Abstract
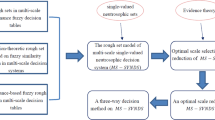
Selecting financial products is one of the most fundamental investment activities to both individuals and companies, and therefore it is very important to establish an efficient and practical method for financial products selection. To address the challenge of the complicated decision-making environment and decision makers’ expression habits for the selection of financial products, this paper develops the incomplete additive probabilistic linguistic preference relation to depict decision makers’ preferences. Considering that, when decision makers express their opinions using probabilistic linguistic preference relation, it is possible that the sum of the value of the probability information is more than 1, this paper also extends the concepts of probabilistic linguistic term set, additive probabilistic linguistic preference relation and incomplete additive probabilistic linguistic preference relation to improve and ensure their practicability. Moreover, an “inverse prospect theory-based” algorithm is proposed to choose proper financial products. The algorithm processes the original incomplete additive probabilistic linguistic preference relation by using the inverse functions of the prospect theory at first. Then, a priority weights deriving model is established based on the extended concepts. Finally, the numerical case and analysis is presented as the evidences to the conclusion that the proposed algorithm is practical and robust.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso, S., Chiclana, F., Herrera, F., Herrera-Viedma, E., Alcalá-Fdez, J., & Porcel, C. (2010). A consistency-based procedure to estimate missing pairwise preference values. International Journal of Intelligent Systems, 23(2), 155–175.
Cabrerizo, F. J., Pérez, I. J., & Herrera-Viedma, E. (2010). Managing the consensus in group decision making in an unbalanced fuzzy linguistic context with incomplete information. Knowledge-Based Systems, 23(2), 169–181.
Dong, Y. C., Nan, L., & Liang, H. M. (2015). Consensus building in multiperson decision making with heterogeneous preference representation structures: A perspective based on prospect theory. Applied Soft Computing, 35, 898–910.
Gou, X. J., Xu, Z. S., & Liao, H. C. (2017). Multiple criteria decision making based on Bonferroni means with hesitant fuzzy linguistic information. Soft Computing, 21(21), 6515–6529.
Gunaratne, J., & Nov, O. (2017). Using interactive “Nutrition labels” for financial products to assist decision making under uncertainty. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 68(8), 836–1849.
Herrera, F., Herrera-Viedma, E., & Verdegay, J. L. (1995). A sequential selection process in group decision making with a linguistic assessment approach. Information Sciences, 85(4), 223–239.
Huang, J., You, X. Y., Liu, H. C., & Si, S. L. (2019). New approach for quality function deployment based on proportional hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets and prospect theory. International Journal of Production Research, 57(5), 1283–1299.
Kahneman, D., & Tversky, A. (1979). Prospect theory: An analysis of decision under risk. Handbook of the Fundamentals of Financial Decision Making, 47(2), 263–292.
Liu, S. L., & Liu, X. W. (2017). A prospect theory-based methodfor linguistic decision making under risk. Journal of Southeast University (English Edition), 33, 370–376.
Liu, X. L., & Wei, Y. (2013). A new multi-period linguistic aggregation operator and its application to financial product selection. In International conference on graphic and image processing.
Luciano, E. V., & Lafuente, A. G. (2008). Clan theory and its application in the selection of financial products. In The 12th conference on information processing and management of uncertainty in knowledge-based systems, Malaga, Spain, pp. 737–744.
Merigo, J. M., & Lafuente, A. G. (2010). New decision-making techniques and their application in the selection of financial products. Information Sciences, 180(11), 2085–2094.
Pang, Q., Wang, H., & Xu, Z. S. (2016). Probabilistic linguistic term sets in multi-attribute group decision making. Information Sciences, 369, 128–143.
Porcel, C., & Herrera-Viedma, E. (2010). Dealing with incomplete information in a fuzzy linguistic recommender system to disseminate information in university digital libraries. Knowledge-Based Systems, 23(1), 32–39.
Ren, P. J., Hao, Z. N., Zeng, X., & Xu, Z. S. (2020). Decision models based on incomplete hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relation with application to site section of hydropower stations. IEEE Transcations on Engineering Management. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEM.2019.2962180.
Rodriguez, R. M., Espinilla, M., Sanchez, P. J., & Martínez, L. (2010). Using linguistic incomplete preference relations to cold start recommendations. Internet Research Electronic Networking Applications and Policy, 20(3), 296–315.
Tversky, A., & Kahneman, D. (1986). Rational choice and the framing of decisions. The Journal of Business, 59, 251–278.
Tversky, A., & Kahneman, D. (1992). Advances in prospect theory: Cumulative representation of uncertainty. Journal of Risk and Uncertainty, 5(4), 297–323.
Wang, H., & Xu, Z. S. (2016). Interactive algorithms for improving incomplete linguistic preference relations based on consistency measures. Applied Soft Computing, 42, 66–79.
Wu, Y. N., Xu, C. B., & Zhang, T. (2018). Evaluation of renewable power sources using a fuzzy MCDM based on cumulative prospect theory: A case in China. Energy, 147, 1227–1239.
Xie, W. Y., Xu, Z. S., & Ren, Z. L. (2019). An analysis on the influence of Chinese “new four inventions” under the incomplete hybrid probabilistic linguistic environment. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 21(5), 1349–1366.
Xu, Z. S. (2004). Goal programming models for obtaining the priority vector of incomplete fuzzy preference relation. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 36(3), 261–270.
Xu, Z. S. (2005). A procedure for decision making based on incomplete fuzzy preference relation. Fuzzy Optimization and Decision Making, 4(3), 175–189.
Zhang, Z., & Guo, C. (2014). An approach to group decision making with heterogeneous incomplete uncertain preference relations. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 71, 27–36.
Zhang, Y. X., Xu, Z. S., Wang, H., & Liao, H. C. (2016). Consistency-based risk assessment with probabilistic linguistic preference relation. Applied Soft Computing, 49, 817–833.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 71571123, 71532007, 71771155) and the Scholarship from China Scholarship Council (No. 201806240059).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, N., Xu, Z., He, Y. et al. An inverse prospect theory-based algorithm in extended incomplete additive probabilistic linguistic preference relation environment and its application in financial products selection. Fuzzy Optim Decis Making 20, 397–428 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10700-020-09348-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10700-020-09348-3