enlargement and padding effective stress, and the influence of water–rock interaction on slope sliding disasters. Then, the influence of rainfall on the displacement field distribution of slope was analyzed during one year of monitoring a typical,natural slope in the Sichuan–Chongqing region. Observations include surface displacement, deep displacement, water level and rainfall. Finally, a targeted reinforced disposal scheme was proposed that considered the rainfall effect. The results provide reference for the instability theory and treatment measures for a high-risk stratified slope.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aijun S, Ning SU, Long L (2010) The internal force analysis and design method for anti-slide pile of typical soil–rock compound slope. J Eng Geol 18(S1):292–296
Bonacci O (2015) Surface waters and groundwater in karst. In: Stevanović Z (ed) Karst aquifers—characterization and engineering. Springer, Berlin, pp 149–169
Cherepov AA, Eremin MO, Makarov PV et al (2014) A possibilities of dangerous dynamic phenomena prediction in a rock mass surrounding the excavations. Am Inst Phys 1623:87–90
Hashiba K, Fukui K (2015) Effect of water on the deformation and failure of rock in uniaxial tension. Rock Mech Rock Eng 48(5):1751–1761
Lau LC (2013) The effect of band engineering of semiconductors on photocatalytic water splitting: a review. Ijret Org 02(11):195–206
Pantelidis L (2009) Rock slope stability assessment through rock mass classification systems. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 46(2):315–325
Tang HX, Zhou ZF, Wang WY (2004) The permeability and mechanism analysis of rock mass in the process of water splitting. Rock Soil Mech 25(8):1320–1322
Wang GH, Yang YY, Zhang H et al (2013) Failure characteristics and its influencing factors of talus-derived rock mass during open-pit mining. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 23(2):462–471
Weijers L, Pater CJ, Hagoort J (1996) A new mechanism for hydraulic initiation. Rock mechanics. Balkeman A A, Rotterdam, pp 1253–1260
Xu SG, Wang MZ, Wang YX et al (2006) Effect of groundwater on slope disaster. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 6:46–51
Yang TH, Tang CN, Zhu WC et al (2001) Coupling analysis of seepage and stress in rock fracture process. Chin J Geotech Eng 23(4):489–493
Zhou Z, Fu HL et al (2007) Study on artificial rainfall simulation of soil rock mixture slope. Rock soil Mech 28(1):1391–1396
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Wang, J., Hou, L. et al. Study on the Instability Mechanisms and Monitoring Control of Stratified Rock Slope with Water-Rich Strata. Geotech Geol Eng 36, 1665–1672 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-017-0421-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-017-0421-7