Abstract
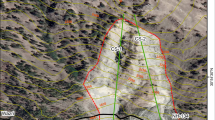
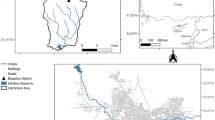
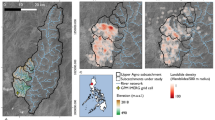
The slope failure and landslide hazard will possess the same properties within a range including the same engineering geological conditions. To assess the landslide risk of a mountainous area, the study of landslides previously having occurred is very important to evaluate the landslide risk around the area in which they took place. Based on the study of the mechanism of a previous landslide recorded in Kumamoto, Japan, this study initially proposes mechanical parameters for evaluating the landslide hazard using a 3D slope stability method. For each slope unit in the study area, the critical slip surface, which reveals the minimum safety factor of a slope, can be obtained. The affected streams and range of possible landslide masses are analyzed based on the debris flow simulation. This is initially applied to simulate the past landslide event and the result shows the landslide-deduced debris flow effectively re-displayed. Overlayered with layers of infrastructure in Geographic Information Systems (GIS), this risk map indicates which houses and road sections remain in dangerous areas.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aleotti P, Chowdhury R (1999) Landslide hazard assessment: summary review and new perspectives. Bull Eng Geol Environ 58:21–44. doi:10.1007/s100640050066
Arai M, Takahashi T (1986) The Karman constant of the flow laden with high sediment. In: Proceedings of 3rd international symposium on river sedimentation, University of Mississippi, pp 824–833
Arattano M, Franzi L (2003) On the evaluation of debris flows dynamics by means of mathematical models. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 3:539–544
Anbalagan D (1992) Landslide hazard evaluation and zonation mapping in mountainous terrain. Eng Geol 32:269–277. doi:10.1016/0013-7952(92)90053-2
Bagnold RA (1954) Experiments in a gravity-free dispersion of large solid spheres in a Newtonian fluid under shear. Proc R Soc Lond A 225:49–63
Bertolo P, Wieczorek GF (2005) Calibration of numerical models for small debris flows in Yosemite Valley, California, USA. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 5:993–1001
Chen C (1988) Generalized viscoplastic modeling of debris flow. J Hydraul Eng 114(3):237–258
Chen H, Lee CF (1999) Numerical simulation of debris flows. Can Geotech J 37:146–160. doi:10.1139/cgj-37-1-146
David RM (2002) Arc Hydro: GIS for water resources. ESRI Press, Redlands, CA, USA
Dent JD, Lang TE (1983) A biviscous modified bingham model of snow avalanche motion. Ann Glaciol 4:42–46
ESRI (2003) ArcGIS online user guidelines
Fraccarollo L, Papa M (2000) Numerical simulation of real debris-flow events. Phys Chem Earth B 25(9):757–763
Huang X, García MH (1997) A perturbation solution for Bingham-plastic mudflows. J Hydraul Eng 123(11):986–994. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1997)123:11(986)
Huang X, García MH (1998) A Herschel-Bulkley model for mud flow down a slope. J Fluid Mech 374:305–333. doi:10.1017/S0022112098002845
Hungr O (1995) A model for the runout analysis of rapid flow slides, debris flows and avalanches. Can Geotech J 32(4):610–623. doi:10.1139/t95-063
Hunt B (1994) Newtonian fluid mechanics treatment of debris flows and avalanches. J Hydraul Eng 120:1350–1363. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1994)120:12(1350)
Imran J, Harff P, Parker G (2001) A number model of submarine debris-flow with a graphical user interface. Comput Geosci 27:717–729. doi:10.1016/S0098-3004(00)00124-2
Iverson RM (1997) The physics of debris flows. Rev Geophys 35:245–296. doi:10.1029/97RG00426
Jan CD (1997) A study on the numerical modelling of debris flow. Debris flow hazards mitigation: mechanics, prediction and assessment. ASCE
Johnson AM (1970) Physical processes in geology. Freeman, San Francisco
Lien HP, Tsai FW (2003) Sediment concentration distribution of debris flow. J Hydraul Eng 129(12):995–1000. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2003)129:12(995)
Liu KF, Mei CC (1989) Slow spreading of a sheet of Bingham fluid on an inclined plane. J Fluid Mech 207:505–529. doi:10.1017/S0022112089002685
Mainali A, Rajaratnam N (1994) Experimental study of debris flows. J Hydraul Eng 120(1):104–123. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1994)120:1(104)
Naef D, Rickenmann D, Rutschmann P, McArdell BW (2006) Comparision of flow resistance relations for debris flows using a one-dimensional finite element simulation model. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 6:155–165
O’Brien JS, Julien PY (1988) Laboratory analysis of mudflow properties. J Hydraul Eng ASCE 114(8):877–887
O’Brien JP, Julien PJ, Fullerton WT (1993) Two-dimensional water flood and mudflow simulation. J Hydraul Res 119(2):244–261. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1993)119:2(244)
Pastor M, Quecedo M, González E, Herreros MI, Fernández Merodo JA, Mira P (2004) Simple approximation to bottom friction for bingham fluid depth integrated models. J Hydraul Eng 130(2):149–155. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2004)130:2(149)
Remaître A, Malet J, Maquaire O, Ancey C, Locat J (2005) Flow behaviour and runout modelling of complex debris flow in a clay-shale basin. Earth Surf Process Landf 30:479–488. doi:10.1002/esp.1162
Rickenmann D (1999) Empirical relationships for debris flows. Nat Hazards 19(1):47–77. doi:10.1023/A:1008064220727
Rickenmann D, Laigle D, McArdell BW, Hübl J (2006) Comparison of 2D debris-flow simulation models with field events. Comput Geosci 10:241–264. doi:10.1007/s10596-005-9021-3
Takahashi T (1978) Mechanical characteristics of debris flow. J Hydraul Div 104(8):1153–1169
Takahashi T (1991) Debris Flow. A. A. Balkema, Brookfield, Vt
Takahashi T, Nakagawa H, Harada T, Yamashiki Y (1992) Routing debris flows with particle segregation. J Hydraul Res 118(11):1490–1507. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1992)118:11(1490)
Trunk FJ, Dent JD, Lang TE (1986) Computer modeling of large rock slides. J Geotech Eng 112(3):348–360
Whipple KX (1997) Open-channel flow of Bingham fluids: applications in debris-flow research. J Geol 105:243–262
Xie M, Esaki T, Zhou G, Mitani Y (2003) Geographic information systems-based three-dimensional critical slope stability analysis and landslide hazard assessment. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 129(12):1109–1118. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2003)129:12(1109)
Xie M, Esaki T, Zhou G (2004) Three-dimensional stability evaluation of landslides and a sliding process simulation using a new geographic information systems component. Nat Hazards 33:265–282. doi:10.1023/B:NHAZ.0000037036.01850.0d
Xie M, Esaki T, Cai M (2006) GIS-based 3D implementation of three-dimensional limit equilibrium approach of slope stability. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 132(3):656–660. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2006)132:5(656)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, M., Esaki, T., Qiu, C. et al. Deterministic Landslide Risk Assessment at a Past Landslide Site. Geotech Geol Eng 27, 355–364 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-008-9232-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-008-9232-1