Abstract
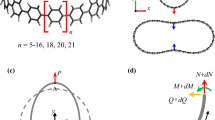
Carbon nanoscrolls (CNSs) are a class of graphene-based nanoscale materials with great potential for applications in nanotechnology and bioengineering. Fundamental description, understanding and regulation of these materials may ultimately lead to a new generation of integrated systems that utilize their unique properties. A particularly interesting property of a CNS is that there exists a stable equilibrium core size which can be uniquely determined from the basal graphene length, the interlayer spacing, the interaction energy between layers, the bending stiffness of graphene, as well as the difference between the pressure inside the core of the CNS and that on its outer surface. Here we investigate the strongly nonlinear constitutive behaviour of a CNS under pressure, focusing on its deformation, stability and biaxial modulus in response to its inner and external pressures. Our study suggests pressure sensitive applications of CNSs such as nanopumps and nanofilters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braga SF, Coluci VR, Baughman RH, Galvao DS (2007) Hydrogen storage in carbon nanoscrolls: an atomistic molecular dynamics study. Chem Phys Lett 441(1–3): 78–82
Braga SF, Coluci VR, Legoas SB, Giro R, Galvao DS, Baughman RH (2004) Structure and dynamics of carbon nanoscrolls. Nano Lett 4(5): 881–884
Chen Y, Lu J, Gao ZX (2007) Structural and electronic study of nanoscrolls rolled up by a single graphene sheet. J Phys Chem C 111(4): 1625–1630
Chuvilin AL, Kuznetsov VL, Obraztsov AN (2009) Chiral carbon nanoscrolls with a polygonal cross-section. Carbon 47(13): 3099–3105
Coluci VR, Braga SF, Baughman RH, Galvao DS (2007) Prediction of the hydrogen storage capacity of carbon nanoscrolls. Phys Rev B 75(12): 125404
Hess B, Kutzner C, van der Spoel D, Lindahl E (2008) Gromacs 4: algorithms for highly efficient, load-balanced, and scalable molecular simulation. J Chem Theory Comput 4(3): 435–447
Mpourmpakis G, Tylianakis E, Froudakis GE (2007) Carbon nanoscrolls: a promising material for hydrogen storage. Nano Lett 7(7): 1893–1897
Pan H, Feng Y, Lin J (2005) Ab initio study of electronic and optical properties of multiwall carbon nanotube structures made up of a single rolled-up graphite sheet. Phys Rev B 72(8): 085415
Pugno N (2008) Flexible nanovectors. J Phys Condens Matter 20: 474205
Roy D, Angeles-Tactay E, Brown RJC, Spencer SJ, Fry T, Dunton TA, Young T, Milton MJT (2008) Synthesis and raman spectroscopic characterisation of carbon nanoscrolls. Chem Phys Lett 465(4–6): 254–257
Rurali R, Coluci VR, Galvao DS (2006) Prediction of giant electroactuation for papyruslike carbon nanoscroll structures: first-principles calculations. Phys Rev B 74(8): 085414
Savoskin MV, Mochalin VN, Yaroshenko AP, Lazareva NI, Konstantinova TE, Barsukov IV, Prokofiev LG (2007) Carbon nanoscrolls produced from acceptor-type graphite intercalation compounds. Carbon 45(14): 2797–2800
Shioyama H, Akita T (2003) A new route to carbon nanotubes. Carbon 41(1): 179–181
Shi XH, Cheng Y, Pugno NM, Gao HJ (2009) Gigahertz breathing oscillators based on carbon nanoscrolls. Appl Phys Lett 95(16): 163113
Shi XH, Pugno NM, Gao HJ (2010a) Tunable core size of carbon nanoscrolls. J Comput Theor Nanosci 7(3): 517–521
Shi XH, Cheng Y, Pugno NM, Gao HJ (2010b) A translational nanoactuator based on carbon nanoscrolls on substrates. Appl Phys Lett 96(5): 053115
Shi XH, Cheng Y, Pugno NM, Gao HJ (2010c) Tunable water channels with carbon nanoscrolls. Small 6(6): 739–744
Viculis LM, Mack JJ, Kaner RB (2003) A chemical route to carbon nanoscrolls. Science 299(5611): 1361
Walther JH, Jaffe R, Halicioglu T, Koumoutsakos P (2001) Carbon nanotubes in water: structural characteristics and energetics. J Phys Chem B 105(41): 9980–9987
Xie X, Ju L, Feng XF, Sun YH, Zhou RF, Liu K, Fan SS, Li QL, Jiang KL (2009) Controlled fabrication of high-quality carbon nanoscrolls from monolayer graphene. Nano Lett 9(7): 2565–2570
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, X., Pugno, N.M. & Gao, H. Constitutive behavior of pressurized carbon nanoscrolls. Int J Fract 171, 163–168 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-010-9545-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-010-9545-y