Abstract
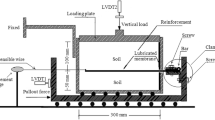
The use of new materials for soil strengthening is crucial for geotechnical engineering, especially in foundation construction. The main objective of this study was to investigate the potential use of two-component water-soluble epoxy resin to improve the physical and mechanical properties of medium sand, because the efficacy of these resins on soil strengthening has not yet been properly investigated. The experiments were conducted using resins with different epoxy resin-to-water ratios. The results of this study indicate that the epoxy resins improve the physical and mechanical properties of the sand significantly, and if successfully grouted into a formation, the resins could provide a suitable solution for the stabilization of the foundation material. In separate experiments, electroosmotic treatment of sand/resin mixtures was conducted with the aim of identifying the effectiveness of electro kinetic method on the early strength development of sand/resin mixtures. From the results it was observed that the electroosmotically treated specimens appeared to have much greater strength enhancement than the one of the untreated specimens.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASTM C 938-80 (1993) Standard practice for proportioning grout mixtures for preplaced-aggregate concrete. American Society for Testing and Materials, West Conshohocken
ASTM C 29/C 29 M-91a (1993) Standard test method for unit weight and voids in aggregate. American Society for Testing and Materials, West Conshohocken
ASTM D 3967-95a (2005) Standard test method for splitting tensile strength of intact rock core specimens. American Society for Testing and Materials, West Conshohocken
Abdullah WS, Al-Abadi AM (2010) Cationic-electrokinetic improvement of an expansive soil. Appl Clay Sci 47(3–4):343–350
Ajayi-Majebi A, Grissom WA, Smith LS, Jones EE (1991) Epoxy-resin-based chemical stabilization of a fine, poorly graded soil system. Transportation Research Record No 1295, National Research Council, Washington, DC
Akbulut S, Saglamer A (2003) Improvement of hydraulic conductivity of soils by grouting. Ground Improv 7(4):157–164
Al-Khanbashi A, Abdalla SW (2006) Evaluation of three waterborne polymers as stabilizers for sandy soil. Geotech Geol Eng 24(6):1603–1625
Alshawabkeh AN, Sheahan TC (2003) Soft soil stabilization by ionic injection under electric fields. Ground Improv 7(4):177–185
Anagnostopoulos CA (2005) Laboratory study of an injected granular soil with polymer grouts. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 20(6):525–533
Anagnostopoulos CA (2006) Physical and mechanical properties of injected sand with latex-superplasticized grouts. Geotech Test J 29(6):490–496
Anagnostopoulos C, Hadjispyrou S (2004) Laboratory study of an epoxy resin grouted sand. Ground Improv 8(1):39–45
Anagnostopoulos CA, Papaliangas T, Manolopoulou S, Dimopoulos S (2011) Physical and mechanical properties of chemically grouted sand. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 26(6):718–724
ASTM D 3080 (2005) Standard test method for direct shear test of soils under consolidated drained conditions. American Society for Testing and Materials, West Conshohocken
ASTM D 4219-02 (2005) Standard test method for unconfined compressive strength index of chemical—grouted soils. American Society for Testing and Materials, West Conshohocken
ASTM D 4320-04 (2005) Standard practice for laboratory preparation of chemically grouted soil specimens for obtaining design strength parameters. American Society for Testing and Materials, West Conshohocken
ASTM D 5084-03 (2005) Standard test methods for measurement of hydraulic conductivity of saturated porous materials using a flexible wall permeameter. American Society for Testing and Materials, West Conshohocken
Bolisetti T, Reitsma S, Balachandar R (2009) Experimental investigations of colloidal silica grouting in porous media. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 135(5):697–700
Cambefort H (1977) The principals and applications of grouting. Q J Eng Geol 10(2):57–95
Dano C, Hicker PY, Taillez S (2004) Engineering properties of grouted sand. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 130(3):328–338
EN 196-1 (2005) Methods of testing cement-Part 1: determination of strength. European Standard. European Committee for Standardization, CEN/TC 51, Brussels
Hoek E, Franklin JA (1968) A simple triaxial cell for field and laboratory testing of rock. Trans Inst Min Metall 77:A22–A26
Huweg AFS, Kamel F, Raine S (2010) Investigating the effect of electro-osmosis on sandy soil near saturated conditions. In: Proceedings of southern region engineering conference. Toowoomba, Australia, USQ, SREC2010-T1-2
Issa CA, Debs P (2007) Experimental study of epoxy repairing of cracks in concrete. Constr Build Mater 21(1):157–163
Kaniraj SR, Yee JHS (2011) Electro-osmotic consolidation experiments on an organic soil. Geotech Geol Eng 29(4):505–518
Liaki C, Rogers CDF, Boardman DI (2010) Physico-chemical effects on clay due to electromigration using stainless steel electrodes. J Appl Electrochem 40(6):1225–1237
Ou CY, Chien SC, Wang YG (2009) On the enhancement of electroosmotic soil improvement by the injection of saline solutions. Appl Clay Sci 44(1–2):130–136
Perret S, Khayat KH, Ballivy G (2000) The effect of degree of saturation on sand groutability-experimental simulation. Ground Improv 4(1):13–22
Vipulanandan C, Ata A (2000) Cyclic and damping properties of silicate-grouted sand. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 126(7):650–656
Widmann R (1996) International society for rock mechanics: commision on rock grouting. Int J Rock Mech Min 33(8):803–847
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anagnostopoulos, C.A., Kandiliotis, P., Lola, M. et al. Improving Properties of Sand Using Epoxy Resin and Electrokinetics. Geotech Geol Eng 32, 859–872 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-014-9763-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-014-9763-6