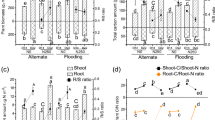
Abstract
Sustainable production of lowland rice (Oryza sativa L.) requires minimising undesirable soil nitrogen (N) losses via nitrate (NO3 −) leaching and denitrification. However, information is limited on the N transformations that occur between rice crops (fallow and land preparation), which control indigenous N availability for the subsequent crop. In order to redress this knowledge gap, changes in NO3 − isotopic composition (δ15N and δ18O) in soil and water were measured from harvest through fallow, land preparation, and crop establishment in a 7 year old field trial in the Philippines. During the period between rice crops, plots were maintained either, continuously flooded, dry, or alternately wet and dry from rainfall. Plots were split with addition or removal of residue from the previous rice crop. No N fertilizer was applied during the experimental period. Nitrogen accumulated during the fallow (20 kg NH4 +–N ha−1 in flooded treatments and 10 kg NO3 −–N ha−1 in treatments with drying), but did not influence N availability for the subsequent crop. Nitrate isotope fractionation patterns indicated that denitrification drove this homogenisation: during land preparation ~50 % of inorganic N in the soil (top 10 cm) was denitrified, and by 2 weeks after transplanting this increased to >80 % of inorganic N, regardless of fallow management. The 17 days between fallow and crop establishment controlled not only N attenuation (3–7 kg NO3 −–N ha−1 denitrified), but also N inputs (3–14 kg NO3 −–N ha−1 from nitrification), meaning denitrification was dependent on soil nitrification rates. While crop residue incorporation delayed the timing of N attenuation, it ultimately did not impact indigenous N supply. By measuring NO3 − isotopic composition over depth and time, this study provides unique in situ measurements of the pivotal role of land preparation in determining paddy soil indigenous N supply.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Redox potential could not be measured in treatment D on days 1 and 32 due to extreme soil dryness causing the electrode to lose contact with the soil.
References
Akiyama H, Yagi K, Yan XY (2005) Direct N2O emissions from rice paddy fields: summary of available data. Glob Biogeochem Cycle 19(1):10. doi:10.1029/2004gb002378
Austin BJ, Strauss EA (2011) Nitrification and denitrification response to varying periods of desiccation and inundation in a western Kansas stream. Hydrobiologia 658(1):183–195. doi:10.1007/s10750-010-0462-x
Barnes RT, Raymond PA (2010) Land-use controls on sources and processing of nitrate in small watersheds: insights from dual isotopic analysis. Ecol Appl 20(7):1961–1978. doi:10.1890/08-1328.1
Becker M, Asch F, Maskey SL, Pande KR, Shah SC, Shrestha S (2007) Effects of transition season management on soil N dynamics and system N balances in rice-wheat rotations of Nepal. Field Crop Res 103(2):98–108. doi:10.1016/j.fcr.2007.05.002
Berger S, Jang I, Seo J, Kang H, Gebauer G (2013) A record of N2O and CH4 emissions and underlying soil processes of Korean rice paddies as affected by different water management practices. Biogeochem 115(1–3):317–332. doi:10.1007/s10533-013-9837-1
Bierke A, Kaiser K, Guggenberger G (2008) Crop residue management effects on organic matter in paddy soils: the lignin component. Geoderma 146(1–2):48–57. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2008.05.004
Bird JA, Horwath WR, Eagle AJ, van Kessel C (2001) Immobilization of fertilizer nitrogen in rice: effects of straw management practice. Soil Sci Soc Am J 65(4):1143–1152
Bird JA, van Kessel C, Horwath WR (2002) Nitrogen dynamics in humic fractions under alternative straw management in temperate rice. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66(2):478–488
Blakemore LC, Searle PL, Daly BK (1987) Methods for chemical analysis of soils. NZ Soil Bureau Sci Rep 80:7
Borken W, Matzner E (2009) Reappraisal of drying and wetting effects on C and N mineralization and fluxes in soils. Glob Change Biol 15(4):808–824. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2008.01681.x
Bouman BAM, Castaneda AR, Bhuiyan SI (2002) Nitrate and pesticide contamination of groundwater under rice-based cropping systems: past and current evidence from the Philippines. Agric Ecosyst Environ 92(2–3):185–199. doi:10.1016/s0167-8809(01)00297-3
Bouman BAM, Humphreys E, Tuong TP, Barker R (2007) Rice and water. In: Sparks DL (ed) Advances in agronomy, Vol 92. Elsevier Academic Press Inc, San Diego, pp 187–237. doi:10.1016/s0065-2113(04)92004-4
Braker G, Schwarz J, Conrad R (2010) Influence of temperature on the composition and activity of denitrifying soil communities. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 73(1):134–148. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.2010.00884.x
Buresh RJ, Patrick WH Jr (1978) Nitrate reduction to ammonium in anaerobic soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42:913–918
Buresh RJ, Woodhead T, Shepherd KD, Flordelis E, Cabangon RC (1989) Nitrate accumulation and loss in a mungbean lowland rice cropping system. Soil Sci Soc Am J 53(2):477–482
Buresh RJ, Castillo EG, Dedatta SK (1993) Nitrogen losses in puddled soils as affected by timing of water-deficit and nitrogen-fertilization. Plant Soil 157(2):197–206. doi:10.1007/bf00011048
Buresh RJ, Reddy KR, Van Kessel C (2008) Nitrogen transformations in submerged soils. In: Stuart J, Schepers WR (eds) Nitrogen in agricultural systems. Agronomy Monograph, vol 49. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, WI pp 401–436
Burns DA, Boyer EW, Elliott EM, Kendall C (2009) Sources and transformations of nitrate from streams draining varying land uses: evidence from dual isotope analysis. J Environ Qual 38(3):1149–1159. doi:10.2134/jeq2008.0371
Cai ZC, Xing GX, Yan XY, Xu H, Tsuruta H, Yagi K, Minami K (1997) Methane and nitrous oxide emissions from rice paddy fields as affected by nitrogen fertilisers and water management. Plant Soil 196(1):7–14. doi:10.1023/a:1004263405020
Canfield DE, Glazer AN, Falkowski PG (2010) The evolution and future of Earth’s nitrogen cycle. Science 330(6001):192–196. doi:10.1126/science.1186120
Casciotti KL, Sigman DM, Ward BB (2003) Linking diversity and stable isotope fractionation in ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Geomicrobiol J 20(4):335–353. doi:10.1080/01490450303895
Casciotti KL, McIlvin M, Buchwald C (2010) Oxygen isotopic exchange and fractionation during bacterial ammonia oxidation. Limnol Oceanogr 55(2):753–762. doi:10.4319/lo.2009.55.2.0753
Casciotti KL, Buchwald C, McIlvin M (2013) Implications of nitrate and nitrite isotopic measurements for the mechanisms of nitrogen cycling in the Peru oxygen deficient zone. Deep-Sea Res Part I-Oceanogr Res Pap 80:78–93. doi:10.1016/j.dsr.2013.05.017
Cassman KG, Peng S, Olk DC, Ladha JK, Reichardt W, Dobermann A, Singh U (1998) Opportunities for increased nitrogen-use efficiency from improved resource management in irrigated rice systems. Field Crop Res 56(1–2):7–39. doi:10.1016/s0378-4290(97)00140-8
Cassman KG, Dobermann A, Walters DT (2002) Agroecosystems, nitrogen-use efficiency, and nitrogen management. Ambio 31(2):132–140. doi:10.1639/0044-7447(2002)031[0132:ANUEAN]2.0.CO;2
Cassman KG, Dobermann A, Walters DT, Yang H (2003) Meeting cereal demand while protecting natural resources and improving environmental quality. Annu Rev Environ Resour 28:315–358. doi:10.1146/annurev.energy.28.040202.122858
Chen M, Wu H, Wo F (2007) Nitrate vertical transport in the main paddy soils of Tai Lake region, China. Geoderma 142(1–2):136–141. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2007.08.004
Davidson EA, Chorover J, Dail DB (2003) A mechanism of abiotic immobilization of nitrate in forest ecosystems: the ferrous wheel hypothesis. Global Change Biol 9(2):228–236. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2486.2003.00592.x
DeDatta SK (1995) Nitrogen transformations in wetland rice ecosystems. Fertil Res 42(1–3):193–203
Dhondt K, Boeckx P, Van Cleemput O, Hofman G (2003) Quantifying nitrate retention processes in a riparian buffer zone using the natural abundance of N-15 in NO3. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 17(23):2597–2604. doi:10.1002/rcm.1226
Dobermann A, Cassman KG (2005) Cereal area and nitrogen use efficiency are drivers of future nitrogen fertilizer consumption. Sci China Ser C-Life Sci 48:745–758. doi:10.1360/062005-268
Dobermann A, Gaunt JL, Neue HU, Grant IF, Adviento MA, Pampolino MF (1994) Spatial and temporal variability of ammonium in flooded rice fields. Soil Sci Soc Am J 58(6):1708–1717
Dong NM, Brandt KK, Sorensen J, Hung NN, Hach CV, Tan PS, Dalsgaard T (2012) Effects of alternating wetting and drying versus continuous flooding on fertilizer nitrogen fate in rice fields in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Soil Biol Biochem 47:166–174. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.12.028
Endo A, Mishima S-I, Kohyama K (2012) Nitrate percolation and discharge in cropped Andosols and Gray lowland soils of Japan. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 1–21. doi:10.1007/s10705-012-9544-7
Fang YT, Koba K, Makabe A, Zhu FF, Fan SY, Liu XY, Yoh M (2012) Low delta O-18 values of nitrate produced from nitrification in temperate forest soils. Environ Sci Technol 46(16):8723–8730. doi:10.1021/es300510r
Fujii C, Nakagawa T, Onodera Y, Matsutani N, Sasada K, Takahashi R, Tokuyama T (2010) Succession and community composition of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in bulk soil of a Japanese paddy field. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 56(2):212–219. doi:10.1111/j.1747-0765.2010.00449.x
Galloway JN, Aber JD, Erisman JW, Seitzinger SP, Howarth RW, Cowling EB, Cosby BJ (2003) The nitrogen cascade. Bioscience 53(4):341–356
George T, Ladha JK, Buresh RJ, Garrity DP (1993) Nitrate dynamics during the aerobic soil phase in lowland rice-based cropping systems. Soil Sci Soc Am J 57(6):1526–1532
Granger J, Sigman DM, Lehmann MF, Tortell PD (2008) Nitrogen and oxygen isotope fractionation during dissimilatory nitrate reduction by denitrifying bacteria. Limnol Oceanogr 53(6):2533–2545. doi:10.4319/lo.2008.53.6.2533
Henckel T, Conrad R (1998) Characterization of microbial NO production, N2O production and CH4 oxidation initiated by aeration of anoxic rice field soil. Biogeochem 40(1):17–36
Hobbie EA, Ouimette AP (2009) Controls of nitrogen isotope patterns in soil profiles. Biogeochem 95(2–3):355–371. doi:10.1007/s10533-009-9328-6
Hogberg P (1997) Tansley review No 95—N-15 natural abundance in soil-plant systems. New Phytol 137(2):179–203. doi:10.1046/j.1469-8137.1997.00808.x
Ishii S, Ikeda S, Minamisawa K, Senoo K (2011) Nitrogen cycling in rice paddy environments: past achievements and future challenges. Microbes Environ 26(4):282–292. doi:10.1264/jsme2.ME11293
Jin ZF, Pan ZY, Jin MT, Li FL, Wan Y, Gu B (2012) Determination of nitrate contamination sources using isotopic and chemical indicators in an agricultural region in China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 155:78–86. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2012.03.017
Johnson-Beebout SE, Angeles OR, Alberto MCR, Buresh RJ (2009) Simultaneous minimization of nitrous oxide and methane emission from rice paddy soils is improbable due to redox potential changes with depth in a greenhouse experiment without plants. Geoderma 149(1–2):45–53. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2008.11.012
Kempers AJ, Zweers A (1986) Ammonium determination in soil extracts by the salicylate method. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 17(7):715–723. doi:10.1080/00103628609367745
Kendall C (1998) Tracing nitrogen sources and cycling in catchments. In: Kendall C, Mcdonell JJ (eds) Isotope tracers in catchment hydrology. Elsevier Science B.V, Amsterdam, pp 519–576
Koba K, Tokuchi N, Wada E, Nakajima T, Iwatsubo G (1997) Intermittent denitrification: the application of a N-15 natural abundance method to a forested ecosystem. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 61(23):5043–5050. doi:10.1016/s0016-7037(97)00284-6
Kögel-Knabner I, Amelung W, Cao ZH, Fiedler S, Frenzel P, Jahn R, Kalbitz K, Kolbl A, Schloter M (2010) Biogeochemistry of paddy soils. Geoderma 157(1–2):1–14. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2010.03.009
Kool DM, Wrage N, Zechmeister-Boltenstern S, Pfeffer M, Brus D, Oenema O, Van Groenigen JW (2010) Nitrifier denitrification can be a source of N2O from soil: a revised approach to the dual-isotope labelling method. Eur J Soil Sci 61(5):759–772. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2389.2010.01270.x
Linquist BA, Brouder SM, Hill JE (2006) Winter straw and water management effects on soil nitrogen dynamics in California rice systems. Agron J 98(4):1050–1059. doi:10.2134/agronj2005.0350
Mandal B, Vlek PLG, Mandal LN (1999) Beneficial effects of blue-green algae and Azolla, excluding supplying nitrogen, on wetland rice fields: a review. Biol Fertil Soils 28(4):329–342. doi:10.1007/s003740050501
Mariotti A, Germon JC, Hubert P, Kaiser P, Letolle R, Tardieux A, Tardieux P (1981) Experimental determination of nitrogen kinetic isotope fractionation: some principles: illustration for the denitrification and nitrification processes. Plant Soil 62(3):413–430. doi:10.1007/bf02374138
Mariotti A, Germon JC, Leclerc A (1982) Nitrogen isotope fractionation associated with the NO2–N2O step of denitrification in soils. Can J Soil Sci 62(2):227–241
McIlvin MR, Altabet MA (2005) Chemical conversion of nitrate and nitrite to nitrous oxide for nitrogen and oxygen isotopic analysis in freshwater and seawater. Anal Chem 77(17):5589–5595. doi:10.1021/ac050528s
Möbius J (2013) Isotope fractionation during nitrogen remineralization (ammonification): implications for nitrogen isotope biogeochemistry. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 105:422–432. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2012.11.048
Olk DC, Cassman KG, Schmidt-Rohr K, Anders MM, Mao JD, Deenik JL (2006) Chemical stabilization of soil organic nitrogen by phenolic lignin residues in anaerobic agroecosystems. Soil Biol Biochem 38(11):3303–3312. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2006.04.009
Rasche F, Cadisch G (2013) The molecular microbial perspective of organic matter turnover and nutrient cycling in tropical agroecosystems. What do we know? Biol Fertil Soils 49(3):251–262. doi:10.1007/s00374-013-0775-9
Ringrose-Voase AJ, Kirby JM, Djoyowasito G, Sanidad WB, Serrano C, Lando TM (2000) Changes to the physical properties of soils puddled for rice during drying. Soil Tillage Res 56(1–2):83–104. doi:10.1016/s0167-1987(00)00124-0
Rivett MO, Buss SR, Morgan P, Smith JWN, Bemment CD (2008) Nitrate attenuation in groundwater: a review of biogeochemical controlling processes. Water Res 42(16):4215–4232. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2008.07.020
Ros GH, Hoffland E, van Kessel C, Temminghoff EJM (2009) Extractable and dissolved soil organic nitrogen: a quantitative assessment. Soil Biol Biochem 41(6):1029–1039. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2009.01.011
Rutting T, Boeckx P, Muller C, Klemedtsson L (2011) Assessment of the importance of dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium for the terrestrial nitrogen cycle. Biogeosciences 8(7):1779–1791. doi:10.5194/bg-8-1779-2011
Santiago-Ventura T, Bravo M, Daez C, Ventura V, Watanabe I, App AA (1986) Effects of N fertilizers, straw, and dry fallow on the nitrogen balance of a flooded soil planted with rice. Plant Soil 93(3):405–411. doi:10.1007/bf02374291
Schimel JP, Bennett J (2004) Nitrogen mineralization: challenges of a changing paradigm. Ecology 85(3):591–602. doi:10.1890/03-8002
Sebilo M, Billen G, Grably M, Mariotti A (2003) Isotopic composition of nitrate–nitrogen as a marker of riparian and benthic denitrification at the scale of the whole Seine River system. Biogeochem 63(1):35–51. doi:10.1023/a:1023362923881
Sherlock RR, Goh KM (1985) Dynamics of ammonia volatilization from simulated urine patches and aqueous urea applied to pasture. 2. Theoretical derivation of a simplified model. Fertil Res 6(1):3–22. doi:10.1007/bf01058161
Sigman DM, Robinson R, Knapp AN, van Geen A, McCorkle DC, Brandes JA, Thunell RC (2003) Distinguishing between water column and sedimentary denitrification in the Santa Barbara Basin using the stable isotopes of nitrate. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 4:20. doi:10.1029/2002gc000384
Stark JM, Firestone MK (1995) Mechanisms for soil-moisture effects on activity of nitrifying bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 61(1):218–221
Wells NS, Clough TJ, Baisden WT (in press) Ammonia volatilisation is not the dominant factor in determining the isotopic composition of soil nitrate in pasture systems. Agric Ecosyst Environ
Witt C, Cassman KG, Ottow JCG, Biker U (1998) Soil microbial biomass and nitrogen supply in an irrigated lowland rice soil as affected by crop rotation and residue management. Biol Fertil Soils 28(1):71–80. doi:10.1007/s003740050465
Witt C, Cassman KG, Olk DC, Biker U, Liboon SP, Samson MI, Ottow JCG (2000) Crop rotation and residue management effects on carbon sequestration, nitrogen cycling and productivity of irrigated rice systems. Plant Soil 225(1–2):263–278. doi:10.1023/a:1026594118145
Xiong ZQ, Huang TQ, Ma YC, Xing GX, Zhu ZL (2010) Nitrate and ammonium leaching in variable- and permanent-charge paddy soils. Pedosphere 20(2):209–216. doi:10.1016/s1002-0160(10)60008-2
Yao SH, Zhang B, Hu F (2011) Soil biophysical controls over rice straw decomposition and sequestration in soil: the effects of drying intensity and frequency of drying and wetting cycles. Soil Biol Biochem 43(3):590–599. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.11.027
Zbieranowski AL, Aherne J (2012) Ambient concentrations of atmospheric ammonia, nitrogen dioxide and nitric acid across a rural–urban–agricultural transect in southern Ontario, Canada. Atmos Environ 62:481–491
Zhang JS, Zhang FP, Yang JH, Wang JP, Cai ML, Li CF, Cao CG (2011) Emissions of N2O and NH3, and nitrogen leaching from direct seeded rice under different tillage practices in central China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 140(1–2):164–173. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2010.11.023
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Angel Bautista, Sonny Pantoja, and Jerone Onoya for assistance with field work at the IRRI experimental farm and to Mia Bunquin (International Rice Research Institute) for assistance in preparing samples for isotope analysis. Thanks especially to Jun Correa for management oversight of the field trial. Thanks to Roger Cresswell and Joy Jiao at Lincoln University for analytical assistance. Research funding came from Lincoln University, W. Troy Baisden at GNS Science, plus additional funding to N.S.W. from the U.S. Student Fulbright Programme/PAEF and the European Community’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013 under Grant Agreement Number 265063).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wells, N.S., Clough, T.J., Johnson-Beebout, S.E. et al. Land management between crops affects soil inorganic nitrogen balance in a tropical rice system. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 100, 315–332 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-014-9644-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-014-9644-7