Abstract
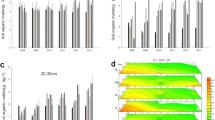
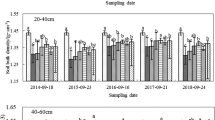
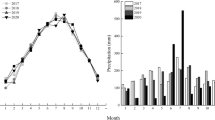
Tillage and straw management are important factors affecting soil quality and crop productivity. However, long-term rotary tillage may form a plough pan in the subsurface (0.1–0.2 m) soil, which limits root growth and crop yields, especially in rice production in the Yangtze and Huai River regions. A 5-year lasting field experiment was conducted to study the effects of three tillage treatments [RT, rotary tillage; SPT, shallow plough tillage (0.15–0.2 m); DPT, deep plough tillage (0.25–0.3 m)], with or without straw return (S) on soil fertility, soil physical properties and rice yields. Olsen phosphorus and available potassium values of the 0.1–0.2 m soil layer were significantly higher (by 36 and 24%, respectively) in SPT + S compared to RT. The soil bulk density of the 0.1–0.2 m soil layer was 13% lower in SPT + S and 9% lower in DPT + S than in RT. Factor analysis revealed that SPT + S had the highest integrated scores of soil fertility for the 0.1–0.2 m soil layer. Rice yields were 10–43% higher in SPT + S compared to RT during the 5-year period. Rice yields were positively correlated with the integrated scores of soil fertility for the 0–0.1 and 0.1–0.2 m soil layers. Our results indicate that shallow plough tillage plus straw return is a promising management strategy for paddy fields following long-term rotary tillage.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtar MS, Qureshi S (1999) Soil hydraulic properties and rice root development as influenced by tillage. Pak J Biol Sci 2:1245–1251
Angers DA, Eriksen-Hamel NS (2008) Full-Inversion tillage and organic carbon distribution in soil profiles: a meta-analysis. Soil Sci Soc Am J 72:1370–1374
Ashagrie Y, Zech W, Guggenberger G, Mamo T (2007) Soil aggregation, and total and particulate organic matter following conversion of native forests to continuous cultivation in Ethiopia. Soil till Res 94:101–108
Balesdent J, Chenu C, Balabane M (2000) Relationship of soil organic matter dynamics to physical protection and tillage. Soil till Res 53:215–230
Bao S (2000) Soil agrochemical analysis, 3rd edn. China Agricultural Press, Beijing
Baumhardt RL, Jones OR, Schwartz RC (2008) Long-term effects of profile-modifying deep plowing on soil properties and crop yield. Soil Sci Soc Am J 72:677–682
Bhagat RM, Sharma PK, Verma TS (1994) Tillage and residue management effects on soil physical properties and rice yield in northwestern Himalayan soils. Soil till Res 29:323–334
Blanco-Canqui H, Lal R (2008) Corn stover removal impacts on micro-scale soil physical properties. Geoderma 145:335–346
Bossuyt H, Denef K, Six J, Frey SD, Merckx R, Paustian K (2001) Influence of microbial populations and residue quality on aggregate stability. Appl Soil Ecol 16:195–208
Chen H, Hou R, Gong Y, Li H, Fan M, Kuzyakov Y (2009) Effects of 11 years of conservation tillage on soil organic matter fractions in wheat monoculture in Loess Plateau of China. Soil till Res 106:85–94
Das S, Bhattacharyya R, Das TK, Sharma AR, Dwivedi BS, Meena MC, Dey A, Biswas S, Aditya K, Aggarwal P, Biswas AK, Chaudhari SK (2021) Soil quality indices in a conservation agriculture based rice-mustard cropping system in North-western Indo-Gangetic Plains. Soil till Res 208:104914
Elliott ET (1986) Aggregate structure and carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in native and cultivated soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 50:627–633
Feng Q, An C, Chen Z, Wang Z (2020) Can deep tillage enhance carbon sequestration in soils? A meta-analysis towards GHG mitigation and sustainable agricultural management. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 133:110293
Getahun GT, Kätterer T, Munkholm LJ, Parvage MM, Keller T, Rychel K, Kirchmann H (2018) Short-term effects of loosening and incorporation of straw slurry into the upper subsoil on soil physical properties and crop yield. Soil till Res 184:62–67
Gill JS, Sale PWG, Peries RR, Tang C (2009) Changes in soil physical properties and crop root growth in dense sodic subsoil following incorporation of organic amendments. Field Crops Res 114:137–146
Hamoud YA, Shaghaleh H, Sheteiwy M, Guo X, Elshaikh NA, Khan NU, Oumarou A, Rahim SF (2019) Impact of alternative wetting and soil drying and soil clay content on the morphological and physiological traits of rice roots and their relationships to yield and nutrient use-efficiency. Agric Water Manag 223:105706
Harden JW, Sharpe JM, Parton WJ, Ojima DS, Fries TL, Huntington TG, Dabney SM (1999) Dynamic replacement and loss of soil carbon on eroding cropland. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 13:885–901
Ibrahim M, Yamin M, Sarwar G, Anayat A, Habib F, Ullah S, Saif-ur-Rehman (2011) Tillage and farm manure affect root growth and nutrient uptake of wheat and rice under semi-arid conditions. Appl Geochem 26:194–197
Kasper M, Buchan GD, Mentler A, Blum WEH (2009) Influence of soil tillage systems on aggregate stability and the distribution of C and N in different aggregate fractions. Soil till Res 105:192–199
Kirchhof G, Priyonob S, Utomob WH, Adisarwanto T, Dacanay EV, So HB (2000) The effect of soil puddling on the soil physical properties and the growth of rice and post-rice crops. Soil till Res 56:37–50
Kögel-Knabner I, Amelung W, Cao Z, Fiedler S, Frenzel P, Jahn R, Kalbitz K, Kölbl A, Schloter M (2010) Biogeochemistry of paddy soils. Geoderma 157:1–14
Kundu DK, Ladha JK (1999) Sustaining productivity of lowland rice soils: issues and options related to N availability. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 53:19–33
Kundu DK, Ladha JK, Guzman EL (1996) Tillage depth influence on soil nitrogen distribution and availability in a rice lowland. Soil Sci Soc Am J 60:1153–1159
Linh TB, Sleutel S, Guong VT, Khoa LV, Cornelis WM (2015) Deeper tillage and root growth in annual rice-upland cropping systems result in improved rice yield and economic profit relative to rice monoculture. Soil till Res 154:44–52
Liu Z, Zhou W, Shen J, Li S, He P, Liang G (2014) Soil quality assessment of Albic soils with different productivities for eastern China. Soil till Res 140:74–81
Liu S, Pu C, Ren Y, Zhao X, Zhao X, Chen F, Xiao X, Zhang H (2016) Yield variation of double-rice in response to climate change in southern China. Eur J Agron 81:161–168
Martínez IG, Prat C, Ovalle C, Pozo A, Stolpe N, Zagal E (2012) Subsoiling improves conservation tillage in cereal production of severely degraded Alfisols under Mediterranean climate. Geoderma 189–190:10–17
McBride RA (2002) Atterberg limits. In: Dane JH, Topp CG (eds) Methods of soil analysis: part 4 physical methods. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, pp 389–398
McDonald AJ, Riha SJ, Duxbury JM, Steenhuis TS, Lauren JG (2006) Soil physical responses to novel rice cultural practices in the rice–wheat system: comparative evidence from a swelling soil in Nepal. Soil till Res 86:163–175
McQueen DJ, Shepherd TG (2002) Physical changes and compaction sensitivity of a fine-textured, poorly drained soil (Typic Endoaquept) under varying durations of cropping, Manawatu Region, New Zealand. Soil till Res 63:93–107
Peng S, Buresh RJ, Huang J, Yang J, Zou Y, Zhong X, Wang G, Zhang F (2006) Strategies for overcoming low agronomic nitrogen use efficiency in irrigated rice systems in China. Field Crops Res 96:37–47
Piovanelli C, Gamba C, Brandi G, Simoncini S, Batistoni E (2006) Tillage choices affect biochemical properties in the soil profile. Soil till Res 90:84–92
Puget P, Lal R (2005) Soil organic carbon and nitrogen in a Mollisol in central Ohio as affected by tillage and land use. Soil till Res 80:201–213
Rahman S, Parkinson RJ (2007) Productivity and soil fertility relationships in rice production systems, Bangladesh. Agric Syst 92:318–333
Schneider F, Don A, Hennings I, Schmittmann O, Seidel SJ (2017) The effect of deep tillage on crop yield—What do we really know? Soil till Res 174:193–204
Shukla MK, Lal R, Ebinger M (2006) Determining soil quality indicators by factor analysis. Soil till Res 87:194–204
Six J, Elliott ET, Paustian K (2000) Soil macroaggregate turnover and microaggregate formation: a mechanism for C sequestration under no-tillage agriculture. Soil Biol Biochem 32:2099–2103
Sun M, Ren A, Gao Z, Wang P, Mo F, Xue L, Lei M (2018) Long-term evaluation of tillage methods in fallow season for soil water storage, wheat yield and water use efficiency in semiarid southeast of the Loess Plateau. Field Crops Res 218:24–32
Ussiri DAN, Lal R (2009) Long-term tillage effects on soil carbon storage and carbon dioxide emissions in continuous corn cropping system from an alfisol in Ohio. Soil till Res 104:39–47
Van der Bom F, Nunes I, Raymond NS, Hansen V, Bonnichsen L, Magid J, Nybroe O, Jensen LS (2018) Long-term fertilisation form, level and duration affect the diversity, structure and functioning of soil microbial communities in the field. Soil Biol Biochem 122:91–103
Xu S, Zhang M, Zhang H, Chen F, Yang G, Xiao X (2013) Soil organic carbon stocks as affected by tillage systems in a double-cropped rice field. Pedosphere 23:696–704
Yao S, Teng X, Zhang B (2015) Effects of rice straw incorporation and tillage depth on soil puddlability and mechanical properties during rice growth period. Soil till Res 146:125–132
Yuan P, Wang J, Li C, Xiao Q, Liu Q, Sun Z, Wang J, Cao C (2020) Soil quality indicators of integrated rice-crayfish farming in the Jianghan Plain, China using a minimum data set. Soil till Res 204:104732
Zhang H, Shan B (2008) Historical records of heavy metal accumulation in sediments and the relationship with agricultural intensification in the Yangtze-Huaihe region, China. Sci Total Environ 399:113–120
Zhang J, Hang X, Lamine SM, Jiang Y, Afreh D, Qian H, Feng X, Zheng C, Deng A, Song Z, Zhang W (2017) Interactive effects of straw incorporation and tillage on crop yield and greenhouse gas emissions in double rice cropping system. Agric Ecosyst Environ 250:37–43
Zhang X, Yang W, Xin X, Zhu A, Ding S (2020) Poor physical structural components restrict soil fertility and crop productivity for wheat–maize cropping. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 117:169–184
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant Number 2018YFD0200505), the Anhui Province Key Research & Development Plan of China (2022107020004) and the Second Level Youth Development Fund from Anhui Academy of Agricultural Sciences (QNYC-202115).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
We confirm that the field studies did not involve endangered or protected species.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, P., Li, L. & Wang, X. Shallow plough tillage with straw return increases rice yield by improving nutrient availability and physical properties of compacted subsurface soils. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 127, 69–83 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-023-10265-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-023-10265-1