Abstract
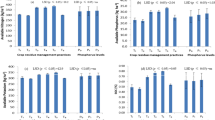
The rice–wheat system (RWS) practiced in northwestern parts of the Indo-Gangetic plains of India is highly productive, but conventional practices are resource (water, labour and energy) and cost intensive. A 4-year field study evaluated the effects of green manure (GM), crop residue and tillage on crop yields, economic profitability and soil fertility in a RWS. Four main plot treatments in rice included combinations of wheat stubble and Sesbania aculeata GM management: (1) puddled transplanted rice (PTR) with no wheat stubble, (2) PTR with 25% wheat stubbles (15–20 cm high) retained, (3) PTR with no wheat stubble plus GM, and (4) PTR with wheat stubble splus GM. Three sub-plots treatments in subsequent wheat included (1) conventional till wheat with rice straw removed (CTWR0), (2) zero till wheat with rice straw removed (ZTWR0) and (3) zero till wheat with 100% rice straw retained as surface mulch (ZTWR100). The results showed that main rice yield was significantly higher (8.0%) with 50% less fertilizer N application in GM compared with conventional PTR with no GM. Rice treatments did not affect the grain yield of subsequent wheat. ZTWR100 produced significantly higher mean wheat grain yield by 7.3% and 17.5% compared with CTWR0 and ZTWR0, respectively. System productivity was 11.5% higher in PTR with wheat stubble + GM followed by ZTWR100 compared with the conventional RWS and resulted in Rs 24,075 ha−1 more net returns. Significant increases in soil organic carbon, available P and available K contents were recorded in ZTWR100 over CTWR0. Recycling rice and wheat stubble in the field in RWS is also environment friendly as it avoids ill effects of straw burning.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arora VK, Sidhu AS, Sandhu KS, Thind SS (2010) Effects of tillage intensity, planting time and nitrogen rate on wheat yield following rice. Exp Agric 46:267–275
Arrobas M, Aguiar P, Rodrigues MA (2016) A comparison of a pasture ley with a maize monoculture on the soil fertility and nutrient release in the succeeding crop. Arch Agron Soil Sci 62:829–839
Aulakh MS, Khera TS, Doran JW, Bronson KF (2001) Managing crop residue with green manure, urea and tillage in a rice-wheat rotation. Soil Sci Soc Am J65:820–827
Balwinder-Singh Eberbach PL, Humphreys E, Kukal SS (2011) The effect of rice straw mulch on evapotranspiration, transpiration and soil evaporation of irrigated wheat in Punjab, India. Agric Water Manag 98:1847–1855
Belder PB, Bouman AM, Spiertz JHJ, Lu G, Quilang EJP (2002) Water use of continuously submerged and no submerged irrigated low land rice. In: Proceedings of a thematic workshop on water-wise rice production, 8–11 April, 2002 at IRRI Headquarters in Los Banos, Philippines
Bera T, Sharma S, Thind HS, Singh Y, Sidhu HS, Jat ML (2017) Soil biochemical changes at different wheat growth stages in response to conservation agriculture practices in rice-wheat system of north-western India. Soil Res 56:91–104
Bhattacharyya R, Kundu S, Pandey SC, Singh KP, Gupta HS (2008) Tillage and irrigation effects on crop yields and soil properties under the rice-wheat system in the Indian Himalayas. Agric Water Manag 95:993–1002
Bhushan L, Ladha JK, Gupta RK, Singh S, Tirol-Padre A, Saharawat YS, Gathala M, Pathak H (2007) Saving of water and labor in a rice-wheat system with no tillage and direct seeding technologies. Agron J 99:1288–1296
Chauhan BS, Mahajan G, Sardana V, Timsina J, Jat ML (2012) Productivity and sustainability of the rice-wheat cropping system in the Indo-Gangetic plains of the Indian subcontinent: problems, opportunities, and strategies. Adv Agron 117:315–369
Chivenge PPM, Giller KE, Mapfumo P, Six J (2007) Long-term impact of reduced tillage and residue management on soil carbon stabilization: implications for conservation agriculture on contrasting soils. Soil Tillage Res 94:328–337
Das A, Lal R, Patel DP, Idapuganti RG, Layek J, Ngachan SV, Ghosh RG, Bordoloi J, Kumar M (2014) Effects of tillage and biomass on soil quality and productivity of lowland rice cultivation by small scale farmers in North Eastern India. Soil Tillage Res 143:50–58
Dıaz-Zorita M, Grove J (2002) Duration of tillage management affects carbon and phosphorus stratification in phosphatic Paleudalfs. Soil Tillage Res 66:165–174
Feller C, Beare MH (1997) Physical control of soil organic matter dynamics in the Tropics. Geoderma 79:69–116
Gajri PR, Ghuman BS, Singh S, Mishra RD, Yadav DS, Singh H (2002) Tillage and residue management practices in rice-wheat system in Indo-Gangetic Plains—a diagnostic survey. Technical Report. National Agricultural Technology Project (NATP), Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi and Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana, India, p 12
Gangwar KS, Singh KK, Sharma SK, Tomar OK (2006) Alternative tillage and crop residue management in wheat after rice in sandy loam soils of Indo-Gangetic plains. Soil Tillage Res 88:242–252
Gathala MK, Ladha JK, Saharawat YS, Kumar V, Sharma PK (2011) Effect of tillage and crop establishment methods on physical properties of a medium-textured soil under a seven-year rice–wheat rotation. Soil Sci Soc Am J 75:1851–1862
Gathala MK, Kumar V, Sharma PC, Saharawat YS, Jat HS, Singh M, Kumar A, Jat ML, Humphreys E, Sharma DK, Sharma S, Ladha JK (2013) Optimizing intensive cereal-based cropping systems addressing current and future drivers of agricultural change in the northwestern Indo-Gangetic Plains of India. Agric Ecosyst Environ 177:85–97
Govaerts B, Verhulst N, Sayre KD, Dixon J, Dendooven L (2009) Conservation agriculture and soil carbon sequestration; between myth and farmer reality. Crit Rev Plant Sci 28:97–122
Hobbs PR, Gupta RK(2003) Resource conserving technologies for wheat in rice–wheat systems. In: Improvingthe productivity and sustainability of rice–wheat systems: issues and impact, vol.65 (eds J K Ladha, J Hill, RKGupta, J Duxbury, RJ Buresh), paper 7, ASA special publications, Madison, WI, pp 149–171
Hossain MS, Hossain A, Sarkar MAR, Jahiruddin M, de Silva Teixeira JA, Hossain MI (2016) Productivity and soil fertility of the rice-wheat system in the High Ganges River Floodplain of Bangladesh is influenced by the inclusion of legumes and manure. Agric Ecosyst Environ 218:40–52
Humphreys E, Kukal SS, Christen EW, Hira GS, Singh Balwinder, Yadav Sudhir, Sharma RK (2010) Halting the groundwater decline in northwestern India—Which crop technologies will be winners? Adv Agron 109:155–217
International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) (2000) IRRISTAT for window (CD-ROM) version 4.02b. IRRI, Los Banos, Philippines
Kirchhof G, So HB (1996) Management of clay soils for rainfed lowland rice-based cropping systems. In: Proceedings of the ACIAR international workshop. ACIAR, Canberra, Australia
Knudsen D, Peterson GA, Pratt PF (1982) Lithium, sodium and potassium. In: Page AL, Miller RM, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis part 2: chemical and microbiological properties. American Society of Agronomy, Soil Science Society of America, Madison, pp 225–246
Kumar S, Pandey DS (2004) Effect of tillage, rice residue and nitrogen management practices on yield of wheat and chemical properties of soil under rice-wheat cropping system. Indian J Agron 49:223–225
Kushwaha CP, Tripathi SK, Singh KP (2001) Soil organic matter and water stable aggregates under different tillage and residue conditions in a tropical dryland agroecosystem. Appl Soil Ecol 16:229–241
Ladha JK, Singh-Yadvinder, Erenstein O, Hardy B (eds) (2009) Integrated crop and resource management in the rice-wheat system of South Asia. International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos, p 395
Lu J, Hirasawa T, Lu J (2001) Study on intermittent irrigation for paddy rice. I. Water use efficiency. Pedosphere 11:49–56
Mishra JS, Singh VP, Namrata J (2010) Long-term effects of tillage and weed control on weed dynamics, soil properties and yield of wheat in rice-wheat system. Indian J Weed Sci 42:9–13
NAAS (2017) Innovative viable solution to rice residue burning in rice-wheat croppingsystem through concurrent use of super straw management system-fitted combines and TurboHappy Seeder. Policy Brief No. 2, National Academy of agricultural Sciences, New Delhi, p 16
Ogle SM, Breidt FJ, Paustian K (2005) Agricultural management impacts on soil organic carbon storage under moist and dry climatic conditions of temperate and tropical regions. Biogeochemistry 72:87–121
Olsen SR, Cole CV, Waternabe FS, Dean LA (1954) Estimation of available phosphorous in soil by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. USDA Circ 939:919
Pinheiro EFM, Pereira MG, Anjos LHC (2004) Aggregates distribution and soil organic matter under different tillage system for vegetable crops in a Red Latosol from Brasil. Soil Till Res 77:79–84
Ram H, Dadhwal V, Vashist KK, Kaur H (2013) Grain yield and water use efficiency of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in relation to irrigation levels and rice straw mulching in North West India. Agric Water Manag 128:92–101
Roldan A, Salinas-Garcia JR, Alguacil MM, Caravaca F (2005) Changes in soilenzyme activity, fertility, aggregation and C sequestration mediated by conservation tillage practices and water regime in a maize field. Appl Soil Ecol 30:11–20
Saharawat YS, Gathala M, Ladha JK, Malik RK, Singh S, Jat ML, Gupta R, Pathak H, Singh K (2010) Evaluation and promotion of integrated crop and resource management in Rice-Wheat system in North West India. In: Ladha JK et al (eds) Integrated crop and resource management in rice-wheat system of South Asia. Los Banos, Phillipines, pp 133–150
Sharma PK, Bhushan L, Ladha JK, Naresh RK, Gupta RK, Balasubramanian BV, Bouman BAM (2002) Crop-water relations in rice-wheat cropping under different tillage systems and water management practices in a marginally sodic medium textured soil. In: Bouman BAM, Hengsdijk B, Hardy B, Bihdraban TPT, Ladha JK (eds) Proceedings of the international workshop on water-wise rice production. International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos, pp 223–235
Sharma S, Kaur J, Thind HS, Singh Y, Sharma N, Kirandip K (2015) A framework for refining soil microbial indices as bioindicators during decomposition of various organic residues in a sandy loam soil. J Appl Nat Sci 7(2):700–708
Sidhu HS, Singh M, Humphreys E, Yadvinder Singh, BalwinderSingh, Dhillon SS, Blackwell J, Bector V, Malkeet-Singh, Sarbjeet-Singh (2007) The Happy seeder enables direct drilling of wheat into rice stubble. Aust J Exp Agric 47:844–854
Sidhu HS, Manpreet- Singh, Yadvinder Singh, Blackwell J, Humphreys E, Jat ML, Singh V (2015) Development and evaluation of the Turbo Happy Seeder for sowing wheat into heavy rice residues in NW India. Field Crops Res 184:201–212
Singh G, Jalota SK, Yadvinder-Singh (2007) Manuring and residue management effects on soil physical properties of a soil under the rice–wheat system in Punjab, India. Soil Till Res 94:229–238
Six J, Conant RT, Paul EA, Paustian K (2002) Stabilization mechanisms of soil organic matter: implications for C-saturation of soils. Plant Soil 241:155–176
Usman K, Khan EA, Khan N, Rasid A, Yazdan F, Din SU (2014) Response of wheat to tillage plus rice residue and nitrogen management in rice-wheat system. J Integr Agric 13:2389–2398
Walkley A, Black TA (1934) An examination of the Degtjaeff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37:29–38
Yadvinder Singh, Sidhu HS (2014) Management of cereal crop residues for sustainable rice- wheat production system in the Indo-Gangetic plains of India. Proc Indian Natl Sci Acad 80:95–114
Yadvinder Singh, Bijay-Singh, Khind CS (1992) Nutrient transformations in soils amended with green manures. Adv Soil Sci 20:238–298
Yadvinder Singh, Bijay-Singh, Ladha JK, Khind CS, Gupta RK, Meelu OP, Pasuquin E (2004a) Long-term effects of organic inputs on yield and soil fertility in the rice-wheat rotation. Soil Sci Soc Am J 68:845–853
Yadvinder Singh, Singh-Bijay, Ladha JK, Khind CS, Khera TS, Bueno CS (2004b) Effects of residue decomposition on productivity and soil fertility in rice-wheat rotation. Soil Sci Soc Am J 68:854–864
Yadvinder Singh, Singh-Bijay, Thind HS (2010) Green manure approaches to crop production and sustainable agriculture. In: Raghuram N (ed) ING bulletin on regional assessment of reactive nitrogen, Bulletin No. 14, SCON-ING, New Delhi pp 1–4 and 1–130
Yadvinder Singh, Thind HS, Sidhu HS (2014) Management options for rice residues for sustainable productivity of rice-wheat cropping system. J Agric ResPAU 51:209–220
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thind, H.S., Sharma, S., Yadvinder Singh et al. Rice–wheat productivity and profitability with residue, tillage and green manure management. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 113, 113–125 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-018-09967-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-018-09967-8