Abstract
Some basic factors which influence the behaviour of the anchored retaining structures are investigated and 2D analyses with three dimensional ones are compared. The parametric analysis under 2D conditions focuses on the influence of significant factors such as the normalized embedded depth of the wall, the resistance of the anchors, the free tendon length, the earth pressure coefficient at rest and the flexibility of the system, on the behaviour of the retaining structure. The analyses are performed in two groups for two representative soil types named S1 (weathered weak rock) and S2 (very stiff clay). Qualitative as well as quantitative conclusions are derived from the analyses concerning the influence of the above mentioned factors, mainly on the safety factor as well as on the displacements. The 3D analyses are carried out for various ratios L/H, where L is the length and H the height of the slope. Several trends are confirmed from the results concerning the influence of the above-mentioned factors. It is concluded that the triaxal conditions strongly affect the safety factor, as well as the distribution of horizontal and vertical displacements, mainly in the cases where the ratios L/H ≤ 2. Some serious deviations between 2D and 3D analyses are pointed out and the physical explanation of these differences is given for several cases.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- B:
-
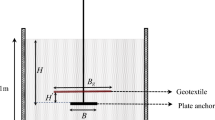
Width of the excavation
- c:
-
Cohesion of the soil
- D:
-
Embedded depth of the retaining piles
- E:
-
Modulus of elasticity of the soil
- FEM:
-
Finite element method
- H:
-
Height of the slope
- K:
-
Earth pressure coefficient at rest
- L:
-
Length of the excavation
- Lfree :
-
Free length of the anchors
- Lfixed :
-
Fixed length of the anchors
- Pi :
-
Prestress force of the anchor (lock-off load)
- Rint :
-
Strength reduction factor at the interface
- Ra,d :
-
Design resistance of the anchorages
- SF:
-
Global safety factor
- s:
-
Axial distance of the piles
- sv :
-
Vertical distance of the anchors
- SSR:
-
Shear strength reduction
- ux, uy, uz :
-
Displacements in the direction x, y, z
- β:
-
Inclination angle of the anchors
- γ:
-
Bulk density of the soil
- ν:
-
Poisson’s ratio
- φ:
-
Angle of internal friction
References
Bakker KJ (2006) Α 3D FE model for excavation analysis. In: Proceedings of the 5th international symposium T.C28 (Geotechnical aspects of underground construction in soft ground), Netherlands, pp 473–478
Brinkgreve RBJ, Bakker HL (1991) Non-linear finite element analysis of safety factors. In: Proceedings of the 7th international conference on computer methods and advances in geomechanics, Cairns, Australia., 1117-1122
Clough GW, O’ Rourkee T-D (1990) Construction induced movements of in situ walls. Geotechnical Special Publication, No 25: Design and performance of earth retaining structures, June 1990, pp 439–470
Clough GW, Smith EM, Sweeney BP (1989) Movement control of excavation support systems by iterative design. In: Proceedings of the ASCE foundation engineering: current principles and practices, vol 2, pp 869–884
Hovland HJ (1977) Three-dimensional slope stability analysis method. J Geotech Eng Div ASCE 103(9):971–986
Huang C-C, Tsai C-C (2000) New method for 3D and asymmetrical slope stability analysis. J Geotech Eng Div ASCE 126(10):917–927
Leshchinsky D, Huang C-C (1992) Generalized three-dimensional slope-stability analysis. J Geotech Eng Div ASCE 118(11):1748–1764
Michalowski RL (2010) Limit analysis and stability charts for 3D slope failures. J Geotech Eng Div ASCE 136(4):583–593
Ou CY, Hsieh PO, Chien DC (1993) Characteristics of ground settlement during excavation. Can Geotech J 30(5):758–767
Papadopoulou K (2011) Parametric analyses of retaining structures by prestressed anchors. Postgraduate thesis in N.T.U.A (in greek)
Plaxis Validation and Verification (2012) Phi-c reduction and comparison with Bishop’s method. Kb Plaxis nl, Knowledge Base
Poulos HG, Carter JP, Small JC (2001) Foundations and retaining structures—research and practice. General Report, proceedings of the 15th JCSMGE, Istanbul, vol 4, pp 2527–2606
Schweiger HF (1998) Results from two geotechnical benchmark problems. In: Cividini A (ed) Proceedings of the 4th European conference on numerical methods in geotechnical engineering, pp 645–654
Schweiger HF (2000): Ergebnisse des Berechnungsbeispieles Nr. 3 “3-fach verankerte Baugrube”. Tagungsband Workshop “Verformungsprognose fϋr tiefe Baugruben”, D.G.G.T./AK 1.6:7–67 (in German)
Yamagami T, Jiang JC (1997) A search for the critical slip surface in three-dimensional slope stability analysis. Soils Found Tokyo 37(3):1–16
Zdrackovic L, Potts DM, St. John HD (2005) Modelling of a 3D excavation in finite element analysis. Geotechnique 55(7):497–513
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Papadopoulou, K., Sofianos, A. Factors Affecting the Behaviour of Retaining Structures with Prestressed Anchorages Under 2D and 3D Conditions. Geotech Geol Eng 34, 1877–1887 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-016-9997-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-016-9997-6