Abstract
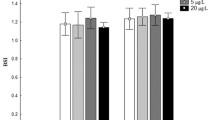
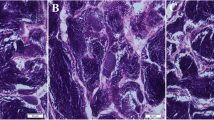
This study aims to explore whether glycerol monolaurate (GML) can improve reproductive performance of female zebrafish (Danio rerio) and the survival percentage of their offspring. Three kinds of isonitrogenous and isolipid diets, including basal diet (control) and basal diet containing 0.75 g/kg GML (L_GML) and 1.5 g/kg GML (H_GML), were prepared for 4 weeks feeding trial. The results show that GML increased the GSI of female zebrafish. GML also enhanced reproductive performance of female zebrafish. Specifically, GML increased spawning number and hatching rate of female zebrafish. Moreover, GML significantly increased the levels of triglycerides (TG), lauric acid, and estradiol (E2) in the ovary (P < 0.05). Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels in the ovary and brain also significantly increased in the L_GML group (P < 0.05). Besides, dietary GML regulated the hypothalamus-pituitary-gonad (HPG) axis evidenced by the changed expression levels of HPG axis-related genes in the brain and ovary of the L_GML and H_GML groups compared with the control group. Furthermore, compared with the control group, the expression levels of HPG axis-related genes (kiss2, kiss1r, kiss2r, gnrh3, gnrhr1, gnrhr3, lhβ, and esr2b) in the brain of the L_GML group were significantly increased (P < 0.05), and the expression levels of HPG axis-related genes (kiss1, kiss2, kiss2r, gnrh2, gnrh3, gnrhr4, fshβ, lhβ, esr1, esr2a, and esr2b) in the brain of the H_GML group were significantly increased (P < 0.05). These results suggest that GML may stimulate the expression of gnrh2 and gnrh3 by increasing the expression level of kiss1 and kiss2 genes in the hypothalamus, thus promoting the synthesis of FSH and E2. The expression levels of genes associated with gonadotropin receptors (fshr and lhr) and gonadal steroid hormone synthesis (cyp11a1, cyp17, and cyp19a) in the ovary were also significantly upregulated by dietary GML (P < 0.05). The increasing expression level of cyp19a also may promote the FSH synthesis. Particularly, GML enhanced the richness and diversity and regulated the species composition of intestinal microbiota in female zebrafish. Changes in certain intestinal microorganisms may be related to the expression of certain genes involved in the HPG axis. In addition, L_GML and H_GML both significantly decreased larvae mortality at 96 h post fertilization and their mortality during the first-feeding period (P < 0.05), revealing the enhanced the starvation tolerance of zebrafish larvae. In summary, dietary GML regulated genes related to HPG axis to promote the synthesis of E2 and FSH and altered gut microbiota in female zebrafish, and improved the survival percentage of their offspring.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Anna H, Thorsten S, Bernd P, Susanne H (2004) Ontogeny of the gut motility control system in zebrafish Danio rerio embryos and larvae. J Exp Biol 207(Pt 23):4085–4094. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.01260
Asil SM, Kenari AA, Miyanji GR, Kraak GVD (2017) The influence of dietary arachidonic acid on growth, reproductive performance, and fatty acid composition of ovary, egg and larvae in an anabantid model fish, blue gourami (Trichopodus trichopterus). Aquaculture 476:8–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2017.03.048
Babu US, Balan KV, Harrison LM (2013) Dietary fatty acids and immune response to food-borne bacterial infections. Nutrients 5(5):1801–1822. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu5051801
Benini E, Politis SN, Nielsen A, Sørensen SR, Tomkiewicz J, Engrola S (2022) Type of hormonal treatment administered to induce vitellogenesis in European eel influences biochemical composition of eggs and yolk-sac larvae. Fish Physiol Biochem 1:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10695-021-01042-4
Cao J, Wang G, Wang T, Chen J, Wenjing G, Wu P, He X, Xie L (2019) Copper caused reproductive endocrine disruption in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat Toxicol 211:124–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2019.04.003
Chang X, Kobayashi T, Senthilkumaran B, Kobayashi-Kajura H, Sudhakumari CC, Nagahama., Y. (2005) Two types of aromatase with different encoding genes, tissue distribution and developmental expression in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Gen Comp Endocrinol 141(2):101–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2004.11.020
Clelland E, Peng C (2009) Endocrine/paracrine control of zebrafish ovarian development. Mol Cell Endocrinol 312(1):42–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2009.04.009
Czarnecki-Maulden GL (2008) Effect of dietary modulation of intestinal microbiota on reproduction and early growth. Theriogenology 70(3):286–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2008.05.041
Ding Z, An X, Liu X, Li W, Xu Y (2018) Progress of nutrient studies on the reprodution, growth and development of aquatic animal. Feed Indust 39(12):1–8. https://doi.org/10.13302/j.cnki.fi.2018.12.001 In Chinese
Dutta A, Sinha DK (2017) Zebrafish lipid droplets regulate embryonic ATP homeostasis to power early development. Open Biol 7(7):170063. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsob.170063
Felipe E, Silvia Z, Ana G (2015) Kiss2 as a regulator of Lh and Fsh secretion via paracrine/autocrine signaling in the teleost fish European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Biol Reprod 93(5):114. https://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod.115.131029
Fernandes D, Schnell S, Porte C (2011) Can pharmaceuticals interfere with the synthesis of active androgens in male fish? An in vitro study. Mar Pollut Bull 62(10):2250–2253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.07.011
Ganesan S, Nadarajah S, Khairuddean M, Teh GB (2019) Studies on lauric acid conversion to methyl ester via catalytic esterification using ammonium ferric sulphate. Renew Energy 140:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.03.031
Gao Y, Jing Q, Huang B, Jia Y (2019) Molecular cloning, characterization, and mRNA expression of gonadotropins during larval development in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Fish Physiol Biochem 45(5):1697–1707. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-019-00656-z
Gong G, Xue M, Wang J, Wu X, Han F, Zheng Y (2014) Nutrition requirement and nutritional regulation of growth and development for fish larvae. Chin J Anim Nutr 26(04):843-851. In Chinese
Harlioğlu MM, Köprücü K, Harlioğlu AG, Yilmaz Ö, Aydin S, Yonar SM, Duran TÇ, Özcan S (2012) The effects of dietary n−3 series fatty acid on the fatty acid composition, cholesterol and fat-soluble vitamins of pleopodal eggs and stage 1 juveniles in a freshwater crayfish, Astacus leptodactylus (Eschscholtz). Aquaculture 356–357:310–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2012.05.001
He Y, Wang Q, Li X, Wang G, Zhao J, Zhang H, Chen W (2020) Lactic acid bacteria alleviate polycystic ovarian syndrome by regulating sex hormone related gut microbiota. Food Funct 11(6):5192–5204. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9fo02554e
Hu Y, Huang X, Zong X, Bi Z, Cheng Y, Xiao X, Wang F, Wang Y, Lu Z (2020) Chicory fibre improves reproductive performance of pregnant rats involving in altering intestinal microbiota composition. J Appl Microbiol 129(6):1693–1705. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.14679
Huang X, Yin Y, Shi Z, Li W, Zhou H, Lv W (2010) Lipid content and fatty acid composition in wild-caught silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus) broodstocks: effects on gonad development. Aquaculture 310(1):192–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2010.10.015
Huang M, Chen J, Liu Y, Chen H, Yu Z, Ye Z, Peng C, Xiao L, Zhao M, Li S, Lin H, Zhang Y (2019) New insights into the role of follicle-stimulating hormone in sex differentiation of the protogynous orange-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 10:304. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2019.00304
Ivan B, Valentina A, Federica M, Valeria V, R MG, Anna C, Luca P, Yoav G, Marco B (2016) The zebrafish: an emerging animal model for investigating the hypothalamic regulation of reproduction. Minerva Endocrinol 41(2):250-265
Izquierdo MS, Fernández-Palacios H, Tacon AGJ (2001) Effect of broodstock nutrition on reproductive performance of fish. Aquaculture 197(1):25–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(01)00581-6
Jia R, Li Y, Cao L, Du J, Zheng T, Qian H, Gu Z, Jeney G, Xu P, Yin G (2019) Antioxidative, anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective effects of resveratrol on oxidative stress-induced liver damage in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 215:56–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2018.10.002
Lan Y, Wang C, Zhang C, Li P, Zhang J, Ji H, Yu H (2022) Dietary sea buckthorn polysaccharide reduced lipid accumulation, alleviated inflammation and oxidative stress, and normalized imbalance of intestinal microbiota that was induced by high-fat diet in zebrafish Danio rerio. Fish Physiol Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10695-022-01105-0
Lan J, Guo X, Tang J, Zhang L, Xu Y, Yang C (2020) Effect of α-glycerol monolaurate on growth performance, fecal microorganism and serum immune factor of weaned piglets. Chin J Anim Nutr 32(03):1136-1142. In Chinese
Leanne G (2011) Live imaging of zebrafish development. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2011(7):770–777. https://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.top119
Li X, Ray GW, Kou S, Liang M, Yang Q, Tan B, Chi S (2022) Glycerol monolaurate (GML), a medium-chain fatty acid derivative, ameliorate growth performance, immune function, disease resistance and intestinal microbiota in juvenile hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus♀ × Epinephelus lanceolatus♂). Fish Shellfish Immunol 128:634–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FSI.2022.08.024
Liu Y, Yao Y, Li H, Qiao F, Wu J, Du Z, Zhang M (2016) Influence of endogenous and exogenous estrogenic endocrine on intestinal microbiota in zebrafish. PLoS ONE 11(10):e0163895. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0163895
Liu T, Tang J, Feng F (2020) Medium-chain alpha-monoglycerides improves productive performance and egg quality in aged hens associated with gut microbiota modulation. Poult Sci 99:7122–7132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psj.2020.07.049
Liu S, Yu H, Li P, Wang C, Liu G, Zhang X, Zhang C, Qi M, Ji H (2022) Dietary nano-selenium alleviated intestinal damage of juvenile grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) induced by high-fat diet: Insight from intestinal morphology, tight junction, inflammation, anti-oxidization and intestinal microbiota. Anim Nutr 8(01):235–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ANINU.2021.07.001
Luo X, Liu W, Zhao M, Huang Y, Feng F (2022) Glycerol monolaurate beyond an emulsifier: synthesis, in vivo fate, food quality benefits and health efficacies. Trends Food Sci Technol 127:291–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TIFS.2022.05.017
Maharajan K, Muthulakshmi S, Karthik C, Nataraj B, Nambirajan K, Hemalatha D, Jiji S, Kadirvelu K, Liu K-C, Ramesh M (2020) Pyriproxyfen induced impairment of reproductive endocrine homeostasis and gonadal histopathology in zebrafish (Danio rerio) by altered expression of hypothalamus-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis genes. Sci Total Environ 735:139496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139496
Manuel T, Ana G, Silvia Z, Manuel C (2011) Comparative insights of the kisspeptin/kisspeptin receptor system: lessons from non-mammalian vertebrates. Gen Comp Endocrinol 175(2):234–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2011.11.015
Mateos J, Mananos E, Carrillo M et al (2002) Regulation of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) gene expression by gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) and sexual steroids in the Mediterranean Sea bass. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 132(1):75–86. https://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod62.5.1262
Nzohabonayo E, Kassam D, Kang’ombe J (2017) Effect of lipid levels on reproductive performance of Oreochromis karongae. Aquac Res 48(5):1998–2003. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.13258
Park JW, Jin YH, Oh S-Y, Kwon JY (2016) Kisspeptin2 stimulates the HPG axis in immature Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 202:31–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2016.07.009
Peng M, Xue J, Hu Y, Wen C, Hu B, Jian S, Liang L, Yang G (2018) Disturbance in the homeostasis of intestinal microbiota by a high-fat diet in the rice field eel (Monopterus albus). Aquaculture 502:347–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.12.062
Qiu W, Fang M, Liu J, Fu C, Zheng C, Chen B, Wang K-J (2019) In vivo actions of bisphenol F on the reproductive neuroendocrine system after long-term exposure in zebrafish. Sci Total Environ 665:995–1002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.154
Ribas L, Piferrer F (2014) The zebrafish (Danio rerio) as a model organism, with emphasis on applications for finfish aquaculture research. Rev Aquac 6(4):209–240. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12041
Rimoldi S, Gliozheni E, Ascione C, Gini E, Terova G (2018) Effect of a specific composition of short- and medium-chain fatty acid 1-monoglycerides on growth performances and gut microbiota of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). PeerJ 6:e5355. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.5355
Roa J, Navarro VM, Tena-Sempere M (2011) Kisspeptins in reproductive biology: consensus knowledge and recent developments. Biol Reprod 85(4):650–660. https://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod.111.091538
Sakineh Y, Sedigheh M, Fatemeh M, Sylvain M (2022) The effects of recombinant GnRH with dopamine antagonist on reproduction performance, sex steroid levels, and stress response in female koi carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquacult Rep 22:101001. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AQREP.2021.101001
Shairah AR, Shaley V, Terence M, John B, Norfarhan M, T SK (2022) Compositional dynamics of gastrointestinal tract microbiomes associated with dietary transition and feeding cessation in lake sturgeon larvae. Microorganisms 10(9):1872. https://doi.org/10.3390/MICROORGANISMS10091872
Shajahan F, Samira S, Manuel AJ, Jesús ZM, Ramón F, Marisol I, Sadasivam K, Daniel M (2022) Selection for high growth improves reproductive performance of gilthead seabream Sparus aurata under mass spawning conditions, regardless of the dietary lipid source. Anim Reprod Sci 241:106989. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ANIREPROSCI.2022.106989
Sheng Y, Ren H, Limbu SM, Sun Y, Qiao F, Zha IW, Du Z, Zhang M (2018) The presence or absence of intestinal microbiota affects lipid deposition and related genes expression in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Front Microbiol 9:1124. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01124
Shi L, Ren T, Han Y (2020) Research progress of nutrients regulating reproductive performance of aquaculture animals: a review. J Dalian Ocean Univ 35(04):620–630. https://doi.org/10.16535/j.cnki.dlhyxb.2019-243 In Chinese
Sun W, Jia Y, Ding X, Dai L, Liu C, Wang J, Zhao G, Zhou H, Yu L (2018) Combined effects of pentachlorophenol and its byproduct hexachlorobenzene on endocrine and reproduction in zebrafish. Chemosphere 220:216–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.12.100
Takashi K, Satoshi O, Parhar SI (2009) Cloning and expression of kiss2 in the zebrafish and medaka. Endocrinology 150(2):821–831. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2008-0940
Tan Q, Wu F, Du H, Liang X, Wei Q (2016) Effects of broodstock nutrition on reproductive performance of fish: a review. J Hydroecol 37(04):1–9. https://doi.org/10.15928/j.1674-3075.2016.04.001 In Chinese
Trent N, Noel J, Michael M, Julia H (2016) Dietary intake influences adult fertility and offspring fitness in zebrafish. PLoS ONE 11(11):e0166394. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0166394
Wang AR, Ran C, Ringø E, Zhou ZG (2018) Progress in fish gastrointestinal microbiota research. Rev Aquac 10(3):626–640. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12191
Wang L, Luo L, Zhao W, Yang K, Shu G, Wang S, Gao P, Zhu X, Xi Q, Zhang Y, Jiang Q, Wang L (2018b) Lauric acid accelerates glycolytic muscle fiber formation through TLR4 signaling. J Agric Food Chem 66(25):6308–6316. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b01753
Wang A, Zhang Z, Ding Q, Yang Y, Jérôme B, Ran C, Zhou Z (2021a) Intestinal Cetobacterium and acetate modify glucose homeostasis via parasympathetic activation in zebrafish. Gut Microbes 13(1):11–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2021.1900996
Wang Y, Abdullah, Zhong H, Wang J, Feng F (2021) Dietary glycerol monolaurate improved the growth, activity of digestive enzymes and gut microbiota in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquacult Rep 20:100670. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AQREP.2021.100670
Wang C, Zhang C, Yu H, Zan Z, Li J, Li P, Zhang X, Ji H, Gao Q (2022) Glycerol monolaurate and triglycerol monolaurate alleviated high-fat diet induced lipid accumulation and damage of liver in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquaculture 561:738616. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AQUACULTURE.2022.738616
Wang Y, Du J, Li Y, Zhang H, Feng F (2019) Effects of glycerol monolaurate on growth, health and nutritional quality of Chinese soft-shelled turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis). Chin J Anim Nutr 31(01):428-436. In Chinese
Weltzien FA, Andersson E, Andersen Ø, Shalchian-Tabrizi K, Norberg B (2004) The brain-pituitary-gonad axis in male teleosts, with special emphasis on flatfish (Pleuronectiformes). Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 137(3):447–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2003.11.007
Xue Y, Huang Z, Lei Z, Wang X (2020) Advances in physiological function of glycerol monolaurate and their application in animal production. Chin J Anim Sci 56(12):19–25. https://doi.org/10.19556/j.0258-7033.20200103-01 In Chinese
Xun W, Cao T, Zhou H, Hou G, Liu Y, Shi L (2017) Effects of different energy sources on growth performance, age of puberty, and uterus and ovarian development for Wuzhishan pigs. J Domest Anim Ecol 38(06):41-45. In Chinese
Yang B, Jiang Q, Chan T, Ko WKW, Wong AOL (2009) Goldfish kisspeptin: molecular cloning, tissue distribution of transcript expression, and stimulatory effects on prolactin, growth hormone and luteinizing hormone secretion and gene expression via direct actions at the pituitary level. Gen Comp Endocrinol 165(1):60–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2009.06.001
Yang B, Xue Y (2020) Advances on the application of glycerol monolaurate in livestock production. Feed Indust 41(18):6–12. https://doi.org/10.13302/j.cnki.fi.2020.18.002 In Chinese
Yoneda M, Kitano H, Selvaraj S, Matsuyama M, Shimizu A (2013) Dynamics of gonadosomatic index of fish with indeterminate fecundity between subsequent egg batches: application to Japanese anchovy Engraulis japonicus under captive conditions. Mar Biol 160(10):2733–2741. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-013-2266-9
Yoshitaka N, Masakane Y (2008) Regulation of oocyte maturation in fish. Dev Growth Differ 50:S195-219. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1440-169X.2008.01019.X
You LS, Takayoshi U, Kazuyoshi T (2021) Regulation of stress response on the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis via gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone. Front Neuroendocrinol 64:100953. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.YFRNE.2021.100953
Yúfera M, Darias MJ (2007) The onset of exogenous feeding in marine fish larvae. Aquaculture 268(1):53–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.04.050
Zhang H, Wei H, Cui Y, Zhao G, Feng F (2009) Antibacterial interactions of monolaurin with commonly used antimicrobials and food components. J Food Sci 74(7):418–421. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3841.2009.01300.x
Zhang Z, Zhou Z, Li Y, Zhou L, Ding Q, Xu L (2016) Isolated exopolysaccharides from Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG alleviated adipogenesis mediated by TLR2 in mice. Sci Rep 6(1):36083. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep36083
Zhang C, Yu H, Li J, Zhang X, Li Y, Ye L, ... Gao Q (2023) Mitochondrial dysfunction and lipometabolic disturbance induced by the co-effect of polystyrene nanoplastics and copper impede early life stage development of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Sci: Nano 10(2):552–566. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00710J
Zhao Y, Wayne NL (2017) Effects of kisspeptin1 on electrical activity of an extrahypothalamic population of gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons in medaka (Oryzias latipes). PLoS ONE 7(5):e37909. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0037909
Zhao M, Cai H, Liu M, Deng L, Li Y, Zhang H, Feng F (2019) Effects of dietary glycerol monolaurate on productive performance, egg quality, serum biochemical indices, and intestinal morphology of laying hens. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 20(11):877–890. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1800530
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Project No. 2019YFD0901002), Northwest A & F University Young Talent Training Program (2452018030), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (31602180).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Boyu Li: methodology, investigation, data curation, writing original draft; Limin Ye: methodology, investigation, data curation; Cheng Zhang: methodology, investigation, data curation; Chi Wang: methodology, investigation; Xiaotian Zhang: methodology, investigation; Hong Ji: resources; Haibo Yu: conceptualization, methodology, resources, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The experiment procedures were conducted in compliance with the Guidelines for Animal Research which was approved by Animal Care Committee of Northwest A&F University (Yangling, China).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, B., Ye, L., Zhang, C. et al. Effects of glycerol monolaurate on estradiol and follicle-stimulating hormones, offspring quality, and mRNA expression of reproductive-related genes of zebrafish (Danio rerio) females. Fish Physiol Biochem (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-024-01345-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-024-01345-2