Abstract
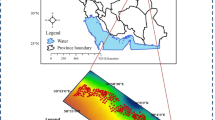
Soil calcium carbonate (CaCO3) content is an important soil property. The prediction of soil CaCO3 content is necessary for the sustainable management of soil fertility. In this work, we attempted to incorporate environmental variables directly and through regression models into the framework of Bayesian maximum entropy (BME) to predict CaCO3 content. Firstly, multiple linear regression (MLR) and geographically weighted regression (GWR) were used to establish a relationship between sampling data and environmental variables, including Digital Elevation Model, pH, temperature, rainfall, and fluvo-aquic soils. Prediction results of MLR and GWR served as soft data and were incorporated into the framework of BME to estimate the CaCO3 content. Secondly, soil samples and environmental variables were combined to generate probability distributions of CaCO3 at unsampled points. These probability distributions were used as soft data for the BME to predict the CaCO3 content. The results showed that the GWR method (r = 0.84, RMSE = 24.0 g kg−1) performed better than the MLR method (r = 0.73, RMSE = 30.1 g kg−1). The BME-GWR method outperformed the BME-EV and BME-MLR methods. The r values of BME-GWR, BME-EV, and BME-MLR methods were 0.87, 0.86, and 0.82, respectively, and the RMSEs of the three methods were 22.2, 23.9, and 25.2 g kg−1, respectively. The spatial distribution of CaCO3 content predicted by the above methods was similar and significantly higher in the southwest than in the northeast.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amini H, Taghavi-Shahri SM, Henderson SB, Naddafi K et al (2014) Land use regression models to estimate the annual and seasonal spatial variability of sulfur dioxide and particulate matter in Tehran, Iran. Sci Total Environ 488–489:343–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.04.106
Chen L, Gao S et al (2018) Spatiotemporal modeling of PM2.5 concentrations at the national scale combining land use regression and Bayesian maximum entropy in China. Environ Int 116:300–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.03.047
Christakos G (1990) A Bayesian/maximum-entropy view to the spatial estimation problem. Math Geol 22:763–777. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00890661
Christakos G (2000) Modern spatiotemporal geostatistics. Oxford University Press, New York
Costa EM, Tassinari WDS, Pinheiro HSK et al (2018) Mapping soil organic carbon and organic matter fractions by geographically weighted regression. J Environ Qual 47:718–725. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2017.04.0178
Douaik A, Meirvenne MV, Tóth T (2005) Soil salinity mapping using spatio-temporal kriging and Bayesian maximum entropy with interval soft data. Geoderma 128:234–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2005.04.006
Everitt BS, Skrondal A (2010) The Cambridge dictionary of statistics. Cambridge University Press
Fei X, Christakos G, Xiao R et al (2019) Improved heavy metal mapping and pollution source apportionment in Shanghai City soils using auxiliary information. Sci Total Environ 661:168–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.149
Feng Z, Tang Y, Yang Y et al (2008) Relief degree of land surface and its influence on population distribution in China. J Geogr Sci 18(2):237–246. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-008-0237-8
Fotheringham AS, Charlton ME, Brunsdon C (1998) Geographically weighted regression: a natural evolution of the expansion method for spatial data analysis. Environ Plan A 30:1905–1927. https://doi.org/10.1068/a301905
Harris P, Brunsdon C, Fotheringham AS (2011) Links, comparisons and extensions of the geographically weighted regression model when used as a spatial predictor. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 25:123–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-010-0444-6
He J, Kolovos A (2018) Bayesian maximum entropy approach and its applications: a review. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 32:859–877. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-017-1419-7
Hengl T, Heuvelink GBM, Rossiter DG (2007) About regression-kriging: from equations to case studies. Comput Geosci 33:1301–1315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2007.05.001
Hu JG, Zhou J, Zhou GM et al (2016) Improving estimations of spatial distribution of soil respiration using the Bayesian maximum entropy algorithm and soil temperature as auxiliary data. PLoS ONE 11:e0146589. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0146589
Jensen JK, Holm PE, Nejrup J et al (2009) The potential of willow for remediation of heavy metal polluted calcareous urban soils. Environ Pollut 157:931–937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2008.10.024
Kumar S (2015) Estimating spatial distribution of soil organic carbon for the Midwestern United States using historical database. Chemosphere 127:49–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.12.027
Lagacherie P, Baret F, Feret JB et al (2008) Estimation of soil clay and calcium carbonate using laboratory, field and airborne hyperspectral measurements. Remote Sens Environ 112:825–835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2007.06.014
Lapenis AG, Lawrence GB, Bailey SW et al (2008) Climatically driven loss of calcium in steppe soil as a sink for atmospheric carbon. Glob Biogeochem Cycles. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007GB003077
Leung Y, Mei CL, Zhang WX (2000) Statistical tests for spatial nonstationarity based on the geographically weighted regression model. Environ Plan A 32:9–32. https://doi.org/10.1068/a3162
Li Y (2010) Can the spatial prediction of soil organic matter contents at various sampling scales be improved by using regression kriging with auxiliary information? Geoderma 159(1–2):63–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2010.06.017
Liang YT, He XD et al (2018) Effects of N:P ratio of Artemisia ordosica on growth influenced by soil calcium carbonate. Sci Cold Arid Regions 010:333–339. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1226.2018.00333
Mahmoudabadi E, Karimi A, Haghnia GH et al (2017) Digital soil mapping using remote sensing indices, terrain attributes, and vegetation features in the rangelands of northeastern Iran. Environ Monit Assess 189:500. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6197-7
Mishra U, Riley WJ (2012) Alaskan soil carbon stocks: spatial variability and dependenceon environmental factors. Biogeosciences 9:3637–3645. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-9-3637-2012
Qiao J, Li Q, Zhao Y et al (2009) The distribution of calcium carbonate in the topsoil of Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Border area. Geogr Geo-Inf Sci (Chin) 25:56–59
Quine TA, Zhang Y (2002) An investigation of spatial variation in soil erosion, soil properties, and crop production within an agricultural field in Devon, United Kingdom. J Soil Water Conserv 57:55–65. https://doi.org/10.1109/SAINTW.2003.1210142
Rasaei Z, Bogaert P (2019) Bayesian data fusion for combining maps of predicted soil classes: a case study using legacy soil profiles and DEM covariates in Iran. CATENA 182:104138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.104138
Reza SK, Baruah U, Sarkar D et al (2016) Spatial variability of soil properties using geostatistical method: a case study of lower Brahmaputra plains, India. Arab J Geosci 9:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2474-y
Sarmadian F, Keshavarzi A, Malekian A (2010) Continuous mapping of topsoil calcium carbonate using geostatistical techniques in a semi-arid region. Aust J Crop Sci 4:603–608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12230-010-9149-0
Song XD, Brus DJ, Liu F et al (2016) Mapping soil organic carbon content by geographically weighted regression: a case study in the Heihe River Basin, China. Geoderma 261:11–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2015.06.024
Sturges HA (1926) The choice of a class interval. J Am Stat Assoc 21:65–66. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.1926.10502161
Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi R, Sarmadian F, Minasny B, Triantafilis J, Omid M (2014) Digital mapping of soil classes using decision tree and auxiliary data in the Ardakan region. Iran Arid Land Res Manag 28:147–168. https://doi.org/10.1080/15324982.2013.828801
Triantafilis J, Odeh IOA, Mcbratney AB (2001) Five geostatistical models to predict soil salinity from electromagnetic induction data across irrigated cotton. Soil Sci Soc Am J 65(3):869–878. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2001.653869x
Verhulst N, Govaerts B, Sayre KD, Deckers J et al (2008) Using NDVI and soil quality analysis to assess influence of agronomic management on within-plot spatial variability and factors limiting production. Plant Soil 317:41–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9787-x
Wang K, Zhang C, Li W (2013) Predictive mapping of soil total nitrogen at a regional scale: a comparison between geographically weighted regression and cokriging. Appl Geogr 42:73–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2013.04.002
Wu J, Li J, Peng J et al (2015) Applying land use regression model to estimate spatial variation of PM2.5 in Beijing, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(9):7045–7061. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3893
Xiao L, Lang Y, Christakos G (2018) High-resolution spatiotemporal mapping of PM2.5 concentrations at Mainland China using a combined BME-GWR technique. Atmos Environ 173:295–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2017.10.062
Yang Y, Zhang CT, Zhang RX (2016) BME prediction of continuous geographical properties using auxiliary variables. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 30(1):9–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-014-1005-1
Yu HL, Kolovos A, Christakos G, Chen JC, Warmerdam S, Dev B (2007) Interactive spatiotemporal modelling of health systems: the SEKS-GUI framework. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 21:555–572. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-007-0135-0
Yu HL, Ku SC, Kolovos A (2016) A GIS tool for spatiotemporal modeling under a knowledge synthesis framework. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 30:665–679. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-015-1078-5
Zeng C, Yang L et al (2016) Mapping soil organic matter concentration at different scales using a mixed geographically weighted regression method. Geoderma 281:69–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.06.033
Zhang CT (2016) Research on key issues of Bayesian maximum entropy spatiotemporal prediction and its application (Chinese). Huazhong Agricultural University
Zhang CT, Yang Y (2019) Can the spatial prediction of soil organic matter be improved by incorporating multiple regression confidence intervals as soft data into BME method? CATENA 178:322–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.03.027
Zhang C, Tang Y, Xu X, Kiely G et al (2011) Towards spatial geochemical modelling: use of geographically weighted regression for mapping soil organic carbon contents in Ireland. Appl Geochem 26:1239–1248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.04.014
Zhang S, Huang Y, Shen C et al (2012) Spatial prediction of soil organic matter using terrain indices and categorical variables as auxiliary information. Geoderma 171–172:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2011.07.012
Zhao LB (2003) A study on soil CaCO3 deposition and soil CO2 in Loess hilly area (Chinese). Shanxi University, Taiyuan
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank National Key Research and Development Program (Grants No. 2016YFC0201700) and Youth Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants No. 41907194) for funding this investigation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shan, M., Liang, S., Fu, H. et al. Spatial prediction of soil calcium carbonate content based on Bayesian maximum entropy using environmental variables. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 120, 17–30 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-021-10135-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-021-10135-8