Abstract
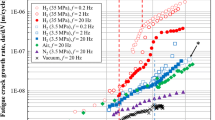
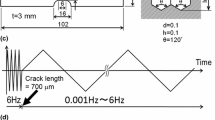
The hydrogen effect on crack growth behaviour in a type 304 austenitic stainless steel was investigated and the following results were obtained. The crack growth rate in hydrogen gas is accelerated compared with that in air. In order to clarify the mechanism of the acceleration, the growth behaviours of a crack propagating in a grain and propagating along the boundary to be a fracture facet were investigated. Slip behaviour, opening displacement and fractography showed that the slip-off mechanism in fatigue crack growth is valid even in hydrogen gas. Hydrogen mainly affects slip behaviour such that slip bands concentrate at a crack tip and result in acceleration of the growth rate. The facets are not significantly responsible for the acceleration. The ratio of facets to the entire area is low, and a crack nearly compensates for the temporary acceleration by the facets with subsequent deceleration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.D. Beachem (1972) ArticleTitleA new model for hydrogen-assisted cracking (hydrogen embrittlement) Metallurgical Transactions 3 437–451 Occurrence Handle1972MT......3..441B
R. B. Benson SuffixJr. R. K. Dann L. W. Roberts SuffixJr. (1968) ArticleTitleHydrogen embrittlement of stainless steel Transactions of the Metallurgical Society of AIME 242 2199–2205
H.K. Birnbaum P. Sofronis (1994) ArticleTitleHydrogen-enhanced localized plasticity–a mechanism for hydrogen-related fracture. Materials Science and Engineering A176 191–202
P.J. Ferreira I.M. Robertson H.K. Birnbaum (1998) ArticleTitleHydrogen effects on the interaction between dislocations Acta Materialia 46 1749–1757
S. Fukuyama K. Yokogawa K. Kudo M. Araki (1985) ArticleTitleFatigue properties of type 304 stainless steel in high pressure hydrogen at room temperature Transactions of Japan Insittute of Metals 26 325–331
S. Gahr M.L Grossbeck H.K. Birnbaum (1977) ArticleTitleA generalized model for hydrogen embrittlement Acta Metallurgica 25 125–134
W.W. Gerberich R.A. Oriani M.-J. Lii X. Chen T. Foecke (1991) ArticleTitleThe necessity of both plasticity and brittleness in the fracture thresholds of iron Philosophical Magazine 63 363–376
G. Han S. Fukuyama K. Yokogawa (1998) ArticleTitleEffect of strain-induced martensite on hydrogen environment embrittlement of sentitized austenitic stainless steels at low temperatures Acta Materialia 46 4559–4570
H. Kimura H. Matsui (1987) ArticleTitle Mechanism of hydrogen-induced softening and hardening in iron Scripta Metallurgica 21 319–324
P. Neumann (1974) ArticleTitleNew experiments concerning the slip processes at propagating fatigue cracks -I Acta Metallugica 22 1155–1165
P. Neumann H. Vefhoff H. Fuhlrott (1977) ArticleTitleOn the mechanisms of fatigue crack growth Proc. 4th International Conference on Fracture 2 1313–1324
Nisitani, H. and Oda, Y. (1994). A study of fatigue crack growth laws in small and large cracks based on COD. Proc. Third Conference of Computer-Aided Assessment and Control of Localized Damage, 47–54.
Y. Oda Y. Furuya H. Noguchi K. Higashida (2002) ArticleTitleAFM and SEM observation on mechanism of fatigue crack growth in an Fe-Si single crystal International Journal of Fracture 113 213–231
R.A. Oriani P.H. Josephic (1974) ArticleTitleEquilibrium aspects of hydrogen-induced cracking of steels Acta Metallurgica 22 1065–1074
R.M.N. Pelloux (1969) ArticleTitleMechanisms of formation of ductile fatigue striations Transactions of ASM 62 281–285
I.M. Robertson (2001) ArticleTitleThe effect of hydrogen on dislocation dynamics Engineering Fracture Mechanics 68 671–692
G. Schuster C. Altstetter (1983a) ArticleTitleFatigue of stainless steel in hydrogen Metallurgical Transactions A–Physical Metallurgy and Materials Science 14A 2085–2090 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02662375 Occurrence Handle1983MTA....14.2085S
G. Schuster C. Altstetter (1983b) ArticleTitleFatigue of annealed and cold worked stable and unstable stainless steels Metallurgial Transactions A, 14A 2077–2084 Occurrence Handle1983MTA....14.2077S
E.A. Steigerwald F.A. Schller A.R. Troiano (1960) ArticleTitleThe role of stress in hydrogen induced delayed failure Transactions of the Metallurgical Society of AIME 218 832–841
Studebaker, P. and Altstetter, C. (1980). Hydrogen Permeation of Stainless Steel under Stress, Hydrogen Effects in Metals, The Metallurgical Society of AIME.
A.R. Troiano (1960) ArticleTitleThe role of hydrogen and other interstitions in the mechanical behavior of metals Transactions of ASM 52 54–80
R.M. Vennett G.S. Ansell (1967) ArticleTitleThe effect of high-pressure hydrogen upon tensile properties and fracture behavior of 304L stainless steel Transactions of ASM 60 242–251
D.G. Westlake (1969) ArticleTitle A generalized model for hydrogen embrittlement. Transactions of ASM 62 1000–1006
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oda, Y., Noguchi, H. Observation of hydrogen effects on fatigue crack growth behaviour in an 18Cr-8Ni austenitic stainless steel. Int J Fract 132, 99–113 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-004-8142-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-004-8142-3