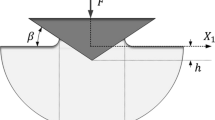
Abstract
The residual stress intensity factors at the surface and at the deepest point of the semi-elliptical Knoop indentation crack is determined from the stresses in the damaged zone below the indenter. For this purpose, the weight function approach by Cruse and Besuner was used and wide-range expressions of the geometric function are given. The solution is then applied to a commercial silicon nitride for which all relevant geometrical data are available.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caspers M, Mattheck C, Munz D (1990) Propagation of surface cracks in notched and unnotched rods. ASTM STP 1060: 365–389
Cook RF, Pharr GM (1990) Direct Observation and Analysis of Indentation Cracking in Glasses and Ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society 73: 787–817
Cruse TA, Besuner PM (1975) Residual life prediction for surface cracks in complex structural details. Journal of Aircraft 12: 369–375
Fett T, Munz D (1997) Stress intensity factors and weight functions. Computational Mechanics Publications, Southampton, UK
Fett T, Fünfschilling S, Hoffmann MJ, Oberacker R (2008) Different R-curves for 2- and 3-dimensional cracks. International Journal of Fracture 153: 153–159
Fett T (2009) Stress intensity factors, T-stresses, Weight function (Supplement Volume), IKM55. KIT Scientific, Publishing, Karlsruhe; (open Access, http://digbib.ubka.uni-karlsruhe.de/volltexte/1000013835).
Fünfschilling S, Fett T, Oberacker R, Hoffmann MJ, Özcoban H, Jelitto H, Schneider GA, Kruzic JJ (2010) R-curves from compliance and optical crack-length measurements. Journal of the American Ceramic Society 93, 2814-21
Görner F, Mattheck C, Munz D (1983) Change in geometry of surface cracks during alternating tension and bending. Zeitschrift für Werkstofftechnik 14: 11–18
Keer LM, Farris TN, Lee JC (1986) Knoop and Vickers indentation in ceramics analyzed as a three-dimensional fracture. Journal of the American Ceramic Society 69, 392-96.
Lawn BR, Evans AG, Marshall DB (1980) Elastic/plastic indentation damage in ceramics: The medial/radial crack system. Journal of the American Ceramic Society 63, 574-81.
Li C-W, Lee D-J, Lui S-C (1992) R-Curve Behaviour and Strength for In-Situ Reinforced Silicon Nitrides with Different Microstructures. Journal of the American Ceramic Society 75, 1777-85.
Lube T (2001) Indentation crack profiles in silicon nitride. Journal of the European Ceramic Society 21: 211–218
Lube T, Fett T (2004) A threshold stress intensity factor at the onset of stable crack extension of Knoop indentation cracks. Engineering Fracture Mechanics 71: 2263–2269
Mahmoud MA (1990) Surface fatigue crack growth under combined tension and bending loading. Engineering Fracture Mechanics 36: 389–395
Marshall DB (1983) Controlled flaws in ceramics: A comparison of Knoop and Vickers indentation. Journal of the American Ceramic Society 66: 127–131
Varfolomeyev IV, Vainshtok VA, Krasowsky AY (1991) Prediction of part-through crack growth under cyclic loading. Engineering Fracture Mechanics 40: 1007–1022
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lube, T., Fett, T., Fünfschilling, S. et al. A Residual Stress Intensity Factor Solution for Knoop Indentation Cracks. Int J Fract 175, 65–71 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-012-9696-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-012-9696-0