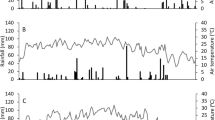
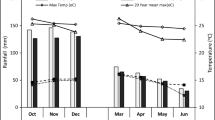
Abstract
Balancing fertilization of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and the use of controlled-release fertilizers are valuable practices for increasing yield and nutrient use efficiency. This 8-year field study was conducted using a mixture of controlled-release urea and soluble urea to evaluate maize yields, net returns and nutrient interactions in the North China Plain. The treatments included nitrogen application rates at 0, 150, 300 and 450 kg ha−1 using mixture; phosphorus application rates at 0, 16, 32 and 48 kg ha−1; and potassium application rates at 0, 125, 250 and 375 kg ha−1. The treatment using only soluble urea as the nitrogen source represented the standard farming practice in the region, with nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium being applied at 300, 16 and 250 kg ha−1, respectively. The results showed that the net return of the treatment with nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium being applied at 300, 16 and 250 kg ha−1, was increased by 14.8% over that of the farming practice treatment. Notably, controlled-release urea reduced the risks of decreased yields associated with price fluctuations. Multiple regression analysis results (R2 = 0.9726, P = 0.009) suggested that the coefficients of nitrogen × phosphorus, nitrogen × potassium were synergistic, while that of phosphorus × potassium was antagonistic. The interaction effects of the two factors decreased in the order nitrogen × potassium > nitrogen × phosphorus > phosphorus × potassium. The optimal maize yield was 9.2–9.3 t ha−1 at nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium application rates of 276–290, 27–29 and 210–226 kg ha−1, respectively. This study demonstrates that balanced fertilization based on controlled-release urea and soluble urea blend can improve maize yields and net returns.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alijani K, Bahrani MJ, Kazemeini SA (2012) Short-term responses of soil and wheat yield to tillage corn residue management and nitrogen fertilization. Soil Tillage Res 124(4):78–82
CRGCST (Cooperative Research Group on Chinese Soil Taxonomy) (2001) Chinese Soil Taxonomy. Science Press, Beijing, pp 166–167
Dash AK, Singh HK, Mahakud T, Pradhan KC, Jena D (2015) Interaction effect of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium with sulphur, boron and zinc on yield and nutrient uptake by rice under rice–rice cropping system in inceptisol of coastal Odisha. Int Res J Agric Sci Soil Sci 5(1):14–21
Douglas LA, Riazi A, Smith CJ (1980) A semi-micro method for determining total N in soils and plant material containing nitrite and nitrate. Soil Sci Soc Am J 44(2):431–433
Gao X, Li C, Zhang M, Wang R, Chen B (2015) Controlled release urea improved the nitrogen use efficiency yield and quality of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) on silt loamy soil. Field Crops Res 181:60–68
Garcia PL, Gonzaléz-Villalba HA, Sermarine RA, Trivelin PCO (2018) Nitrogen use efficiency and nutrient partitioning in maize as affected by blends of controlled-release and conventional urea. Arch Agron Soil Sci 64(14):1944–1962
Geng J, Sun Y, Zhang M, Li C, Yang Y, Liu Z, Li S (2015a) Long–term effects of controlled release urea application on crop yields and soil fertility under rice–oilseed rape rotation system. Field Crops Res 184:65–73
Geng J, Ma Q, Zhang M, Li C, Liu Z, Lyu X (2015b) Synchronized relationships between nitrogen release of controlled release nitrogen fertilizers and nitrogen requirements of cotton. Field Crops Res 184:9–16
Geng J, Chen J, Sun Y, Zheng W, Tian X, Yang Y, Zhang M (2016) Controlled release urea improved nitrogen use efficiency and yield of wheat and corn. Agron J 108(4):1666–1673
Grant CA, Wu R, Selles F, Harker KN, Clayton GW, Bittman S (2012) Crop yield and nitrogen concentration with controlled release urea and split applications of nitrogen as compared to non-coated urea applied at seeding. Field Crops Res 127(1):170–180
Guo J, Wang Y, Blaylock AD, Chen X (2017) Mixture of controlled release and normal urea to optimize nitrogen management for high-yielding (%3e15 Mg ha-1) maize. Field crops Res 204:23–30
Hartmann TE, Yue SC, Schulz R, He XK, Chen XP, Zhang FS, Müller T (2015) Yield and N use efficiency of a maize–wheat cropping system as affected by different fertilizer management strategies in a farmer’s field of the North China Plain. Field Crops Res 174(5):30–39
Kannan R, Ghinea G, Swaminathan S (2014) Salient region detection using patch level and region level image abstractions. IEEE Signal Process Lett 22(6):686–690
Kanter DR, Zhang X, Mauzerall DL (2015) Reducing nitrogen pollution while decreasing farmers' costs and increasing fertilizer industry profits. J Environ Qual 44(2):325
Kong L (2014) Maize residues soil quality and wheat growth in China. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 34(2):405–416
Liu K, Ma BL, Luan L, Li C (2011) Nitrogen phosphorus and potassium nutrient effects on grain filling and yield of high-yielding summer corn. J Plant Nutr 34(10):1516–1531
Liu X, Zhang Y, Han W, Tang A, Shen J, Cui Z, Fangmeier A (2013) Enhanced nitrogen deposition over China. Nature 494(7438):459
Liu TQ, Fan DJ, Zhang XX, Chen J, Li CF, Cao CG (2015) Deep placement of nitrogen fertilizers reduces ammonia volatilization and increases nitrogen utilization efficiency in no-tillage paddy fields in central china. Field Crops Res 184:80–90
Lu RK (ed) (1999) Analytical methods of soil agricultural chemistry. Agriculture, Science and Technology Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Ma BL, Zheng ZM, Morrison MJ, Gregorich EG (2016) Nitrogen and phosphorus nutrition and stoichiometry in the response of maize to various n rates under different rotation systems. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 104(1):1–13
Ma L, Zhao B, Guo Z, Wang D, Li D, Xu J, Li Z, Zhang J (2019) Divergent responses of bacterial activity, structure, and co-occurrence patterns to long-term unbalanced fertilization without nitrogen, phosphorus, or potassium in a cultivated vertisol. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(13):12741–12754
Miao Y, Zhang F (2011) Long–term experiments for sustainable nutrient management in china. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 31(2):397–414
Miller WP, Miller DM (1987) A micro-pipette method for soil mechanical analysis. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 18(1):1–15
Nguyen ML, Luo J, Quin B (2018) The role of nitrogen stable isotopes to investigate soil nitrogen transformations and cycling in agricultural systems. In: Soil nitrogen uses and environmental impacts. pp 40–63
Otteson BN, Mergoum M, Ransom JK (2007) Seeding rate and nitrogen management effects on spring wheat yield and yield components. Agron J 99(6):1615–1621
Postma JA, Lynch JP (2011) Root cortical aerenchyma enhances the growth of maize on soils with suboptimal availability of nitrogen phosphorus and potassium. Plant Physiol 156(3):1190–1201
Silva JG, França MGC, Gomide FTF, Magalhaes JR (2013) Different nitrogen sources affect biomass partitioning and quality of potato production in a hydroponic system. Am J Potato Res 90(2):179–185
Singh SR, Kundu DK, Tripathi MK, Dey P, Saha AR, Kumar M (2015) Impact of balanced fertilization on nutrient acquisition fibre yield of jute and soil quality in new gangetic alluvial soils of india. Appl Soil Ecol 92:24–34
Sun H, Zhang X, Wang E, Chen S, Shao L, Qin W (2016) Assessing the contribution of weather and management to the annual yield variation of summer maize using APSIM in the North China Plain. Field Crops Res 194:94–102
Than TH, Hla T, Nang HH, Htay HO, Kyaw KW, Mar MK (2016) Effect of different rates of nitrogen and potassium fertilizers application on growth and yield of Yezin-10 hybrid maize (Zea mays L.). J Agric Res 3(1):25–32
Thiraporn R, Feil B, Stamp P (1992) Effect of nitrogen fertilization on grain yield and accumulation of nitrogen phosphorus and potassium in the grains of tropical maize. J Agron Crop Sci 169(1–2):9–16
USDA, N (2010) Keys to soil taxonomy. Soil Survey Staff, Washington
Van Berkum EEM, Pauwels B, Upperman PM (2000) D-optimal designs for quadratic regression models. In: Balakrishnan N, Melas VB, Ermakov S (eds) Advances in stochastic simulation methods. Statistics for industry and technology. Birkhäuser, Boston, MA, pp 189–195
Wang XJ (2016) Effects of N, P K fertilizer on maize. Agric Technol 36(15):39–41 (in Chinese)
Wang XY, Gao CB, Liu ZY (2012) Effects of postponing N application on wheat grain yield protein quality and fertilizer-N use efficiency in a low-yield field in Jianghan plain. Adv J Food Sci Technol 4(6):357–361
Wen P, Wu Z, He Y, Ye BC, Han Y, Wang J, Guan X (2016a) Microwave-assisted synthesis of a semi-interpenetrating polymer network slow-release nitrogen fertilizer with water absorbency from cotton stalks. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4(12):6572–6579
Wen ZH, Shen JB, Blackwell M, Li HG, Zhao BQ, Yuan HM (2016b) Combined applications of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers with manure increase maize yield and nutrient uptake via stimulating root growth in a long-term experiment. Pedosphere 26(1):62–73
Yang J, Liao S, Li Y, Cao B, Sun Y, Zou G, Liu B (2018) Reducing nitrogen pollution while improving tomato production by controlled-release urea application. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 64(5):632–641
Zhang X, Zhu A, Xin X, Yang W, Zhang J, Ding S (2018) Tillage and residue management for long-term wheat–maize cropping in the North China Plain: I. Crop yield and integrated soil fertility index. Field Crops Res 221:157–165
Zhao S, Qiu S, Cao C, Zheng C, Zhou W, He P (2014) Responses of soil properties microbial community and crop yields to various rates of nitrogen fertilization in a wheat–maize cropping system in north-central China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 194:29–37
Zheng W, Zhang M, Liu Z, Zhou H, Lu H, Zhang W, Chen B (2016) Combining controlled-release urea and normal urea to improve the nitrogen use efficiency and yield under wheat–maize double cropping system. Field Crops Res 197:52–62
Zheng W, Liu Z, Zhang M, Shi Y, Zhu Q, Sun Y (2017) Improving crop yields nitrogen use efficiencies and profits by using mixtures of coated controlled-released and uncoated urea in a wheat–maize system. Field Crops Res 205: 106–115
Acknowledgements
We thank Cliff G. Martin for review of this manuscript.
Funding
The present study was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant Nos. 2017YFD0200706 and 2018YFD0200604) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41571236).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest, and there is no conflict of interest with Kingenta. This manuscript has been approved for publication by all the authors. All the listed authors have approved the enclosed manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, H., Zhang, M., Liu, Z. et al. Maize yield and economic return with controlled-release urea. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 115, 427–440 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-019-10020-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-019-10020-5