Abstract
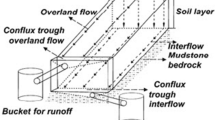
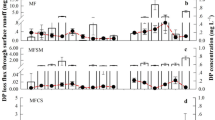
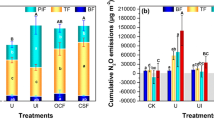
The transportation of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) from croplands to aquatic ecosystems potentially negatively influences water quality. Sustaining crop yields while decreasing the environmental impacts of the DON from nitrogen fertilizer application is a key challenge in sustainable agriculture. However, few field datasets have measured the lateral transportation of DON via hydrological routes under different nitrogen fertilizer applications, particularly in sloping croplands. Using lysimeter plots (8 × 4 m2), we measured DON loss via overland flow, interflow, and soil erosion under different fertilizer applications under a long-term field experiment. There were four treatments, including no fertilizer (CK), mineral fertilizer (NPK), mineral fertilizer combined with swine manure (MNPK), and mineral fertilizer combined with crop straw (CNPK). In comparison to the NPK treatment, the annual DON loss fluxes via overland flow, interflow, and soil erosion for the MNPK treatment were significantly (P < 0.05) increased by 68.8, 100.6, and 63.7%, respectively. Conversely, this was significantly decreased by 182.6, − 14.1, and 49.4%, respectively, under the CNPK treatment. Correspondingly, the yield-scaled total DON losses for the MNPK and CNPK treatments were significantly increased by 78.8 and − 18.2% compared to the NPK treatment (0.33 ± 0.04 kg N t−1 grain). Therefore, long-term continuous manure application is associated with an increased risk of DON environmental pollution. Alternatively, the incorporation of crop straw can be recommended as a means of decreasing DON pollution while maintaining crop yield.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashworth D, Alloway B (2004) Soil mobility of sewage sludge-derived dissolved organic matter, copper, nickel and zinc. Environ Pollut 127:137–144
Fang YT, Zhu WX, Gundersen P, Mo JM, Zhou GY, Yoh M (2009) Large loss of dissolved organic nitrogen from nitrogen-saturated forests in Subtropical China. Ecosystems 12:33–45
Fujii K, Funakawa S, Hayakawa C, Sukartiningsih Kosaki T (2013) Fluxes of dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen in cropland and adjacent forests in a clay-rich Ultisol of Thailand and a sandy Ultisol of Indonesia. Soil Tillage Res 126:267–275
Ge S, Zhao X, Wang SQ, Xing GX, Zhu ZL (2015) Dissolved organic nitrogen leaching from rice-wheat rotated agroecosystem in southern China. Pedosphere 25:93–102
Ghosh PK, Ramesh P, Bandyopadhyay KK, Tripathi AK, Hati KM, Misra AK, Acharya CL (2004) Comparative effectiveness of cattle manure, poultry manure, phosphor compost and fertilizer-NPK on three cropping systems in Vertisols of semi-aridtropics. I. Crop yields and system performance. Bioresour Technol 95:77–83
Hua KK, Zhu B, Wang XG (2014a) Dissolved organic carbon loss fluxes through runoff and sediment on sloping upland of purple soil in the Sichuan Basin. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 98:125–135
Hua KK, Zhu B, Wang XG, Guo XS, Wang DZ, Guo ZB (2014b) Effect of long-term fertilization on soil aggregate-associated dissolved organic nitrogen on sloping cropland of purple soil. Plant Soil Environ 24:51–56
Hua KK, Zhu B, Wang XG, Tian LL (2016) Forms and fluxes of soil organic carbon transport via overland flow, interflow, and soil erosion. Soil Sci Soc Am J 80:1011–1019
Huang MX, Liang T, Yang ZO, Wang LQ, Zhang CS, Zhou CH (2011) Leaching losses of nitrate nitrogen and dissolved organic nitrogen from a yearly two crops system, wheat-maize, under monsoon situations. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 91:77
Imhoff PT, Nakhli SAA (2017) Reducing storm water runoff through biochar addition to roadway soils. AGU fall meeting. AGU fall meeting abstracts
IUSS Working Group WRB (2006) World reference base for soil resources 2006, 2nd edn. World soil resources rep. no. 103. FAO, Rome, Italy
Jones DL, Shannon D, Murphy DV, Farrar J (2004) Role of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) in soil N cycling in grassland soils. Soil Biol Biochem 36:749–756
Kalbitz K, Solinger S, Park JH, Michalzik B, Matzner E (2000) Controls on the dynamics of dissolved organic matter in soils: a review. Soil Sci 165:277–304
Kušlienė G, Eriksen J, Rasmussen J (2015) Leaching of dissolved organic and inorganic nitrogen from legume-based grasslands. Biol Fertil Soils 51:217–230
Li ZM, Zhang XW, He YR, Tang SJ (1991) Purple soil in China (A). Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Long GQ, Jiang YJ, Sun B (2015) Seasonal and inter-annual variation of leaching of dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen under long-term manure application in an acidic clay soil in subtropical China. Soil Tillage Res 146:270–278
Lu RK (1999) Soil agro-chemical analysis methods. China Agro-science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Luo J, Ma M, Liu C, Zha JM, Wang ZJ (2009) Impacts of particulate organic carbon and dissolved organic carbon on removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, organ chlorine pesticides, and nonylphenols in a wetland. J Soils Sediments 9:180–187
Lusk M, Toor G (2016) Dissolved organic nitrogen in urban streams: biodegradability and molecular composition studies. Water Res 96:225–235
Maillard E, Angers DA (2014) Animal manure application and soil organic carbon stocks: a meta-analysis. Glob Change Biol 20:666–679
Ministry of Water Resources, The People’s Republic of China (2015) Handbook of water and soil conservation monitoring in runoff plots and small watershed. China Water & Power Press, China (in Chinese)
Nakhli SAA, Delkash M, Bakhshayesh BE, Kazemian H (2017) Application of zeolites for sustainable agriculture: a review on water and nutrient retention. Water Air Soil Pollut 228:464
Nardi S, Morari F, Berti A, Tosoni M, Giardini L (2004) Soil organic matter properties after 40 years of different use of organic and mineral fertilisers. Eur J Agron 21:357–367
Polyakov VO, Lal R (2008) Soil organic matter and CO2 emission as affected by water erosion on field runoff plots. Geoderma 143:216–222
Qualls RG, Haines BL, Swank WT, Tyler SW (2002) Retention of soluble organic nutrients by a forested ecosystem. Biogeochemistry 61:135–171
Stutter MI, Richards S, Dawson JC (2013) Biodegradability of natural dissolved organic matter collected from a UK moorland stream. Water Res 47:1169–1180
Tranvik LJ (1993) Microbial transformation of labile dissolved organic matter into humic-like matter in seawater. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 12:177–183
Vinther FP, Hansen EM, Eriksen J (2006) Leaching of soil organic carbon and nitrogen in sandy soils after cultivating grass-clover swards. Biol Fertil Soils 43:12–19
Wang T, Zhu B (2011) Nitrate loss via overland flow and interflow from a sloped farmland in the hilly area of purple soil, China. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 90:309–319
Wang T, Zhu B, Kuang FH (2012) Reducing interflow nitrogen loss from hillslope cropland in a purple soil hilly region in southwestern China. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 93:285–295
Wei X, Li XG, Wei N (2017) Reducing runoff and soil loss using corn stalk juice at plot scale. Soil Tillage Res 168:63–70
Xiong Y, Li QK (1986) Soils in China. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Zhou MH, Zhu B, Brüggemann N, Bergmann J, Wang YQ, Butterbach-Bahl K (2014) N2O and CH4 emissions, and NO3 − leaching on a crop-yield basis from a subtropical rain-fed wheat–maize rotation in response to different types of nitrogen fertilizer. Ecosystems 17:286–301
Zhu B, Wang T, Kuang FH, Luo ZX, Tang JL, Xu TP (2009) Measurements of nitrate leaching from a hillslope cropland in the Central Sichuan Basin, China. Soil Sci Soc Am J 73:1419–1426
Acknowledgements
Funding for this research was provided by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41430750), Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (Grant No. 1608085QD78), and the Foundation of Anhui Academic of Agricultural Science (Grant Nos. 16A1028 and 18C1033).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Ethical standard
We confirm that the field studies did not involve endangered or protected species.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hua, K., Zhu, B. Dissolved organic nitrogen fluxes and crop yield after long-term crop straw incorporation. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 112, 133–146 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-018-9937-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-018-9937-3