Abstract
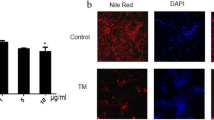
It has been extensively claimed that endoplasmic reticulum stress (ER stress) is related to lipid accumulation in mammals, but little is known in fish. This study aims at elucidating the role of ER stress in mediating lipid accumulation induced by monounsaturated oleic acid (OA) with a focus on the transcriptional level. We treated the adipocytes of grass carp with 200 μM and 400 μM OA, respectively, while the control group was treated with 2% bovine serum albumin (BSA). The results showed that cell viability was significantly improved, while 400 μM OA treatment promoted neutral lipid accumulation along with stimulating ER stress more obviously. Although lipolysis and fatty acid β-oxidation were activated simultaneously, the primary effect of OA seems to be promotion of lipid accumulation. To further explore whether ER stress affects lipid accumulation, 4-phenyl butyric acid (4-PBA), an effective inhibitor of ER stress, was used to pretreat the cells for 4 h. Unsurprisingly, it was found that the mRNA expressions of genes linked with ER stress were decreased. Intracellular triglyceride (TG) content was also decreased, which was in accordance with the mRNA expressions of adipogenic and lipogenic transcription factors as well as their target genes. Collectively, our data shows that ER stress may take part in OA-induced lipid accumulation in adipocytes via activating adipogenesis and lipogenesis. Based on this, strategies for protecting ER could be used to alleviate excessive accumulation of lipid in grass carp adipose tissue.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bian C, Huang X, Hu Z, Ji S, Yang M, Ji H (2020) Glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella): synteny, structure, tissue distribution and expression in oleic acid (OA)-induced adipocytes and hepatocytes. Comp Biochem Physiol B: Biochem Mol Biol 241:110391
Bobrovnikova-Marjon E, Hatzivassiliou G, Grigoriadou C, Romero M, Cavener DR, Thompson CB, Diehl JA (2008) PERK-dependent regulation of lipogenesis during mouse mammary gland development and adipocyte differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105(42):16314–16319
Cao XF, Dai YJ, Liu MY, Yuan XY, Wang CC, Huang YY et al (2019) High-fat diet induces aberrant hepatic lipid secretion in blunt snout bream by activating endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated IRE1/XBP1 pathway. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids 1864(3):213–223
Fuentes, E., Fuentes, F., Vilahur, G., Badimon, L., & Palomo, I. (2013). Mechanisms of chronic state of inflammation as mediators that link obese adipose tissue and metabolic syndrome. Mediators of inflammation, 2013
Gregor, M. F. (2007). Adipocyte stress: the endoplasmic reticulum and metabolic disease. 48, 1905–1914
Huang X, Sun J, Bian C, Ji S, Ji H (2020) Perilipin 1-3 in grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idella: molecular characterization, gene structure, tissue distribution, and mRNA expression in DHA-induced lipid droplet formation in adipocytes. Fish Physiol Biochem 46(6):2311–2322
Janevski M, Ratnayake S, Siljanovski S, McGlynn MA, Cameron-Smith D, Lewandowski P (2012) Fructose containing sugars modulate mRNA of lipogenic genes ACC and FAS and protein levels of transcription factors ChREBP and SREBP1c with no effect on body weight or liver fat. Food Funct 3(2):141–149
Kammoun HL, Chabanon H, Hainault I, Luquet S, Magnan C, Koike T et al (2009) GRP78 expression inhibits insulin and ER stress-induced SREBP-1c activation and reduces hepatic steatosis in mice. J Clin Invest 119(5):1201–1215
Kang SU, Kim HJ, Kim DH, Han CH, Lee YS, Kim CH (2018) Nonthermal plasma treated solution inhibits adipocyte differentiation and lipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes via ER stress signal suppression. Sci Rep 8(1):1–12
Kim JY, Garcia-Carbonell R, Yamachika S, Zhao P, Dhar D, Loomba R et al (2018) ER stress drives lipogenesis and steatohepatitis via caspase-2 activation of S1P. Cell 175(1):133–145
Kliewer SA, Sundseth SS, Jones SA, Brown PJ, Wisely GB, Koble CS et al (1997) Fatty acids and eicosanoids regulate gene expression through direct interactions with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors α and γ. Proc Natl Acad Sci 94(9):4318–4323
Koc M, Mayerová V, Kračmerová J, Mairal A, Mališová L, Štich V et al (2015) Stress of endoplasmic reticulum modulates differentiation and lipogenesis of human adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 460(3):684–690
Ling SC, Wu K, Zhang DG, Luo Z (2019) Endoplasmic reticulum stress–mediated autophagy and apoptosis alleviate dietary fat-induced triglyceride accumulation in the intestine and in isolated intestinal epithelial cells of yellow catfish. J Nutr 149(10):1732–1741
Longo M, Zatterale F, Naderi J, Parrillo L, Formisano P, Raciti GA et al (2019) Adipose tissue dysfunction as determinant of obesity-associated metabolic complications. Int J Mol Sci 20(9):2358
Lowe CE, Dennis RJ, Obi U, O’rahilly S, Rochford JJ (2012) Investigating the involvement of the ATF6α pathway of the unfolded protein response in adipogenesis. Int J Obes 36(9):1248–1251
Malodobra-Mazur M, Cierzniak A, Dobosz T (2019) Oleic acid influences the adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 cells via DNA methylation and may predispose to obesity and obesity-related disorders. Lipids Health Dis 18(1):1–15
Prinz WA (2014) Bridging the gap: membrane contact sites in signaling, metabolism, and organelle dynamics. J Cell Biol 205(6):759–769
Regassa A, Kim WK (2013) Effects of oleic acid and chicken serum on the expression of adipogenic transcription factors and adipogenic differentiation in hen preadipocytes. Cell Biol Int 37(9):961–971
Rellmann, Y., Gronau, I., Hansen, U., & Dreier, R. (2019). 4-Phenylbutyric acid reduces endoplasmic reticulum stress in chondrocytes that is caused by loss of the protein disulfide isomerase ERp57. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity, 2019
Schweiger M, Schreiber R, Haemmerle G, Lass A, Fledelius C, Jacobsen P et al (2006) Adipose triglyceride lipase and hormone-sensitive lipase are the major enzymes in adipose tissue triacylglycerol catabolism. J Biol Chem 281(52):40236–40241
Sha H, He Y, Chen H, Wang C, Zenno A, Shi H et al (2009) The IRE1α-XBP1 pathway of the unfolded protein response is required for adipogenesis. Cell Metab 9(6):556–564
Shen WJ, Patel S, Yu Z, Jue D, Kraemer FB (2007) Effects of rosiglitazone and high fat diet on lipase/esterase expression in adipose tissue. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids 1771(2):177–184
Sicari D, Delaunay-Moisan A, Combettes L, Chevet E, Igbaria A (2020) A guide to assessing endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis and stress in mammalian systems. FEBS J 287(1):27–42
Song T, Kuang S (2019) Adipocyte dedifferentiation in health and diseases. Clin Sci 133(20):2107–2119
Song YF, Hogstrand C, Wei CC, Wu K, Pan YX, Luo Z (2017) Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and cAMP/PKA pathway mediated Zn-induced hepatic lipolysis. Environ Pollut 228:256–264
Song YF, Huang C, Shi X, Pan YX, Liu X, Luo Z (2016) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and dysregulation of calcium homeostasis mediate cu-induced alteration in hepatic lipid metabolism of javelin goby Synechogobius hasta. Aquat Toxicol 175:20–29
Stevenson J, Huang EY, Olzmann JA (2016) Endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation and lipid homeostasis. Annu Rev Nutr 36:511–542
Sun J, Xiao PZ, Chang ZG, Ji H, Du ZY, Chen LQ (2017) Forkhead box O1 in grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idella: molecular characterization, gene structure, tissue distribution and mRNA expression in insulin-inhibited adipocyte lipolysis. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 204:76–84
Tontonoz P, Hu E, Graves RA, Budavari AI, Spiegelman BM (1994) mPPAR gamma 2: tissue-specific regulator of an adipocyte enhancer. Genes Dev 8(10):1224–1234
Wilfling F, Wang H, Haas JT, Krahmer N, Gould TJ, Uchida A et al (2013) Triacylglycerol synthesis enzymes mediate lipid droplet growth by relocalizing from the ER to lipid droplets. Dev Cell 24(4):384–399
Zeng X, Zhu M, Liu X, Chen X, Yuan Y, Li L et al (2020) Oleic acid ameliorates palmitic acid induced hepatocellular lipotoxicity by inhibition of ER stress and pyroptosis. Nutrition & metabolism 17(1):1–14
Zhao T, Wu K, Hogstrand C, Xu YH, Chen GH, Wei CC, Luo Z (2020) Lipophagy mediated carbohydrate-induced changes of lipid metabolism via oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and ChREBP/PPARγ pathways. Cell Mol Life Sci 77(10):1987–2003
Availability of data and material
The datasets and materials used in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Funding
The study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (31772863, 32072989, and 32002403).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Chenchen Bian: contributed to the conception and designed of the study, wrote original draft. Jian Sun: data curation and revised the manuscript. Xiaocheng Huang: investigation and revised the manuscript. Shanghong Ji: methodology and revised the manuscript. Hong Ji: project administration and revised the manuscript. All authors contributed to interpreting the results, and read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
We promised that all procedures of the experiment were performed in accordance with the Guide for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and approved by the Northwest A&F University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
This study was supported by College of Animal Science and Technology, Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University. The authors disclose no conflicts of interest. All authors listed have approved to submit to your journal.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 150 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bian, C., Sun, J., Huang, X. et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress is involved in lipid accumulation induced by oleic acid in adipocytes of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella): focusing on the transcriptional level. Fish Physiol Biochem 48, 275–284 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-021-01031-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-021-01031-7