Abstract
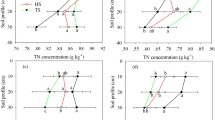
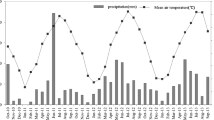
A field experiment was conducted in Jurong of Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, China from 2006 to 2008 to investigate N2O emission during the wheat-growing season as affected by various rice straw returning methods prior to wheat cultivation. The study was designed to have four treatments: no rice straw applied (CK), rice straw burnt in situ (RB), rice straw evenly incorporated into the topsoil (RI), rice straw evenly spread over the field as mulch (RM). Results showed that N2O emission was decreased by 24–29% in Treatment RB and by 3–18% in Treatment RI, but increased by 15–39% in Treatment RM, compared with that in Treatment CK. The contents of soil total C and N at wheat harvest were significantly increased by 7–13% and by 8–12% in Treatment RI, respectively, compared with that in Treatment CK. The wheat grain yield in Treatment RI was 1.0–1.2 times that in the Treatment CK. Based on these results, the best management practice of returning rice straw to the soil prior to wheat cultivation is evenly incorporating rice straw into the topsoil, as the method tended to reduce N2O emission during the wheat-growing season and increase wheat yield and soil fertility.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreae MO, Merlet P (2001) Emissions of trace gases and aerosols from biomass burning. Global Biogeochem Cycles 15:955–966
Aulakh MS, Rennie DA, Paul EA (1984) The influence of plant residues on denitrification rates in conventional and zero tilled soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 48:790–794
Aulakh MS, Doran JW, Mosier AR (1992) Soil denitrification-significance, measurement, and effects of management. Adv Soil Sci 18:1–57
Bacon PE (1987) Effect of nitrogen fertilization and rice stubble management techniques on soil moisture content, soil nitrogen status, and nitrogen uptake by wheat. Field Crops Res 17:75–90
Batjes NH, Bridges EM (1992) World inventory of soil emissions. No. 92/4. Working Paper and Preprint, pp 11–79
Blackmer AM, Bremner JM, Schmidt EL (1980) Production of N2O by ammonia-oxidizing chemoautotrophic microorganisms in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 40:1060–1066
Butchaiah G, Sebastien B, Christoph M, Savitri G (2009) Air pollutant emissions from rice straw open field burning in India, Thailand and the Philippines. Environ Pollut 157:1554–1558
Cai ZC, Laughlin RJ, Stevens RJ (2001) Nitrous oxide and dinitrogen emissions from soil under different water regimes and straw amendment. Chemosphere 42:113–121
Cicerone RJ (1987) Changes in stratospheric ozone. Science 237:35–42
Davidson EA (1992) Sources of nitric oxide and nitrous oxide following wetting of dry soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 56:95–102
Dobermann A, Fairhurst T (2000) Rice: nutrient disorders and nutrient management. International Rice Research Institute, Philippines
Drury CF, McKennev DJ, Findlay WI (1992) Nitric oxide and nitrous oxide production from soil: water and oxygen effects. Soil Sci Soc Am J 56:766–770
Han LJ, Yan QJ, Liu XY, Hu JY (2002) Straw resources and their utilization in China. Trans CASE 18(3):87–91 (In Chinese)
Hao X, Chang C, Carefoot JM, Janzen HH, Ellert BH (2001) Nitrous oxide emissions from an irrigated soil as affected by fertilizer and straw management. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 60:1–8
Hu HQ, Wang QZ, Li MQ, Chen Y (2004) Production increase effect and mechanism for straw covering of wheat field in Jingmen city. Soils Fertilizers 5:30–35 (In Chinese)
Huang YZ, Zhang FZ, Liu SQ, Cao MQ (1999) Effect of allelochemicals on N2O emission from soil. ACTA Sci Ciecumstantiae 19:478–482 (In Chinese)
Huke R, Huke E, Woodhead T, Huang J (1993) Rice–wheat atlas of China. CNRRI Publication, IRRI, CIMMYT, p 37
IPCC (2007a) Climate change 2007: changes in atmospheric constituents and in radiative forcing. http://www.ipcc.ch/pdf/assessment-report/ar4/wg1/ar4-wg1-chapter2.pdf. Accessed 17 Jan 2008
IPCC (2007b) Climate change 2007: mitigation. Contribution of working group III to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, USA
Jensen ES (1994) Dynamics of mature pea residue nitrogen turnover in unplanted soil under field conditions. Soil Biol Biochem 26:455–464. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(94)90177-5
Liang W, Shi Y, Zhang H, Yue J, Huang GH (2007) Greenhouse gas emissions from Northeast China rice fields in fallow season. Pedosphere 17(5):630–638
Linn DM, Doran JW (1984) Effect of water-filled pore space on carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide production in tilled and non-tilled soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 48:1267–1272
McKenney DJ, Wang SW, Drury CF, Findlay WI (1993) Denitrification and mineralization in soil amended with legume, grass, and corn residues. Soil Sci Soc Am J 57:1013–1020
Nye PH, Greenland DJ (1964) Changes in the soil after clearing tropical forest. Plant Soil 21:101–112
Pathak H, Singh R, Bhatia A, Jain N (2006) Recycling of rice straw to improve wheat yield and soil fertility and reduce atmospheric pollution. Paddy Water Environ 4(2):111–117
Verma TS, Bhagat RM (1992) Impact of rice straw management practices on yield, nitrogen uptake and soil properties in a wheat-rice rotation in northern India. Fert Res 33:97–106
Weier KL, Gilliam JM (1986) Effect of acidity on denitrification and nitrous oxide evolution from atlantic coastal plain soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 50:1202–1205
Zou JW, Huang Y, Zong LG, Zheng XH, Wang YS (2004) Carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide and methane emissions from a rice–wheat rotation as affected by crop residue incorporation and temperature. Adv Atmos Sci 21(5):691–698
Acknowledgments
Funding for this research work was provided by the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (Grant No. 40921061), the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KZCX2-YW-Q1-07), and the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2008DAF21330).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, E., Zhang, G., Ma, J. et al. Effects of rice straw returning methods on N2O emission during wheat-growing season. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 88, 463–469 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-010-9369-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-010-9369-1