Abstract
In 1996, kiss was reported to regulate feeding in mammals, but studies are limited in fish. Our study aimed to explore the possible role of kiss in the regulation of feeding in Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii). kiss1 and kiss2 were cloned, and the expression patterns were analyzed in Siberian sturgeon. The complete coding regions of kiss1 and kiss2 genes were 393 and 471 bp. Both kiss1 and kiss2 showed the highest expression level in the hypothalamus. During the periprandial and fasting experiments, the expression of kiss1 and kiss2 highly significantly increased in the hypothalamus after feeding (P < 0.01). Compared with the feeding group, in hypothalamus, kiss1 expression in the fasting group highly significantly decreased (P < 0.01). In contrast, kiss2 expression had no significant difference on days 1 and 7 (P > 0.05) but highly significantly increased on day 14 (P < 0.01). Subsequently, the feeding function was verified by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of Kp1(10) and Kp1(10) into fish. The results showed that i.p. injection of 1 µg/g BW Kp1(10) or 0.01 µg/g BW Kp2(10) could significantly reduce 0–1 h food intake (P < 0.05) and affected the expression levels of apelin, ghrelin, leptin, nmu, etc. in the hypothalamus. These results suggested that kiss1 plays an anorexic role in both short- and long-term feeding regulation, while kiss2 plays a short-term anorexic and long-term orexigenic role. This study described kiss as a novel regulator of appetite in fish and laid the groundwork for further studies focused on physiological function.
Highlights
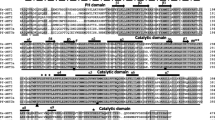
• The kiss1 and kiss2 of Siberian sturgeon were cloned.
• The expression levels of kiss1 and kiss2 mRNA were the highest in the hypothalamus.
• Postprandial hypothalamic kiss1 and kiss2 expression levels increased in the periprandial experiment.
• In the fasting test, the expression of hypothalamic kiss1 decreased after fasting, while the expression of kiss2 increased after fasting on the 14th day.
• Siberian sturgeon food intake was reduced, and appetite factors expression levels in the hypothalamus were altered after intraperitoneal injection of Kp1(10) and Kp2(10).









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Atre I, Mizrahi N, Hausken K et al (2021) Molecular characterization of kisspeptin receptors and gene expression analysis during oogenesis in the Russian sturgeon (Acipenser gueldenstaedtii). Gen Comp Endocrinol 302:113691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2020.113691
Bertucci JI, Blanco AM, Sundarrajan L, Rajeswari JJ, Velasco C, Unniappan S (2019a) Nutrient regulation of endocrine factors influencing feeding and growth in fish. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 10:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2019.00083
Bertucci JI, Blanco AM, Sundarrajan L, Rajeswari JJ, Velasco C, Unniappan S (2019b) Nutrient regulation of endocrine factors influencing feeding and growth in fish. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 10:83. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2019.00083
Bohórquez MOT, Mechaly AS, Hughes LC, Campanella D, Ortí G, Canosa LF, Somoza GM (2017) Kisspeptin system in pejerrey fish (Odontesthes bonariensis). Characterization and gene expression pattern during early developmental stages. Com Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 204:146–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2016.11.014
Castellano J, Navarro V, Fernandez-Fernandez R et al (2005) Changes in hypothalamic KiSS-1 system and restoration of pubertal activation of the reproductive axis by kisspeptin in undernutrition. Endocrinology 146:3917–3925. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2005-0337
Dong TS, Vu JP, Oh S, Sanford D, Pisegna JR, Germano P (2020) Intraperitoneal treatment of kisspeptin suppresses appetite and energy expenditure and alters gastrointestinal hormones in mice. Dig Dis Sci 65:2254–2263. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-019-05950-7
Dore R, Krotenko R, Reising JP et al (2020) Nesfatin-1 decreases the motivational and rewarding value of food. Neuropsychopharmacology 45:1645–1655. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-020-0682-3
Du K, Stöck M, Kneitz S et al (2020) The sterlet sturgeon genome sequence and the mechanisms of segmental rediploidization. Nat Ecol Evol 4:841–852. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-020-1166-x
Dunham LA, Lutterschmidt DI, Wilczynski W (2009) Kisspeptin-like immunoreactive neuron distribution in the green anole (Anolis carolinensis). Brain Behav Evol 73:129–137. https://doi.org/10.1159/000215930
Escobar S, Felip A, Zanuy S, Carrillo M (2016) Is the kisspeptin system involved in responses to food restriction in order to preserve reproduction in pubertal male sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax)? Com Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 199:38–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2016.05.005
Fairgrieve MR, Shibata Y, Smith EK, Hayman ES, Luckenbach JA (2016) Molecular characterization of the gonadal kisspeptin system: cloning, tissue distribution, gene expression analysis and localization in sablefish (Anoplopoma fimbria). Gen Comp Endocrinol 225:212–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2015.07.015
Felip A, Zanuy S, Pineda R, Pinilla L, Carrillo M, Tena-Sempere M, Gómez A (2009) Evidence for two distinct KiSS genes in non-placental vertebrates that encode kisspeptins with different gonadotropin-releasing activities in fish and mammals. Mol Cell Endocrinol 312:61–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2008.11.017
Glasauer SM, Neuhauss SC (2014) Whole-genome duplication in teleost fishes and its evolutionary consequences. Mol Genet Genomics 289:1045–1060. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-014-0889-2
Hao J, Liu Q, Zhang X et al (2017) The evidence of apelin has the bidirectional effects on feeding regulation in Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii). Peptides 94:78–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2017.05.007
Kanda S, Akazome Y, Matsunaga T et al (2008) Identification of KiSS-1 product kisspeptin and steroid-sensitive sexually dimorphic kisspeptin neurons in medaka (Oryzias latipes). Endocrinology 149:2467–2476. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2007-1503
Khan MSI, Ohkubo T, Masuda N, Tachibana T, Ueda H (2009) Central administration of metastin increases food intake through opioid neurons in chicks. Com Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 153:209–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2009.02.013
Jin S, Sun D, Xi Q et al (2016) Identification of genes in the hypothalamus-pituitary-gonad axis in the brain of Amur sturgeons (Acipenser schrenckii) by comparative transcriptome analysis in relation to kisspeptin treatment. Gene 595(1):53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2016.09.026
Lawson EA, Olszewski PK, Weller A, Blevins JE (2020) The role of oxytocin in regulation of appetitive behaviour, body weight and glucose homeostasis. J Neuroendocrinol 32:e12805. https://doi.org/10.1111/jne.12805
Lee J-H, Miele ME, Hicks DJ, Phillips KK, Trent JM, Weissman BE, Welch DR (1996) KiSS-1, a novel human malignant melanoma metastasis-suppressor gene. J Natl Cancer Inst 88:1731–1737. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/88.23.1731
Lee YR, Tsunekawa K, Moon MJ et al (2009) Molecular evolution of multiple forms of kisspeptins and GPR54 receptors in vertebrates. Endocrinology 150:2837–2846. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2008-1679
Lenard NR, Berthoud HR (2008) Central and peripheral regulation of food intake and physical activity: pathways and genes. Obesity 16:S11–S22. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2008.511
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Luque RM, Kineman RD, Tena-Sempere M (2007) Regulation of hypothalamic expression of KiSS-1 and GPR54 genes by metabolic factors: analyses using mouse models and a cell line. Endocrinology 148:4601–4611. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2007-0500
McConn BR, Gilbert ER, Cline MA (2018) Appetite-associated responses to central neuropeptide Y injection in quail. Neuropeptides 69:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.npep.2018.03.001
Mechaly AS, Vinas J, Piferrer F (2011) Gene structure analysis of kisspeptin-2 (Kiss2) in the Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis): characterization of two splice variants of Kiss2, and novel evidence for metabolic regulation of kisspeptin signaling in non-mammalian species. Mol Cell Endocrinol 339:14–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2011.03.004
Mechaly Alejandro S, Bohórquez M, Mechaly Ariel E (2018) Evidence of alternative splicing as a regulatory mechanism for Kissr2 in pejerrey fish. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 9:604. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2018.00604
Muir AI, Chamberlain L, Elshourbagy NA et al (2001) AXOR12, a novel human G protein-coupled receptor, activated by the peptide KiSS-1. J Biol Chem 276:28969–28975. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M102743200
Ohga H, Selvaraj S, Matsuyama M (2018) The roles of kisspeptin system in the reproductive physiology of fish with special reference to chub mackerel studies as main axis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 4(9):147. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2018.00147
Onaka T, Takayanagi Y (2019) Role of oxytocin in the control of stress and food intake. J Neuroendocrinol 31:e12700. https://doi.org/10.1111/jne.12700
Osugi T, Ohtaki N, Sunakawa Y et al (2013) Molecular evolution of Kiss2 genes and peptides in vertebrates. Endocrinology 154:4270–4280. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2012-2267
Park JW, Kwon JY, Jin YH, Oh S-Y (2016) Effects of fasting on brain expression of Kiss2 and GnRH I and plasma levels of sex steroid hormones, in nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Ocean Polar Res 38:81–88. https://doi.org/10.4217/OPR.2016.38.1.081
Pasquier J, Lafont A-G, Rousseau K, Quérat B, Chemineau P, Dufour S (2014) Looking for the bird Kiss: evolutionary scenario in sauropsids. BMC Evol Biol 14:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-14-30
Pedroso JA, Wasinski F, Donato J Jr (2020) Prolonged fasting induces long-lasting metabolic consequences in mice. J Nutr Biochem 84:108457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108457
Sahin Z, Canpolat S, Ozcan M, Ozgocer T, Kelestimur H (2015) Kisspeptin antagonist prevents RF9-induced reproductive changes in female rats. Reproduction 149:465–473. https://doi.org/10.1530/REP-14-0683
Saito R, Tanaka K, Nishimura H et al (2019) Centrally administered kisspeptin suppresses feeding via nesfatin-1 and oxytocin in male rats. Peptides 112:114–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2018.12.003
Shi Y, Zhang Y, Li S et al (2010) Molecular identification of the Kiss2/Kiss1ra system and its potential function during 17alpha-methyltestosterone-induced sex reversal in the orange-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides. Biol Reprod 83:63–74. https://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod.109.080044
Somoza Gustavo M, Mechaly Alejandro S, Trudeau V (2020) Kisspeptin and GnRH interactions in the reproductive brain of teleosts. Gen Comp Endocrinol 298:113568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2020.113568
Terao Y, Kumano S, Takatsu Y, Hattori M, Nishimura A, Ohtaki T, Shintani Y (2004) Expression of KiSS-1, a metastasis suppressor gene, in trophoblast giant cells of the rat placenta. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) Gene Struct Express 1678: 102–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbaexp.2004.02.005
Tian Z, Xu S, Wang M et al (2020) Identification, tissue distribution, periprandial expression, and anorexigenic effect of spexin in Siberian sturgeon, acipenser baeri. Fish Physiol Biochem 46:2073–2084. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-020-00856-y
Um HN, Han JM, Hwang JI, Hong SI, Vaudry H, Seong JY (2010) Molecular coevolution of kisspeptins and their receptors from fish to mammals. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1200:67–74. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05508.x
Van Aerle R, Kille P, Lange A, Tyler C (2008) Evidence for the existence of a functional Kiss1/Kiss1 receptor pathway in fish. Peptides 29:57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2007.10.018
Volkoff H (2016) The neuroendocrine regulation of food intake in fish: a review of current knowledge. Front Neurosci 10:540. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2016.00540
Wahab F, Ullah F, Chan Y-M, Seminara SB, Shahab M (2011) Decrease in hypothalamic Kiss1 and Kiss1r expression: a potential mechanism for fasting-induced suppression of the HPG axis in the adult male rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta). Horm Metab Res 43:81–85. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1269852
West A, Vojta PJ, Welch DR, Weissman BE (1998) Chromosome localization and genomic structure of the KiSS-1 metastasis suppressor gene (KISS1). Genomics 54:145–148. https://doi.org/10.1006/geno.1998.5566
Yang Y, Gao J, Yuan C, Zhang Y, Guan Y, Wang Z (2016) Molecular identification of Kiss/GPR54 and function analysis with mRNA expression profiles exposure to 17α-ethinylestradiol in rare minnow Gobiocypris rarus. Mol Biol Rep 43:737–749. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-016-4014-y
Yuan D, Gao Y, Zhang X et al (2019) NPY and NPY receptors in the central control of feeding and interactions with CART and MC4R in Siberian sturgeon. Gen Comp Endocrinol 284:113239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2019.113239
Yuan D, Wang B, Tang T, Lei L, Zhou C, Li Z, Li L (2021) Characterization and evaluation of the tissue distribution of CRH, apelin, and GnRH2 reveal responses to feeding states in Schizothorax davidi. Fish Physiol Biochem 47:421–438. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-020-00922-5
Yue H-m, Ye H, Ruan R, Du H, Li C-j, Wei Q (2019) Feedback regulation of 17β-estradiol on two kisspeptin genes in the Dabry’s sturgeon (Acipenser dabryanus). Com Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2019.01.006
Zhan C (2018) POMC neurons: feeding, energy metabolism, and beyond. Adv Exp Med Biol 1090:17–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-1286-1_2
Zhang X, Wu Y, Hao J et al (2016) Intraperitoneal injection urocortin-3 reduces the food intake of Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii). Peptides 85:80–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2016.09.007
Zhang X, Tang N, Qi J et al (2017) CCK reduces the food intake mainly through CCK1R in Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii Brandt). Sci Rep 7:12413. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-12646-3
Zhang X, Gao Y, Tang N et al (2018a) One evidence of cocaine-and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) has the bidirectional effects on appetite in Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii). Fish Physiol Biochem 44:411–422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-017-0444-2
Zhang X, Wang S, Chen H et al (2018b) The inhibitory effect of NUCB2/nesfatin-1 on appetite regulation of Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii Brandt). Horm Behav 103:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2018.06.008
Zhou C, Lei L, Deng X et al (2019) Three forms of cocaine-and amphetamine-regulated transcript may be involved in food intake regulation in gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio). Fish Physiol Biochem 45:921–933. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-018-0596-8
Funding
This work was supported by the Opening Fund of Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province for Fishes Conservation and Utilization in the Upper Reaches of the Yangtze River (no. NJTCCJSYSYS03) and the Sichuan Science and Technology Program grants (no. 2019YJ0438).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SX and MW contributed equally to this work; they analyzed the data and wrote the paper. ZL, DC, JW, and HC conceived and designed the experiments; YL, SZ, YL, and NT performed the experiments; ZL contributed reagents, materials, and analysis tools. The draft manuscript was revised by ZL, NT, and XZ.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All animal handling procedures were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Sichuan Agricultural University and followed the guidelines of animal experiments on Sichuan Agricultural University.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
The people involved in the article agreed to publish it.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Shaoqi Xu and Mei Wang paid a similar a mount of work and carried out experiments and thesis writing
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, S., Wang, M., Li, Y. et al. Cloning and expression of kiss genes and regulation of feeding in Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii). Fish Physiol Biochem 48, 419–436 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-022-01055-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-022-01055-7