Abstract
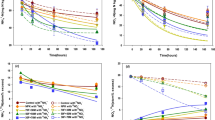
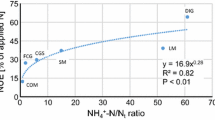
The effect of the application of organic amendments of contrasting C/N ratio, combined with mineral N fertilizer, on the N budget of a potato crop was evaluated. The hypothesis was that the combination of substrates of contrasting chemical composition can improve the synchronization between N crop requirements and N availability in the soil, increasing yields and reducing losses to the environment. Potato plants were cultivated in microplots (0.225 m2) in the tropical uplands of Venezuela, using mineral N (labeled with 15N), poultry manure (C/N = 12), and rice hulls (C/N = 90) as N sources. Four treatments with the same total dose of N (25.0 g N m−2) were applied: (1) MF: mineral fertilizer; (2) P + F: poultry manure and mineral fertilizer; (3) R + F: rice hulls and mineral fertilizer and (4) P + R + F: poultry manure, rice hulls and mineral fertilizer. Labeled and non-labeled N was measured in drained water and plant and soils compartments, and a N budget was established for each treatment. The ratio of N crop uptake to N losses was proposed as an ecological indicator of N use efficiency. The highest value (3.0) of this ratio was obtained in the treatment combining the two organic substrates of contrasting quality, P + R + F, followed by the R + F (2.0) and P + F (1.8) and the lowest ratio was obtained in the MF treatment (0.9). The P + R + F combination may represent a good soil amendment to obtain a high yield with a lower environmental impact, at least in the short-term. The generalization of these results to other soils and climates is discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abreu Z, Sarmiento L, Bottner P (2007) Destino del nitrógeno agregado por fertilización en un cultivo de papa en los Andes de Venezuela. Rev Fac Agron LUZ 24(2):203–228
Allen R, Pereira L, Raes D, Smith M (1998) Crop evapotranspiration (guidelines for computing crop water requirements). Paper no. 56 FAO irrigation and drainage, Rome
Appel T, Mengel K (1993) Nitrogen fractions in sandy soils in relation to plant nitrogen uptake and organic matter incorporation. Soil Biol Biochem 25:685–691
Arauzo M, Martínez-Bastida J, Valladolid M, Díez J (2010) Field evaluation of Gee passive capillary lysimeter for monitoring drainage in non-gravelly and gravelly alluvial soils: a useful tool to estimate nitrogen leaching from agriculture. Agric Water Manage 97:465–474
Axmann H, Sebastianelli A, Arrillaga JL (1990) Sample preparation techniques of biological material for isotopes analysis. In: IAEA (ed) Use of nuclear techniques in studies of soil–plant relationships. Vienna, Austria
Bélanger G, Ziadi N, Walsh JR, Richards JE, Milburn PH (2003) Residual soil nitrate after potato harvest. J Environ Qual 32:607–612
Beloso MC (1991) Estudio de la gallinaza como fertilizante agrícola. PhD Dissertation, Universidad de Santiago de Compostela, Santiago de Compostela, España
Bohlool BB, Ladha JK, Garrity DP, George T (1992) Biological nitrogen fixation for sustainable agriculture: a perspective. Plant Soil 141:1–12
Bouyoucos GJ (1962) Hydrometer method improved for making particle size analyses of soils. Agronomy J 54:464–465
Bremner JM (1965) Total nitrogen. In: Black CA (ed) Methods of soil analysis, part 2. Agronomy 9:1149–1178
Bremner JM, Mulvaney CS (1982) Total nitrogen. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis, part 2. Agronomy 9:594–624
Brookes PC, Landman A, Pruden G, Jenkinson DS (1985) Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: a rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 17:837–842
Chambers B, Smith K, Pain B (2000) Strategies to encourage better use of nitrogen in animal manures. Soil Use Manag 16:157–161
Chapin FS, Matson PA, Mooney HA (2002) Principles of terrestrial ecosystem ecology. Springer, New York
Corpoandes (1995) Proyecto Desarrollo Integral Las Cuadras, Mérida, Venezuela
Díaz C (2009) Balance hídrico y de nutrientes y procesos erosivos en un agroecosistema de papa en diferentes posiciones topográficas en los Andes venezolanos. PhD Dissertation, Universidad de Los Andes, Mérida, Venezuela
Friedel JK, Gabel D, Stahr K (2001) Nitrogen pools and turnover in arable soils under different durations of organic farming: II source-and-sink function of the soil microbial biomass or competition with growing plants? J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 164:421–429
Frissel MJ (ed) (1977) Cycling of mineral nutrients in agricultural ecosystems. Agroecosystems 4:1–354
Grant RF (1994) Simulation of ecological controls on nitrification. Soil Biol Biochem 26:305–315
Guiraud G (1984) Contribution du marquage isotopique à l’évaluation des transferts d’azote entre les compartments organiques et minéraux dans les systèmes sol-plante. PhD Dissertation, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris
Guiraud G, Fardeaux JC (1980) Détermination isotopique par spectrométrie optique de composés faiblement enrichis en azote 15. Analusis 8:148–152
Halitligil MB, Akin A, Ýlbeyi A (2002) Nitrogen balance of nitrogen-15 applied as ammonium sulphate to irrigated potatoes in sandy texture soils. Biol Fertil Soils 35:369–378
Hart PBS, Rayner JH, Jenkinson DS (1986) Influence of pool substitution on the interpretation of fertilizer experiments with 15N. J Soil Sci 37:389–403
IGAC (1978) Métodos analíticos del laboratorio de suelos. Instituto Geográfico Agustín Codazzi, Ministerio de Hacienda y Crédito Público, Bogotá
IPCC (1992) Climate change. In: Houghton JT, Callander BA, Varney SK (eds) The supplementary report to the IPCC scientific assessment, intergovernmental panel on climate change. Meteorological Office, Bracknell
Joergensen RG, Mueller T (1996) The fumigation-extraction method to estimate soil microbial biomass: calibration of the kEN value. Soil Biol Biochem 28:33–37
Kandeler E (1996) Nitrification during long-term incubation. In: Schinner F, Öhlinger R, Kandeler E, Margesin R (eds) Methods in soil biology. Springer, Berlin, pp 149–151
Keeney KR (1982) Nitrogen management for maximum efficiency and minimum pollution. In: Stevenson FJ (ed) Nitrogen in agricultural soils. Agronomy 22:605–649
Klute A (1986) Water retention: laboratory methods. In: Klute A (ed) Methods of soil analysis. Physical and mineralogical methods. Part 1. Agronomy 9:635–662
MacDonald AJ, Poulton PR, Powlson DS, Jenkinson DS (1997) Effects of season, soil type and cropping on recoveries, residues and losses of 15N-labelled fertilizer applied to arable crops in spring. J Agric Sci 129:125–154
Machado D (2005) Un enfoque agroecosistémico para el manejo eficiente del suministro de nitrógeno en el cultivo de papa en los Andes venezolanos. PhD Dissertation, Universidad de Los Andes, Mérida, Venezuela
Maidl F, Brunner H, Sticksel E (2002) Potato uptake and recovery of 15N- enriched ammonium nitrate. Geoderma 105:167–177
Mosier AR, Syers JK, Freney JR (2004) Nitrogen fertilizer: an essential component of increased food, feed and fiber production. In: Mosier AR, Syers JK, Freney JR (eds) Agriculture and the nitrogen cycle. Island Press, Washington
Myers RJK, Palm CA, Cuevas E, Gunatilleke IUN, Brossard M (1994) The synchronization of nutrient demand. In: Woomer PL, Swift MJ (eds) The biological management of tropical soil fertility. John Wiley, Chichester
Peralta JM, Stockle CO (2002) Dynamics of nitrate leaching under irrigated potato rotation in Washington State: a long-term simulation study. Agric Ecosyst Environ 88:23–34
Powlson DD, Hart PBS, Poulton PR, Johnston AE, Jenkinson DS (1992) Influence of soil type, crop management and weather on the recovery of 15N-labelled fertilizer applied to winter wheat in spring. J Agric Sci (Camb) 118:83–100
Preston CM (1999) Optical emission analysis of 15N: pressure effects and identification of NO and Gaydon-Herman N2 bands in the discharge. Appl Spectrosc 53:1628–1637
Rojas LA, Castillo LE (1989) Determinación de amonio, nitratos y nitritos. In: Instituto Colombiano Agropecuario, ICA (ed) El Análisis de Suelos, Plantas y Aguas para Riego. Manual de Asistencia Técnica 47, Bogotá, pp 27–40
Rojas LA, Collazos EA (1989) Determinación de fósforo en el suelo. In: Instituto Colombiano Agropecuario, ICA (ed) El Análisis de suelos, plantas y aguas para riego. Manual de Asistencia Técnica 47, Bogotá, pp 42–56
Ruser R, Flessa H, Schilling R, Steindl H, Beese F (1998) Soil compaction and fertilization effects on nitrous oxide and methane fluxes in potato fields. Soil Sci Soc Am J 62:1587–1595
Salazar FJ, Chadwick D, Pain BF, Hatch D, Owen E (2005) Nitrogen budgets for three cropping systems fertilized with cattle manure. Biores Technol 96:235–245
Scrimgeour CM, Robinson D (2003) Stable isotope analysis and applications. In: Smith KA, Cresser NS (eds) Soil and environmental analysis: modern instrumental techniques. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 381–432
Sheehy JE, Mitchell PL, Kirk GJ, Ferrer AB (2005) Can smarter nitrogen fertilizers be designed? Matching nitrogen supply to crop requirements at high yields using a simple model. Field Crop Res 94:54–66
Soil Survey Staff (1992) Keys to soil taxonomy. SMS technical monograph 19, 5th edn. Pocahontas Press, Blacksburg, Virginia
Swift MJ (ed) (1984) Soil biological processes and tropical soil fertility. A proposal for collaborative program of research. Biol Int 5:1–37
Swift MJ (ed) (1987) Tropical soil biology and fertility. Inter-regional research planning workshop. Biol Int 13:28–34
Tran TS, Giroux M (1991) Effects of N rates and harvest dates on the efficiency of 15N-labelled fertilizer on early harvested potatoes (Solanum tuberosum L.). Can J Soil Sci 71:519–532
Ünlü K, Özenïrler G, Yurteri C (1999) Nitrogen fertilizer leaching from cropped and irrigated sandy soil in Central Turkey. Eur J Soil Sci 50:609–620
Van Delden A, Schröder JJ, Kropff MJ, Grashoff C, Booij R (2003) Simulated potato yield, and crop and soil nitrogen dynamics under different organic nitrogen management strategies in The Netherlands. Agric Ecosyst Environ 96:77–95
Vermoesen A, Groot C, Nollet L, Boeck P, van Cleemput O (1996) Effect of ammonium and nitrate application on the NO and N2O emission out of different soils. Plant Soil 181:153–162
Zhong Z, Makeschin F (2003) Soluble organic nitrogen in temperate forest soils. Soil Biol Biochem 35:333–338
Acknowledgments
This research was founded by FONACIT (grants S1-2000000810 and F-2002000424) and framed within the MOSANDES project (CYTED, project XII.4). We wish to thank Francis Guillén, Zulay Mendez, Sonia Morales, Nelson Marquez and Alexander Suarez for their technical assistance, Carlos Díaz for his support during fieldwork and the fruitful discussions, Gloria and Ana Graziella Machado for all their kind cooperation and Julia K. Smith for the English revision.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Machado, D., Sarmiento, L. & Gonzalez-Prieto, S. The use of organic substrates with contrasting C/N ratio in the regulation of nitrogen use efficiency and losses in a potato agroecosystem. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 88, 411–427 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-010-9366-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-010-9366-4