Abstract
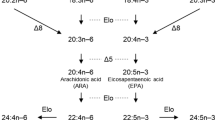
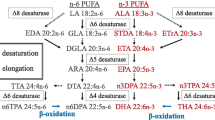
The splendid alfonsino Beryx splendens is a commercially important deep-sea fish in East Asian countries. Because the wild stock of this species has been declining, there is an urgent need to develop aquaculture systems. In the present study, we investigated the long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid (LC-PUFA) requirements of B. splendens, which are known as essential dietary components in many carnivorous marine fish species. The fatty acid profiles of the muscles, liver, and stomach contents of B. splendens suggested that it acquires substantial levels of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) from its natural diet. The functional characterization of a fatty acid desaturase (Fads2) and three elongases (Elovl5, Elovl4a, and Elovl4b) from B. splendens confirmed their enzymatic capabilities in LC-PUFA biosynthesis. Fads2 showed Δ6 and Δ8 bifunctional desaturase activities. Elovl5 showed preferential elongase activities toward C18 and C20 PUFA substrates, whereas Elovl4a and Elovl4b showed activities toward various C18–22 substrates. Given that Fads2 showed no Δ5 desaturase activity and no other fads-like sequence was found in the B. splendens genome, EPA and arachidonic acid cannot be synthesized from C18 precursors; hence, they can be categorized as dietary essential fatty acids in B. splendens. EPA can be converted into DHA in B. splendens via the so-called Sprecher pathway. However, given that fads2 is only expressed in the brain, it is unlikely that the capacity of B. splendens to biosynthesize DHA from EPA can fulfill its physiological requirements. These results will be useful to researchers developing B. splendens aquaculture methods.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All sequences isolated from B. splendens in the present study were deposited into the NCBI GenBank with the accession numbers MZ2991134 to MZ2991137.
References
Betancor, M.B., Oboh, A., Ortega, A., Mourente, G., Navarro, J.C., Gándara, F. de la, Tocher, D.R., Monroig, Ó., 2019. Molecular and functional characterisation of a putative elovl4 gene and its expression in response to dietary fatty acid profile in Atlantic bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus). Comp Biochem Physiol B 110372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2019.110372
Capella-Gutierrez S, Silla-Martinez JM, Gabaldón T (2009) trimAl: a tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 25:1972–1973. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp348
Castro LFC, Monroig O, Leaver MJ, Wilson J, Cunha I, Tocher DR (2012) Functional desaturase Fads1 (Δ5) and Fads2 (Δ6) orthologues evolved before the origin of jawed vertebrates. Plos One 7:31950. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0031950
Darriba D, Posada D, Kozlov AM, Stamatakis A, Morel B, Flouri T (2019) ModelTest-NG: a new and scalable tool for the selection of DNA and protein evolutionary models. Mol Biol Evol 37:291–294. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msz189
Dürr J, González JA (2002) Feeding habits of Beryx splendens and Beryx decadactylus (Berycidae) off the Canary Islands. Fish Res 54:363–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0165-7836(01)00269-7
FAO. 2016. Global review of alfonsino (Beryx spp.), their fisheries, biology and management, by Ross Shotton. FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Circular No. 1084. Rome, Italy.
Flores A, Wiff R, Gálvez P, Díaz E (2012) Reproductive biology of alfonsino Beryx splendens. J Fish Biol 81:1375–1390. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.2012.03424.x
Folch J, Lees M, Stanley GS (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226(497):509
Hashimoto K, Yoshizawa AC, Okuda S, Kuma K, Goto S, Kanehisa M (2008) The repertoire of desaturases and elongases reveals fatty acid variations in 56 eukaryotic genomes. J Lipid Res 49:183–191. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.m700377-jlr200
Horn PL, Forman J, Dunn MR (2010) Feeding habits of alfonsino Beryx splendens. J Fish Biol 76:2382–2400. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.2010.02630.x
Jakobsson A, Westerberg R, Jacobsson A (2006) Fatty acid elongases in mammals: their regulation and roles in metabolism. Prog Lipid Res 45:237–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2006.01.004
Jin M, Monroig O, Navarro JC, Tocher DR, Zhou Q-C (2017) Molecular and functional characterisation of two elovl4 elongases involved in the biosynthesis of very long-chain (>C24) polyunsaturated fatty acids in black seabream Acanthopagrus schlegelii. Comp Biochem Physiol B 212:41–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2017.06.008
Kabeya N, Yamamoto Y, Cummins SF, Elizur A, Yazawa R, Takeuchi Y, Haga Y, Satoh S, Yoshizaki G (2015) Polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolism in a marine teleost, Nibe croaker Nibea mitsukurii: functional characterization of Fads2 desaturase and Elovl5 and Elovl4 elongases. Comp Biochem Physiol B 188:37–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2015.06.005
Kabeya N, Chiba M, Haga Y, Satoh S, Yoshizaki G (2017) Cloning and functional characterization of fads2 desaturase and elovl5 elongase from Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Comp Biochem Physiol 214:36–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2017.09.002
Kabeya N, Ogino M, Ushio H, Haga Y, Satoh S, Navarro JC, Monroig Ó (2021) A complete enzymatic capacity for biosynthesis of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA, 22: 6n–3) exists in the marine Harpacticoida copepod Tigriopus californicus. Open Biol 11:200402. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsob.200402
Katoh, K., Rozewicki, J., Yamada, K.D., 2017. MAFFT online service: multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief Bioinform 30, bbx108. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbx108
Kozlov AM, Darriba D, Flouri T, Morel B, Stamatakis A (2019) RAxML-NG: a fast, scalable and user-friendly tool for maximum likelihood phylogenetic inference. Bioinform Oxf Engl 35:4453–4455. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz305
Lopes-Marques M, Kabeya N, Qian Y, Ruivo R, Santos MM, Venkatesh B, Tocher DR, Castro LFC, Monroig Ó (2018) Retention of fatty acyl desaturase 1 (fads1) in Elopomorpha and Cyclostomata provides novel insights into the evolution of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid biosynthesis in vertebrates. Bmc Evol Biol 18:157. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12862-018-1271-5
Luo J, Monroig O, Liao K, Ribes-Navarro A, Navarro JC, Zhu T, Li J, Xue L, Zhou Q, Jin M (2021) Biosynthesis of LC-PUFAs and VLC-PUFAs in Pampus argenteus: characterization of Elovl4 elongases and regulation under acute salinity. J Agr Food Chem 69:932–944. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c06277
Machado AM, Tørresen OK, Kabeya N, Couto A, Petersen B, Felício M, Campos PF, Fonseca E, Bandarra N, Lopes-Marques M, Ferraz R, Ruivo R, Fonseca MM, Jentoft S, Monroig Ó, da Fonseca RR, Castro LFC (2018) “Out of the Can”: a draft genome assembly, liver transcriptome, and nutrigenomics of the European sardine Sardina pilchardus. Genes 9:485. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9100485
Matsushita Y, Miyoshi K, Kabeya N, Sanada S, Yazawa R, Haga Y, Satoh S, Yamamoto Y, Strüssmann CA, Luckenbach JA, Yoshizaki G (2020) Flatfishes colonised freshwater environments by acquisition of various DHA biosynthetic pathways. Commun Biol 3:516. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-020-01242-3
Monroig Ó, Rotllant J, Sánchez E, Cerdá-Reverter JM, Tocher DR (2009) Expression of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid (LC-PUFA) biosynthesis genes during zebrafish Danio rerio early embryogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta - Mol Cell Biol Lipids 1791:1093–1101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2009.07.002
Monroig Ó, Rotllant J, Cerdá-Reverter JM, Dick JR, Figueras A, Tocher DR (2010) Expression and role of Elovl4 elongases in biosynthesis of very long-chain fatty acids during zebrafish Danio rerio early embryonic development. Biochim Biophys Acta - Mol Cell Biol Lipids 1801:1145–1154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2010.06.005
Monroig Ó, Li Y, Tocher DR (2011) Delta-8 desaturation activity varies among fatty acyl desaturases of teleost fish: high activity in delta-6 desaturases of marine species. Comp Biochem Physiol B 159:206–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2011.04.007
Monroig Ó, Navarro JC, Hontoria F, Venkatesh B, Tocher DR (2016) Evolutionary functional elaboration of the Elovl2/5 gene family in chordates. Sci Rep 6:20510. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep20510
Monroig, Ó., Shu-Chien, A.C., Kabeya, N., Tocher, D.R., Castro, L.F.C., 2022. Desaturases and elongases involved in long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid biosynthesis in aquatic animals: from genes to functions. Prog Lipid Res 101157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2022.101157
Morais S, Monroig O, Zheng X, Leaver MJ, Tocher DR (2009) Highly unsaturated fatty acid synthesis in Atlantic salmon: characterization of ELOVL5- and ELOVL2-like elongases. Mar Biotechnol 11:627–639. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-009-9179-0
Morais S, Mourente G, Ortega A, Tocher JA, Tocher DR (2011) Expression of fatty acyl desaturase and elongase genes, and evolution of DHA:EPA ratio during development of unfed larvae of Atlantic bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus L.). Aquaculture 313:129–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2011.01.031
Morais S, Torres M, Hontoria F, Monroig Ó, Varó I, Agulleiro MJ, Navarro JC (2020) Molecular and functional characterization of Elovl4 genes in Sparus aurata and Solea senegalensis pointing to a critical role in very long-chain (>C24) fatty acid synthesis during early neural development of fish. Int J Mol Sci 21:3514. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103514
Oboh A, Kabeya N, Carmona-Antoñanzas G, Castro LFC, Dick JR, Tocher DR, Monroig O (2017) Two alternative pathways for docosahexaenoic acid (DHA, 22:6n–3) biosynthesis are widespread among teleost fish. Sci Rep 7:3889. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-04288-2
Onishi K (1966) Artificial fertilization of the eggs of Beryx splendens. Japan J Ichthyol 14:27–33
Park WJ, Kothapalli KSD, Lawrence P, Tyburczy C, Brenna JT (2009) An alternate pathway to long-chain polyunsaturates: the FADS2 gene product Δ8-desaturates 20:2n–6 and 20:3n–3. J Lipid Res 50:1195–1202. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.m800630-jlr200
Ribes-Navarro A, Navarro JC, Hontoria F, Kabeya N, Standal IB, Evjemo JO, Monroig Ó (2021) Biosynthesis of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in marine gammarids: molecular cloning and functional characterisation of three fatty acyl elongases. Mar Drugs 19:226. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040226
Saito H, Murata M (1996) The high content of monoene fatty acids in the lipids of some midwater fishes: family Myctophidae. Lipids 31:757–763. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02522892
Saito H, Watanabe T, Murase T (1995) The fatty acid composition characteristic of a highly migratory fish, with seasonal variation of docosahexaenoic acid content in lipid of Bonito (Euthynnus pelamis). Biosci Biotech Biochem 59:2186–2188. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.59.2186
Saito H, Seike Y, Ioka H, Osako K, Tanaka M, Takashima A, Keriko JM, Kose S, Souza JCR (2005) High docosahexaenoic acid levels in both neutral and polar lipids of a highly migratory fish: Thunnus tonggol (Bleeker). Lipids 40:941–953. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-005-1455-4
Tocher DR (2010) Fatty acid requirements in ontogeny of marine and freshwater fish. Aquac Res 41:717–732. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2008.02150.x
Zheng X, Ding Z, Xu Y, Monroig O, Morais S, Tocher DR (2009) Physiological roles of fatty acyl desaturases and elongases in marine fish: characterisation of cDNAs of fatty acyl Δ6 desaturase and elovl5 elongase of cobia (Rachycentron canadum). Aquaculture 290:122–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2009.02.010
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the fishermen Yuzuru Sano (from Minamiizu-cho), Naohisa Uchiyama, and Yuto Uchiyama (both from Inatori, Higashiizu-cho) as well as their vessels “Ai-maru” and “Inari-maru,” respectively, for their cooperation in collecting B. splendens samples.
Funding
This study was fully supported by Shizuoka Prefecture through The Promotion of R&D and Industrial Application (“Seeds” Creation Research) program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NK and GY initially conceived the study and design experiments. NK, KK, and YM performed overall experimental analyses. SSu, YN, HN, KT, and KO prepared all the B. splendens samples for RNA extraction and fatty acid analysis. RK confirmed B. splendens gene sequences. MM performed cloning of desaturase and elongase genes. YH and SSa analyzed fatty acids and interpreted the results. NK prepared the first draft of the manuscript and edited with GY. The manuscript was further finalized and approved by all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All experiments using animals conformed to the guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals of the Tokyo University of Marine Science and Technology.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kabeya, N., Kimura, K., Matsushita, Y. et al. Determination of dietary essential fatty acids in a deep-sea fish, the splendid alfonsino Beryx splendens: functional characterization of enzymes involved in long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid biosynthesis. Fish Physiol Biochem 49, 425–439 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-023-01192-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-023-01192-7