Abstract
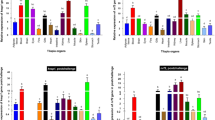
Some diseases related to lipid metabolism increase yearly in cultured fish, and the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) is a nuclear protein that plays a key role in inflammatory responses and lipid metabolism. However, the roles of FXR in hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus♀ × E. lanceolatus♂) remain poorly understood. The main objective of this study was to explore the roles of hepatic FXR in triggering the immune response and the potential functions of FXR in regulating the lipid metabolism. In the present study, the full-length sequence of fxr from hybrid grouper was cloned and characterized for the first time. Upon the Vibrio parahaemolyticus stimulation, the transcriptional level of fxr was rapidly elevated in the head kidney tissue in the early stage of infection. In vivo and vitro, activation of FXR by obeticholic acid (OA) significantly increased the concentrations and mRNA levels of hepatic inflammatory cytokines. These effects were inversed when FXR was inhibited by guggulsterone (GU). Moreover, the activation of FXR to suppress the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway improves hepatic lipid metabolism and reduces hepatic lipid accumulation in vivo and vitro. In addition, the inhibition of FXR activated the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, decreased the lipolysis and increased the lipogenesis, and subsequently increased the lipid accumulation in fish. These results revealed the positive roles of FXR in triggering immune responses and improving lipid metabolism and accumulation in hybrid grouper.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable
Code availability
Not applicable
Abbreviations
- 3-pdk1:
-
3-Phosphoinositide dependent kinase-1
- 6pgd:
-
6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase
- acc:
-
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase
- AKT:
-
Serine/threonine-protein kinase
- atgl:
-
Adipose triglyceride lipase
- cpt1:
-
Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1
- deptor:
-
DEP domain-containing mTOR-interacting protein
- dgka:
-
Diacylglycerol kinase alpha
- fas:
-
Fatty acid synthase
- FXR:
-
Farnesoid X receptor
- g6pd:
-
Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase
- GU:
-
Guggulsterone
- hl:
-
Hepatic lipase
- hsl:
-
Hormone-sensitive lipase
- lxr:
-
Liver X receptor alpha
- me:
-
Malic enzyme
- mlst8:
-
Target of rapamycin complex subunit lst 8
- il1β:
-
Interleukin 1β
- mTORC1:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1
- OA:
-
Obeticholic acid
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- pi3k-rs5:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit 5
- pras40:
-
Proline-rich Akt1 substrate 1
- prr5:
-
Proline-rich protein 5
- pparα:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha
- PPARγ:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma
- raptor:
-
Regulatory associated protein of mTOR
- RHEB:
-
Ras homolog enriched in brain
- RICTOR:
-
Rapamycin-insensitive companion of mTOR
- SIN1:
-
Target of rapamycin complex 2 subunit
- SREBP1:
-
Sterol-regulator element-binding protein 1
- tel:
-
Telomere length regulation protein
- TG:
-
Triglycerides
- tsc1:
-
Tuberous 1
- tnfα:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
References
Chao L, Zhe Z, Qing-heng W, Rong-lian H, Yue-Wen D, Jun-hui L (2017) Molecular characterization and expression analysis of Pm-ApoL2 gene from Pinctada fucata martensii. J Guangdong Ocean Univ 37(3):7
Chen Q, Liu H, Tan B, Dong X, Chi S, Yang Q, Zhang S (2016) Effects of dietary cholesterol level on growth performance, blood biochemical parameters and lipid metabolism of juvenile cobia (Rachycentron canadum). J Guangdong Ocean Univ 36(1):35–43
Claudel T, Inoue Y, Barbier O, Duran-Sandoval D, Kosykh V, Fruchart J, Fruchart JC, Gonzalez FJ, Staels B (2003) Farnesoid X receptor agonists suppress hepatic apolipoprotein CIII expression. Gastroenterology 125(2):544–555. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0016-5085(03)00896-5
Czaja MJ, Ding WX, Donohue TM Jr, Friedman SL, Kim JS, Komatsu M, Lemasters JJ, Lemoine A, Lin JD, Ou JH, Perlmutter DH, Randall G, Ray RB, Tsung A, Yin XM (2013) Functions of autophagy in normal and diseased liver. Autophagy 9(8):1131–1158. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.25063
Du J, Chen Q, Li Y, Xiang X, Xu W, Mai K, Ai Q (2020) Activation of the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) suppresses linoleic acid-induced inflammation in the large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). J Nutr 150(9):2469–2477. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/nxaa185
Du J, Xiang X, Li Y, Ji R, Xu H, Mai K, Ai Q (2018) Molecular cloning and characterization of farnesoid X receptor from large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) and the effect of dietary CDCA on the expression of inflammatory genes in intestine and spleen. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 216:10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2017.09.007
Fiorucci S, Rizzo G, Donini A, Distrutti E, Santucci L (2007) Targeting farnesoid X receptor for liver and metabolic disorders. Trends Mol Med 13(7):298–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2007.06.001
Fuentes EN, Björnsson BT, Valdés JA, Einarsdottir IE, Lorca B, Alvarez M, Molina A (2011) IGF-I/PI3K/Akt and IGF-I/MAPK/ERK pathways in vivo in skeletal muscle are regulated by nutrition and contribute to somatic growth in the fine flounder. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 300(6):R1532–R1542
Gai Z, Visentin M, Gui T, Zhao L, Thasler WE, Hausler S, Hartling I, Cremonesi A, Hiller C, Kullak-Ublick GA (2018) Effects of farnesoid X receptor activation on arachidonic acid metabolism, NF-kB signaling, and sepatic inflammation. Mol Pharmacol 94(2):802–811. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.117.111047
Gamper CJ, Powell JD (2012) All PI3Kinase signaling is not mTOR: dissecting mTOR-dependent and independent signaling pathways in T cells. Front Immunol 3:312
Gui L, Mai H, Chi S, Zhou W, Li Y, Tan B (2019) Effects of yeast culture on growth performance, hematological parameters, immunity and disease resistance of Litopenaeus vannamei. J Guangdong Ocean Univ 39(3):30–37
Hagiwara A, Cornu M, Cybulski N, Polak P, Betz C, Trapani F, Terracciano L, Heim MH, Rüegg MA, Hall MN (2012) Hepatic mTORC2 activates glycolysis and lipogenesis through Akt, glucokinase, and SREBP1c. Cell Metab 15(5):725–738
He Y, Ye G, Chi S, Tan B, Dong X, Yang Q, Liu H, Zhang S (2020) Integrative transcriptomic and small RNA sequencing reveals immune-related miRNA-mRNA regulation network for soybean meal-induced enteritis in hybrid grouper, Epinephelus fuscoguttatusfemale symbol x Epinephelus lanceolatusmale symbol. Front Immunol 11:1502. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.01502
Hirschfield GM, Mason A, Luketic V, Lindor K, Gordon SC, Mayo M, Kowdley KV, Vincent C, Bodhenheimer HC Jr, Pares A, Trauner M, Marschall HU, Adorini L, Sciacca C, Beecher-Jones T, Castelloe E, Bohm O, Shapiro D (2015) Efficacy of obeticholic acid in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis and inadequate response to ursodeoxycholic acid. Gastroenterology 148(4):751-761 e758. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2014.12.005
Hong-yu L, Li-xian L, Stephen A, Ze T, Wei F, Bei-ping T, Xiao-hui D, Shu-yan C, Qi-hui Y, Shuang Z, Wen-hao Z (2021) Effects of dietary yeast culture supplementation on growth, intestinal morphology, immunity, and disease resistance in Epinephelus fuscoguttatus♀× Epinephelus lanceolatu♂. J Guangdong Ocean Univ 41(3):11
Hortsch SK, Kremling A (2018) Characterization of noise in multistable genetic circuits reveals ways to modulate heterogeneity. PLoS ONE 13(3):e0194779
Howarth DL, Hagey LR, Law SH, Ai N, Krasowski MD, Ekins S, Moore JT, Kollitz EM, Hinton DE, Kullman SW (2010) Two farnesoid X receptor alpha isoforms in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) are differentially activated in vitro. Aquat Toxicol 98(3):245–255
Huang F, Zheng X, Ma X, Jiang R, Zhou W, Zhou S, Zhang Y, Lei S, Wang S, Kuang J, Han X, Wei M, You Y, Li M, Li Y, Liang D, Liu J, Chen T, Yan C, Wei R, Rajani C, Shen C, Xie G, Bian Z, Li H, Zhao A, Jia W (2019) Theabrownin from Pu-erh tea attenuates hypercholesterolemia via modulation of gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism. Nat Commun 10(1):4971. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12896-x
Iracheta-Vellve A, Calenda CD, Petrasek J, Ambade A, Kodys K, Adorini L, Szabo G (2018) FXR and TGR5 agonists ameliorate liver injury, steatosis, and inflammation after binge or prolonged alcohol feeding in mice. Hepatol Commun 2(11):1379–1391. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep4.1256
Jadhav K, Xu Y, Xu Y, Li Y, Xu J, Zhu Y, Adorini L, Lee YK, Kasumov T, Yin L, Zhang Y (2018) Reversal of metabolic disorders by pharmacological activation of bile acid receptors TGR5 and FXR. Mol Metab 9:131–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2018.01.005
Ji K, Liang H, Ren M, Ge X, Mi H, Pan L, Yu H (2020) The immunoreaction and antioxidant capacity of juvenile blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) involves the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 and NF-kappaB signal pathways in response to dietary methionine levels. Fish Shellfish Immunol 105:126–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2020.07.005
Jia W, Xie G, Jia W (2018) Bile acid-microbiota crosstalk in gastrointestinal inflammation and carcinogenesis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 15(2):111–128. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2017.119
Jiang C, Xie C, Li F, Zhang L, Nichols RG, Krausz KW, Cai J, Qi Y, Fang ZZ, Takahashi S, Tanaka N, Desai D, Amin SG, Albert I, Patterson AD, Gonzalez FJ (2015) Intestinal farnesoid X receptor signaling promotes nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Invest 125(1):386–402. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI76738
Jung K, Kim M, So J, Lee SH, Ko S, Shin D (2021) Farnesoid X receptor activation impairs liver progenitor cell–mediated liver regeneration via the PTEN-PI3K-AKT-mTOR Axis in zebrafish. J Hepatology 74(1):397–410
Kim K, Qiang L, Hayden MS, Sparling DP, Purcell NH, Pajvani UB (2016) mTORC1-independent raptor prevents hepatic steatosis by stabilizing PHLPP2. Nat Commun 7(1):10255. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10255
Li Z, Xu G, Qin Y, Zhang C, Tang H, Yin Y, Xiang X, Li Y, Zhao J, Mulholland M (2014) Ghrelin promotes hepatic lipogenesis by activation of mTOR-PPARγ signaling pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111(36):13163–13168
Liang H, Huang D, Wu Y, Wang C, Zhong W (2013) Effects of temperature and salinity on survival and food intake of grouper hybrid (Epinephelus lanceolatus♂× E fuscoguttatus♀). J Guangdong Ocean Univ 33(4):22–26
Liu DD, Han CC, Wan HF, He F, Xu HY, Wei SH, Du XH, Xu F (2016) Effects of inhibiting PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway on lipid metabolism homeostasis in goose primary hepatocytes. Animal 10(8):1319–1327. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1751731116000380
Mao Z, Zhang W (2018) Role of mTOR in glucose and lipid metabolism. Int J Mol Sci 19(7):2043. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072043
Pasquier J, Cabau C, Nguyen T, Jouanno E, Severac D, Braasch I, Journot L, Pontarotti P, Klopp C, Postlethwait JH (2016) Gene evolution and gene expression after whole genome duplication in fish: the PhyloFish database. BMC Genom 17(1):1–10
Pineda Torra IS, Claudel T, Duval C, Kosykh V, Fruchart J-C, Staels B (2003) Bile acids induce the expression of the human peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α gene via activation of the farnesoid X receptor. J Molec Endocrinol 17(2):259–272
Rahimnejad S, Bang IC, Park J-Y, Sade A, Choi J, Lee S-MJA (2015) Effects of dietary protein and lipid levels on growth performance, feed utilization and body composition of juvenile hybrid grouper, Epinephelus fuscoguttatus × E. lanceolatus. Aquaculture 446:283–289
Ricoult SJ, Yecies JL, Ben-Sahra I, Manning BD (2016) Oncogenic PI3K and K-Ras stimulate de novo lipid synthesis through mTORC1 and SREBP. Oncogene 35(10):1250–1260. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.179
Ryan KK, Tremaroli V, Clemmensen C, Kovatcheva-Datchary P, Myronovych A, Karns R, Wilson-Perez HE, Sandoval DA, Kohli R, Backhed F, Seeley RJ (2014) FXR is a molecular target for the effects of vertical sleeve gastrectomy. Nature 509(7499):183–188. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13135
Saxton RA, Sabatini DM (2017) mTOR signaling in growth, metabolism, and disease. Cell 168(6):960–976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.02.004
Schmitt J, Kong B, Stieger B, Tschopp O, Schultze SM, Rau M, Weber A, Mullhaupt B, Guo GL, Geier A (2015) Protective effects of farnesoid X receptor (FXR) on hepatic lipid accumulation are mediated by hepatic FXR and independent of intestinal FGF15 signal. Liver Int 35(4):1133–1144. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.12456
Schneider KM, Albers S, Trautwein C (2018) Role of bile acids in the gut-liver axis. J Hepatol 68(5):1083–1085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2017.11.025
Sengupta S, Peterson TR, Laplante M, Oh S, Sabatini DM (2010) mTORC1 controls fasting-induced ketogenesis and its modulation by ageing. Nature 468(7327):1100–1104. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09584
Shaik FB, Prasad DV, Narala VR (2015) Role of farnesoid X receptor in inflammation and resolution. Inflamm Res 64(1):9–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-014-0780-y
Shao-hong M, Yu-chong H, Ji-chang J, Shuang-hu C (2019) Cloning and Prokaryotic Expression of PspF Gene from Vibrio Harveyi. J Guangdong Ocean Univ 39(5):1–7
Sinal CJ, Tohkin M, Miyata M, Ward JM, Lambert G, Gonzalez FJ (2000) Targeted disruption of the nuclear receptor FXR/BAR impairs bile acid and lipid homeostasis. Cell 102(6):731–744. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)00062-3
Tian J-J, Jin Y-Q, Yu E-M, Sun J-H, Xia Y, Zhang K, Li Z-F, Gong W-B, Wang G-J, Xie J (2021) Farnesoid X receptor is an effective target for modulating lipid accumulation in grass carp Ctenopharyngodon Idella. Aquaculture 534:736248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.736248
Wagner EF, Eferl R (2005) Fos/AP-1 proteins in bone and the immune system. J Immunol Rev 208(1):126–140
Wahlstrom A, Sayin SI, Marschall HU, Backhed F (2016) Intestinal crosstalk between bile acids and microbiota and its impact on host metabolism. Cell Metab 24(1):41–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2016.05.005
Wang A, Yang Q, Tan B, Xiao W, Jia J, Dong X, Zhang S (2018) Effects of enzymolytic soybean meal on growth performance, serum biochemical indices, non-specific immunity and disease resistance of juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei. J Guangdong Ocean Univ 38(1):14–21
Watanabe M, Houten SM, Wang L, Moschetta A, Mangelsdorf DJ, Heyman RA, Moore DD, Auwerx J (2004) Bile acids lower triglyceride levels via a pathway involving FXR, SHP, and SREBP-1c. J Clin Invest 113(10):1408–1418. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI21025
Wu K, Zhao T, Hogstrand C, Xu YC, Ling SC, Chen GH, Luo Z (2020) FXR-mediated inhibition of autophagy contributes to FA-induced TG accumulation and accordingly reduces FA-induced lipotoxicity. Cell Commun Signal 18(1):47. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-020-0525-1
Xie J, Qiu D, Liu C, Zhu W, Zeng L (2013) Effcets of Vibrio alginolyticus peptidoglycan on astaxanthin Level, immune indicators and protection in Litopenaeus vannamei. J Guangdong Ocean Univ 33(01):50–55
Xiu-ping F, Xiao-ming Q, Chao-hua Z, Jian-ping C, Qian-feng Z (2018) Nutritional and volatile flavor components of dorsal and ventral muscle from hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus♀ × E. lanceolatus♂). J Guangdong Ocean Univ 38(1):8
Xu J, Li X, Yao X, Xie S, Chi S, Zhang S, Cao J, Tan B (2022a) Protective effects of bile acids against hepatic lipid accumulation in hybrid grouper fed a high-lipid diet. Front Nutr 9:813249. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2022.813249
Xu J, Xie S, Chi S, Zhang S, Cao J, Tan B (2022b) Protective effects of taurocholic acid on excessive hepatic lipid accumulation via regulation of bile acid metabolism in grouper. Food Funct 13(5):3050–3062
Xu J, Xie S, Chi S, Zhang S, Cao J, Tan B (2022c) Short-term dietary antibiotics altered the intestinal microbiota and improved the lipid metabolism in hybrid grouper fed medium and high-lipid diets. Aquaculture 547:737453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.737453
Xu P, Xu K, Wang J, Jiang JP, Chen LQ (2011) Pioglitazone: a promising therapeutic tool in sodium taurocholate-induced severe acute pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci 56(4):1082–1089. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-010-1393-0
Yamauchi Y, Furukawa K, Hamamura K, Furukawa K (2011) Positive feedback loop between PI3K-Akt-mTORC1 signaling and the lipogenic pathway boosts Akt signaling: induction of the lipogenic pathway by a melanoma antigen. Cancer Res 71(14):4989–4997. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-4108
Zhang S, Wang J, Liu Q, Harnish DC (2009) Farnesoid X receptor agonist WAY-362450 attenuates liver inflammation and fibrosis in murine model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J Hepatol 51(2):380–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2009.03.025
Zhang Y, Lee FY, Barrera G, Lee H, Vales C, Gonzalez FJ, Willson TM, Edwards PA (2006) Activation of the nuclear receptor FXR improves hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia in diabetic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(4):1006–1011. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0506982103
Zhi-xin W, Hai-ying L, Xiao-dong D, Rong-lian H, Yue-wen D, Qing-heng W, Yu J (2013) Cloning and express characters of HSP60 gene from Pinctada martensii. J Guangdong Ocean Univ 33(006):14–23
Zhu S, Xiang X, Xu X, Gao S, Mai K, Ai Q (2019) TIR domain-containing adaptor-inducing interferon-beta (TRIF) participates in antiviral immune responses and hepatic lipogenesis of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys Crocea). Front Immunol 10:2506. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02506
Zhu W, Qiu D, Gan Z, Lu Y, Jian J (2015) Antivirus effects of Vibrio alginolyticus peptidoglycan on Litopenaeus vannamei against white spot syndrome virus. J Guangdong Ocean Univ 35(6):40–46
Zhu Y, Li F, Guo GL (2011) Tissue-specific function of farnesoid X receptor in liver and intestine. Pharmacol Res 63(4):259–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2010.12.018
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank Xiaohui Dong, Hongyu Liu, and Qihui Yang (Laboratory of Aquatic Animal Nutrition and Feed of Fisheries College of the Guangdong Ocean University of Zhanjiang in China) for providing methodological help during the experiments and proofreading the article.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China [2019YFD0900200], the China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA [CARS-47], the Science and Technology Project of Zhanjiang [2020A05003], the National Natural Science Foundation of China [no. 31772864], and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province [2018A030313154&2020A1515011129].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jia Xu conducted the methodology, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, and writing—original draft; Xinzhou Yao conducted the data curation, investigation, and writing—original draft; Xiaoyue Li conducted the investigation, data curation, and visualization; Shiwei Xie conducted the conceptualization, resources, and visualization; Shuyan Chi conducted the methodology and conceptualization; Shuang Zhang conducted the conceptualization and funding acquisition; Junming Cao conducted the methodology, conceptualization, and funding acquisition; and Beiping Tan conducted the methodology, conceptualization, writing—review and editing, and funding acquisition. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The experimental procedures were approved by the Animal Ethical and Welfare Committee of Guangdong Ocean University (Guangdong, China), processing ID: GDOU-AEWC-20180063.
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• The full-length sequence of fxr from hybrid grouper was cloned for the first time.
• Tnhibition of FXR decreased the expression of inflammatory cytokines.
• Activation of hepatic FXR improved the lipid accumulation and metabolism.
• Inhibition of FXR activated the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in vivo and vitro.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Yao, X., Li, X. et al. Farnesoid X receptor regulates PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, lipid metabolism, and immune response in hybrid grouper. Fish Physiol Biochem 48, 1521–1538 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-022-01130-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-022-01130-z