Abstract
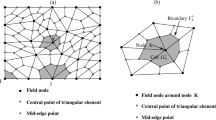
Accurate and efficient simulation of the slope stability, certainly gives the reliable approach for the hazard preparedness. However, inherent difficulties associated with the slope failure make the situation very difficult. First, the computation of fracture path based on the strict mathematical formalism is cumbersome especially for the progressive failure phenomenon. Second, due to the lack of reliable knowledge on material properties, stochastic simulation is necessary. Stochastic modeling together with the progressive failure phenomenon is apparently difficult task. In this paper, heterogeneous slope is simulated considering the progressive failure phenomenon using the modified finite element method introducing the fracture along the edge of the meshes thus incorporating the time evolution of the fracture surface. This is achieved by restructuring the tessellation in every fracture stage. Unlike remeshing this technique only increases the number of total nodes while number of meshes remaining same, which is simple and natural. Further, in this research, effect of uncertainty in the material properties upon the uncertainty in the response of soil slope has been evaluated, hence giving the reliable probabilistic estimation of the factor of safety, failure surface and deformation of the slope. Thus the simulation based on the more reliable understanding of the material properties and the efficient numerical procedure for the progressive failure phenomenon can give the reliable result of the simulation for the heterogeneous soil slope thus enabling the more accurate way for hazard preparedness.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bathe KJ (1996) Finite element procedures. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersy, 07f58
Bishop AW (1955) The use of the slip circle in the stability analysis of slopes. Geotechnique 5(1):7–17
Bishop AW, Morgenstern N (1960) Stability coefficients for earth slopes. Geotechnique 10(4):129–150
Cramer SL (2003) Geotechnical earthquake engineering. Pearson education (Singapore) Pte. Ltd., Indian branch, 482, F.I.E. Patparganj, Delhi 110092, India
Cundall PA, Potyondy DO, Lee C (1996) Modeling rock using bonded assemblies of circular particles. In: Rock Mechanics Tool and Techniques-Proc. Second North American Rock Mechanics Symposium – NARMS’ 96, pp 1937–1944
Ghanem RG, Spanos PD (2003) Stochastic finite element. Dover Publications, Inc., Minwla, New York, pp 1–72
Hicks MA, Samy K (2002) Influence of heterogeneity on undrained clay slope stability. Quart J Eng Geol Hydrol 35:41–49
Sakaguchi H, Muhlhaus HS (1997) Mesh free modeling of failure and localization in brittle rock deformation and progressive failure in geomechanics. Pergamon, pp 15–21
Yagawa G, Furukawa T (2000) Recent developments of free mesh method. Int J Numer Methods Eng 47:1419–1443
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pathak, D.R., Gharti, H.N., Singh, A.B. et al. Stochastic Modeling of Progressive Failure in Heterogeneous Soil Slope. Geotech Geol Eng 26, 113–120 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-007-9151-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-007-9151-6