Abstract
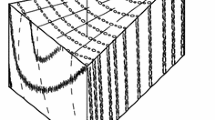
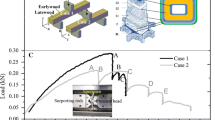
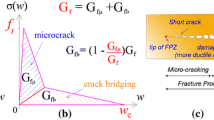
Investigations on the fracture properties of wood in relation to its microstructure are reported. The inhomogeneous and hierarchical structure of wood is addressed. Wood species, the influence of orientation, the role of structural features, like rays are considered and discussed. Likewise the mode of loading, which determines the mode of fracturing, and the influence of humidity have been studied by using new fracture mechanical techniques and ways of evaluation. The specific fracture energy has been determined under crack opening conditions. In-situ loading in an environmental scanning electron microscope (ESEM), which allows observation in moistured condition, has been performed in order to investigate the mechanisms of fracturing of wood on a sub-microscopic scale. In the nanometer range, especially the influence of the microfibril angle on deformation and fracture behaviour has been studied.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S Aicher HW Reinhardt (1993) ArticleTitleEinfluß der Bauteilgröße in der linearen und nichtlinearen (Holz-) Bruchmechanik Holz als Roh- und Werkstoff 51 215–220
MF Ashby KE Easterling R Harrysson SK Maiti (1985) ArticleTitleThe fracture and toughness of woods Proc R Soc Lond 398 261–280 Occurrence Handle1985RSPSA.398..261A Occurrence Handle10.1098/rspa.1985.0034
SWJ Boatright GG Garrett (1983) ArticleTitleThe effect of microstructure and stress state on the fracture behaviour of wood J Mat Sci 18 2181–2199 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00555013
Boström L (1994) the stress-displacement relation of wood perpendicular to the grain. Part II. Application of the fictitious crack model to the compact tension specimen. Wood Sci Techn 319–327
I Burgert D Eckstein (2001) ArticleTitleThe tensile strength of isolated rays of beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) and its significance for the biomechanics of living trees Trees 15 168–170 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004680000086
Burgert I, Frühmann K (2003) Micromechanics of wood-surface-function relationships on the tissue and fiber level. In: Proc. Second Int. Conf ESWM, ed. STFI, Stockholm, Sweden, pp 85–94
RJA Ehart SE Stanzl-Tschegg EK Tschegg (1996) ArticleTitleCharacterization of crack propagation in particle board Wood Sci Techn 30 307–321
Fengel D and Wegener G (2003) Wood. Verlag Kessel, Remagen, D, www.forstbuch.de
K Frühmann I Burgert SE Stanzl-Tschegg (2003) ArticleTitleDetection of the fracture path under tensile loads through in situ Tests in an ESEM Chamber Holzforschung 57 326–332 Occurrence Handle10.1515/HF.2003.048
LJ Gibson MF Ashby (1997) Cellular solids. Cambridge Solid State Sci Ser EditionNumber2 Cambridge University Press Cambridge
Harmuth H, Rieder K, Krobath M, Tschegg EK (1996) Investigation of the nonlinear fracture behaviour of ordinary ceramic refractory materials. Mat Sci Eng A214, 53
MJ He JW Hutchinson (1989) ArticleTitleCrack deflection at an interface of dissimilar elastic materials Int J Solids Struct 25 1053–1067 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0020-7683(89)90021-8
A Hillerborg M Modeer PE Petersson (1976) ArticleTitleAnalysis of crack formation and crack growth in concrete by means of fracture mechanics and finite elements Cement Concrete Res 6 773–782 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0008-8846(76)90007-7
H Jakob P Fratzl SE Stanzl-Tschegg (1994) ArticleTitleSize and arrangement of elementary cellulose fibrils in wood: a small-angle X-ray scattering study of Picea Abies J Struct Biol 113 13–22 Occurrence Handle10.1006/jsbi.1994.1028
Jeronimidis G (1980) The fracture behaviour of wood and the relations between toughness and morphology. In: Proc. R. Soc Lond B 208, pp 447–460
Keckes J, Burgert I, Frühmann K, Müller M, Kölln K, Hamilton M, Burghammer M, Roth S, Stanzl-Tschegg S, Fratzl P (2003) Cell-wall recovery after irreversible deformation of wood. Nature Materials, 2, 811; publ. online: 16 Nov. 2003; doi10.1038/nmat1019
Keckes J, Burgert I, Müller M, Kölln K, Hamilton M, Burghammer M, Roth S, Stanzl-Tschegg S and Fratzl P (2004) In-situ synchrotron studies of structural changes in wood during microtensile tests. In: Stanzl-Tschegg SE, Gindl M and Sinn G (eds) Proc. of the 2nd Internat. symposium on Wood Machining, Vienna, Austria
Lichtenegger H, Reiterer A, Stanzl-Tschegg SE, Müller M, Paris O, and Fratzl P (2000). Cellulose orientation in the wood cell wall. In: Stanzl-Tschegg SE and Reiterer A, (eds) Proc Internat symposium on wood machining, Vienna, Austria; pp. 31–37
Morel S, Valentin G (1999) R-curve behaviour and roughness of wood fractured surfaces. Size effect. In: Damage in wood. COST E8. Mechanical performance of wood and wood products, Bordeaux, France
Niemz P (1993) Physik des Holzes und der Holzwerkstoffe. DRW-Verlag Leinfelden – Echterdingen
RP Petterson J Bodig (1983) ArticleTitlePrediction of Fracture Toughness of conifers Wood Fib Sci 15 IssueID4 302–316
A Reiterer SE Stanzl-Tschegg EK Tschegg (2000) ArticleTitleMode I fracture and acoustic emission of softwood and hardwood Wood Sci Techn 34 417–430 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002260000056
A Reiterer H Lichtenegger P Fratzl SE Stanzl-Tschegg (2001) ArticleTitleDeformation and energy absorption of wood cell walls with different nanostructure under tensile loading J Mat Sci 36 4681–4686 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1017906400924
A Reiterer G Sinn SE Stanzl-Tschegg (2002a) ArticleTitleFracture characteristics of different wood species under mode I loading perpendicular to the grain Mat Sci Eng A 332 29–36 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0921-5093(01)01721-X
A Reiterer I Burgert G. Sinn SE Tschegg (2002b) ArticleTitleThe radial reinforcement of the wood structure and its implication on mechanical and fracture mechanical properties – A comparison between two tree species J Mat Sci 37 935–940 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1014339612423
A Reiterer SE Tschegg (2002) ArticleTitleThe influence of moisture content on the mode I fracture behaviour of sprucewood J Mat Sci 37 4487–4491 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1020610231862
AP Schniewind T Ohgama T Aoki T Yamada (1982) ArticleTitleEffect of specific gravity, moisture content and temperature on fracture toughness of wood Wood Sci 5 IssueID2 101–109
AP Schniewind RA Pozniak (1971) ArticleTitleOn the fracture toughness of douglas fir wood Eng Fract Mech 2 223–233 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0013-7944(71)90026-9
SE Stanzl-Tschegg DM Tan EK Tschegg (1995) ArticleTitleNew splitting method for wood fracture characterization Wood Sci Techn 29 31–50
Tschegg EK (1986) Equipment and appropriate specimen shape for tests to measure fracture values (in German), Patent AT-390328
Valentin GH, Boström L, Gustafsson PJ, Ranta-Maunus A, Gowda S (1991) Application of fracture mechanics to timber structures RILEM state-of-the-art report. Technical Research Centre of Finland, Research Notes 1262
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stanzl-Tschegg, S.E. Microstructure and fracture mechanical response of wood. Int J Fract 139, 495–508 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-006-0052-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-006-0052-0