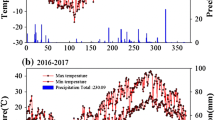
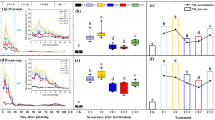
Abstract
The Chinese government aims at reducing nutrients losses from agriculture through incentivising the substitution of synthetic fertilizer by animal manure applications. This paper addresses the question how different substitution ratios affect crop yield, nitrogen (N) utilization efficiency (NUE), ammonia (NH3) volatilization and the N balance of a typical winter wheat–summer maize double cropping system. A field experiment was conducted with six treatments, including a no N treatment and five N substitution ratios (100%, 75%, 50%, 25% and 0%), between October 2016 and September 2018. The yield and NUE were highest with a partial N substitution (75% inorganic N fertilizer + 25 manure N). Mean yields were 8553 kg ha−1 for wheat and 10,620 kg ha−1 for maize in the treatment with 75% inorganic N + 25% manure N. Mean NUE was 55% for wheat and 45% for maize in this treatment. The mean N balance, N uptake, and soil residual Nmin increased, while NH3 emissions and N surpluses decreased with an increasing substitution of synthetic N fertilizer by manure N. A substitution of 25% of the inorganic N fertilizer by manure N showed the best performance. Selecting the appropriate ratio of synthetic N fertilizer to manure is an effective pathway for green agricultural development, as it ensures a high crop yield and N utilization, and reduces the environmental cost of food production.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agegnehu G, Nelson PN, Bird MI (2016) Crop yield, plant nutrient uptake and soil physicochemical properties under organic soil amendments and nitrogen fertilization on Nitisols. Soil Till Res 160:1–13
Alberto SC, Thomas MB, Vicci C, Vallejo A (2010) Effect of water addition and the urease inhibitor NBPT on the abatement of ammonia emission from surface applied urea. Atmos Environ 45(8):1517–1524
Bai Z, Ma L, Jin S, Ma W, Velthof GL, Oenema O, Liu L, Chadwick D, Zhang FS (2016) Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium flows through the manure management chain in china. Environ Sci Technol 50:13409–13418
Bao SD (2000) Soil Agro-chemistrical Analysis. China Agriculture Press, Beijing
Berry PM, Sylvester-Bradley R, Philipps L, Hatch DJ, Cuttle SP, Rayns FW, Gosling P (2002) Is the productivity of or‐ganic farms restricted by the supply of available nitrogen? Soil Use Manag 18:248–255
Bittman S, Dedina M, Howard C, Oenema O, Sutton M (2014) Options for ammonia mitigation: guidance from the UNECE task force on reactive nitrogen. Centre for Ecology and Hydrology, Edinburgh
Bosch-Serra ÀD, Yague MR, Teira-Esmatges MR (2014) Ammonia emissions from different fertilizing strategies in mediterranean rainfed winter cereals. Atmos Environ 84:204–212
Cao CG, Li CF, Kou ZK, Yang JH, Wang JP (2010) Effects of N source and tillage on NH3 volatilization from paddy soils. Acta Agric Univ Jiangxiensis 32(5):881–886
Cassity-Duffey K, Cabrera M, Gaskin J, Franklin D, Kissel D, Saha U (2020) Nitrogen mineralization from organic materials and fertilizers. Soil Sci Soc Am J 84:522–533
Chivenge P, Vanlauwe B, Six J (2011) Does the combined application of organic and mineral nutrient sources influence maize productivity? A meta-analysis. Plant Soil 342(1–2):1–30
Cui SH, Shi YL, Groffman PM, Schlesinger WH, Zhu YG (2013) Centennial-scale analysis of the creation and fate of reactive nitrogen in China (1910–2010). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:2052–2057
Cui X, Guo L, Li C, Liu M, Wu G, Jiang G (2021) The total biomass nitrogen reservoir and its potential of replacing chemical fertilizers in China. Renew Sust Energ Rev 135:110215
Cusick PR, Kelling KA, Powell JM, Muñoz GR (2006) Estimates of residual dairy manure nitrogen availability using various techniques. J Environ Qual 35:2170–2177
David MK, Gentry LE, Kovacic DA, Smith KM (1997) Nitrogen balance in and export from an agricultural watershed. J Environ Qual 26:1038–1048
Edmeades DC (2003) The long-term effects of manures and fertilisers on soil productivity and quality: a review. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 66(2):165–180
Gai X, Liu H, Liu J, Zhai L, Yang BO, Wu S, Ren T, Lei Q, Wang H (2018) Long-term benefits of combining chemical fertilizer and manure applications on crop yields and soil carbon and nitrogen stocks in North China Plain. Agric Water Manag 208(12):384–392
Galloway JN, Townsend AR, Erisman JW, Bekunda M, Cai ZC, Freney JR, Martinelli LA, Seitzinger SP, Sutton MA (2008) Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 320:889–892
Gasser MO, Laverdière MR, Lagacé R, Carbon J (2002) Impact of potato-cereal rotations and slurry applications on nitrate leaching and nitrogen balance in sandy soils. Can J Soil Sci 82:469–480
Gil MV, Carballo MT, Calvo LF (2008) Fertilization of maizewith compost from cattle manure supplemented with additional mineral nutrients. Waste Manag 28(8):1432–1440
Goucher L, Bruce R, Cameron DD, Koh SCL, Horton P (2017) The environmental impact of fertilizer embodied in a wheat-to-bread supply chain. Nat Plants 3(3):17012
Gu BJ, Ju XT, Chang J, Ge Y, Vitousek PM (2015) Integrated reactive nitrogen budgets and future trends in China. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:8792–8797
Gusmini G, Nishimura K, Masuda K, Adrinal A, Tamai T, Itani T (2015) Nitrogen balance in forage rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. Tachisuzuka) cultivation in pots with animal manure application. Plant Prod Sci 18:529–534
Hijbeek R, van Ittersum MK, ten Berge HFM, Gort G, Spiegel H, Whitmore AP (2017) Do organic inputs matter a meta-analysis of additional yield effects for arable crops in Europe. Plant Soil 411:293–303
Hijbeek R, ten Berge HFM, Whitmore AP, Barkusky D, Schröder JJ, van Ittersum MK (2018) Apparent long-term fertilizer replacement value of organic amendments depends on mineral fertilizer N range itself. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 4:1–11
Hou Y, Velthof GL, Oenema O (2015) Mitigation of ammonia, nitrous oxide and methane emissions from manure management chains: a meta-analysis and integrated assessment. Glob Change Biol 21(3):1293–1312
Huang J, Duan YH, Xu MG, Zhai LM, Zhang XB, Wang BR, Zhang YZ, Gao SD, Sun N (2017) Nitrogen mobility, ammonia volatilization, and estimated leaching loss from long-term manure incorporation in red soil. J Integr Agric 16(9):2082–2092
Jensen LS (2013) Animal manure fertiliser value, crop utilisation and soil quality impacts. In: Sommer SG, Christensen ML, Schmidt T, Jensen LS (eds) Animal manure recycling: treatment and management. Wiley, Chichester
Ju XT, Liu XJ, Zhang FS (2002) Study on effect of nitrogen fertilizer and nitrogen balance in winter wheat and summer maize rotation system. Sci Agric Sin 35:1361–1368
Ju XT, Kou CL, Zhang FS, Christie P (2006) Nitrogen balance and groundwater nitrate contamination: comparison among three intensive cropping systems on the north china plain. Environ Pollut 143(1):117–125
Ju XT, Xing GX, Chen XP, Zhang SL, Zhang LJ, Liu XJ, Cui ZL, Yin B, Christie P, Zhu ZL, Zhang FS (2009) Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:3041–3046
Kramer SB, Reganold JP, Glover JD, Bohannan B, Mooney HA (2006) Reduced nitrate leaching and enhanced denitrifier activity and efficiency in organically fertilized soils. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(12):4522–4527
Lassaletta L, Billen G, Garnier J, Bouwman L, Velazquez E, Mueller ND, Gerber J (2016) Nitrogen use in the global food system: past trends and future trajectories of agronomic performance, pollution, trade, and dietary demand. Environ Res Lett 11:095007
Li QQ, Cui XQ, Liu XJ, Roelcke M, Pasda G, Zerulla W, Wissemeier AH, Chen XP, Goulding K, Zhang FS (2017) A new urease-inhibiting formulation decreases ammonia volatilization and improves maize nitrogen utilization in North China Plain. Sci Rep 7:43853
Li MN, Wang YL, Adeli A, Yan H (2018) Effects of application methods and urea rates on ammonia volatilization, yields and fine root biomass of alfalfa. Field Crop Res 218:115–125
Liu E, Yan C, Mei X, He W, Bing SH, Ding L, Liu Q, Liu S, Fan T (2010) Long-term effect of chemical fertilizer, straw, and manure onsoil chemical and biological properties in northwest China. Geoderma 158(3–4):173–180
Liu MX, Huang X, Song Y, Tang J, Cao JJ, Zhang XY, Zhang Q, Wang S, Xu T, Kang L, Cai X, Zhang H, Yang F, Wang H, Yu J, Lau AKH, He L, Huang X, Duan L, Ding A, Xue L, Gao J, Liu B, Zhu T (2019) Ammonia emission control in China would mitigate haze pollution and nitrogen deposition, but worsen acid rain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116:7760–7765
Ma BL, Wu TY, Tremblay N, Deen W, Mclaughlin NB, Morrison MJ, Stewart G (2010) On-fram assessment of the amount and timing of nitrogen fertilizer on ammonia volatilization. Agron J 102:134–144
National Bureau of Statistics of China (2020) China statistical yearbook. Agricluture. China Statistics Press, Beijing, pp 375–377
Pelster DE, Watt D, Strachan IB, Rochette P, Chantigny MH (2019) Effects of initial soil moisture, clod size, and clay content on ammonia volatilization after subsurface band application of urea. J Environ Qual 48(3):549–558
Roelcke M, Li SX, Tian XH, Gao YJ, Richter J (2002) In situ comparisons of ammonia volatilization from N fertilizers in Chinese loess soils. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 62:73–88
Sanchita M, Donner E, Smith E, Sarkar B, Lombi E (2019) Biochar with nearneutral pH reduces ammonia volatilization and improves plant growth in a soil–plant system: a closed chamber experiment. Sci Total Environ 697:114–134
Singh DK, Pandey PC, Nanda G, Gupta S (2019) Long-term effects of inorganic fertilizer and farmyard manure application on productivity, sustainability and profitability of rice–wheat system in Mollisols. Arch Agron Soil Sci 65(2):139–151
Sommer SG, Olesen JE, Christensen BT (1991) Effects of temperature, wind speed and air humidity on ammonia volatilization from surface applied cattle slurry. J Agric Sci 117:91–100
Subehia SK, Sepehya S, Rana SS, Negi SC, Sharma SK (2013) Long-term effect of organic and inorganic fertilizers on rice (Oryza sativa L.)–wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) yield, and chemical properties of an acidic soil in the western Himalayas. Exp Agric 49:382–394
Sutton MA, Bleeker A, Howard CM, Bekunda M, Grizzetti B, de Vries W, van Grinsven HJM, Abrol YP, Adhya TK, Billen G, Davidson EA, Datta A, Diaz R, Erisman JW, Liu XJ, Oenema O, Palm C, Raghuram N, Reis S, Scholz RW, Sims T, Westhoek H, Zhang FS (2013) Our nutrient World: the challenge to produce more food and energy with less pollution. Global Overview of Nutrient Management. Centre for Ecology and Hydrology, Edinburgh on behalf of the Global Partnership on Nutrient Management and the International Nitrogen Initiative
Ti CP, Xia LL, Chang SX, Yan XY (2019) Potential for mitigating global agricultural ammonia emission: a meta-analysis. Environ Pollut 245:141–148
Wang J, Zhu B, Zhang JB, Müller C, Cai ZC (2015) Mechanismsof soil N dynamics following long-term application of organic fertilizers to subtropical rain-fed purple soil in China. Soil Biol Biochem 91:222–231
Xia LL, Lam SK, Yan XY, Chen DL (2017) How does recycling of livestock manure in agroecosystems affect crop productivity, reactive nitrogen losses, and soil carbon Balance? Environ Sci Technol 51:7450–7457
Yang J, Gao W, Ren SR (2015) Long-term effects of combined application of chemical nitrogen with organic materials on crop yields, soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in fluvo-aquic soil. Soil Till Res 151:67–74
Zhang Y, Li C, Wang Y, Hu Y, Christie P, Zhang J, Li X (2016) Maize yield and soil fertility with combined use of compost and inorganic fertilizers on a calcareous soil on the North China Plain. Soil Till Res 155:85–94
Zhang XY, Fang QC, Zhang T, Ma WQ, Velthof GL, Hou Y, Oenema O, Zhang FS (2019) Benefits and trade-offs of replacing synthetic fertilizers by animal manures in crop production in China: a meta-analysis. Glob Change Biol 26:14826
Zhao X, Liu B, Liu Y, Qi JY, Wang X, Pu C, Li SS, Zhang XZ, Yang XG, Lal R, Chen F, Zhang HL (2020) Sustaining crop production in China’s cropland by crop residue retention: a meta-analysis. Land Degrad Dev 31(6):694–709
Zhou M, Zhu B, Brüggemann N, Dannenmann M, Wang Y, Butterbach-Bahl K (2016) Sustaining crop productivity while reducing environmental nitrogen losses in the subtropical wheat–maize cropping systems: a comprehensive case study of nitrogen cycling and balance. Agric Ecosyst Environ 231:1–14
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number 31272247) and the Program of International S&T Cooperation, Ministry of Science and Technology, China (Grant Number 2015DFG91990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tong, B., Hou, Y., Wang, S. et al. Partial substitution of urea fertilizers by manure increases crop yield and nitrogen use efficiency of a wheat–maize double cropping system. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 127, 11–21 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-022-10219-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-022-10219-z