Abstract
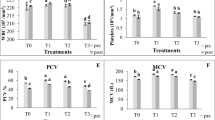
The present study aims to delineate the effect of exogenous enzyme supplementation of fermented or non-fermented de-oiled rice bran (DORB) on haematology, histology and expression of IGF I gene expression of Labeo rohita. Four test diets, namely, T1 (DORB), T2 (fermented DORB), T3 (DORB+exogenous enzyme) and T4 (fermented DORB+exogenous enzyme) were formulated and fed to the L. rohita for a period of 60 days. The test diets T3 and T4 were supplemented with 0.1 g kg-1 xylanase (16,000 U kg−1) and 0.1 g kg-1 phytase (500 U kg−1) enzymes. A total of 120 juveniles of L. rohita (average weight 5.01 ± 0.02 g) were stocked in 12 rectangular tanks with 10 fish per tank in triplicates. At the end of the experiment, haematology, histology and IGF I gene expression of the different groups were analysed. The haemoglobin (Hb) content, RBC count and WBC count of L. rohita varied significantly (p < 0.05) among different groups. T3 diet–fed group had the highest Hb content, RBC count and WBC count as compared to the other groups. The MCV content was significantly (p < 0.05) lower in T3 group. The DORB type, exogenous enzyme supplementation and their interaction have no significant (p > 0.05) effect on MCH, MCHC and lymphocyte content of the cultured fish. The group which were fed T3 diet had significantly (p < 0.05) higher IGF-I gene expression as compared to other groups. The histological examination of liver revealed no pathological alteration of this organ. Similarly, there were no pathological changes observed in intestinal tissue in any dietary treatment group. Based on the findings of the present study, it is concluded that exogenous enzyme supplementation of DORB-based diets improves the physiological status and growth performances of Labeo rohita.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Adeola O, Cowieson AJ (2011) Opportunities and challenges in using exogenous enzymes to improve non-ruminant animal production. J Anim Sci 89:3189–3218
Adeoye A, Jaramillo-Torres A, Fox S, Merrifield D, Davies S (2016) Supplementation of formulated diets for tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) with selected exogenous enzymes: Overall performance and effects on intestinal histology and microbiota. Anim Feed Sci Technol 215:133–143
Ai Q, Mai K, Zhang W, Xu W, Tan B, Zhang C, Li H (2007) Effects of exogenous enzymes (phytase, non-starch polysaccharide enzyme) in diets on growth, feed utilization, nitrogen and phosphorus excretion of Japanese seabass, Lateolabrax japonicus. Comp Biochem Physiol 147(2):502–508
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, Washigton DC, 20th Edition, pp. 1220
Caballero M, Izquierdo M, Kjørsvik E, Montero D, Socorro J, Fernández A, Rosenlund G (2003) Morphological aspects of intestinal cells from gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) fed diets containing different lipid sources. Aquaculture 225:325–340
Cao L, Wang W, Yang C, Yang Y, Diana J, Yakupitiyage A, Luo Z, Li D (2007) Application of microbial phytase in fish feed. Enzym Microb Technol 40:497–507
Cao Y, Chen X, Wang S, Chen XC, Wang YX, Chang JP, Du JZ (2009) Growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor of naked carp (Gymnocypris przewalskii) in Lake Qinghai: expression in different water environments. Gen Comp Endocrinol 161:400–406
Cruz EMV, Brown CL, Luckenbach JA, Picha ME, Bolivar RB, Borski RJ (2006) Insulin-like growth factor-I cDNA cloning, gene expression and potential use as a growth rate indicator in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Aquaculture 251(2):585–595
Dawood MAO, Mohsen M, El-dakar A, Abdelraouf E, Moustafa ME, Ahmed HA (2019) Effectiveness of exogenous digestive enzymes supplementation on the performance of rabbitfish (Siganus rivulatus). Slov Vet Res 56:409–419
Duan C (1998) Nutritional and developmental regulation of insulin like growth factors in fish. J Nutr 128:306S–314S
Dyer AR, Barlow CG, Bransden MP, Carter CG, Glencross BD, Richardson N, Thomas PM, Williams KC, Carragher JF (2004) Correlation of plasma IGF-I concentrations and growth rate in aquacultured finfish: a tool for assessing the potential of new diets. Aquaculture 236:583–592
Ehsani M, Torki M (2010) Effects of dietary inclusion of guar meal supplemented by β-mannanase on performance of laying hens, egg quality characteristics and diacritical counts of white blood cells. Am J Anim Vet Sci 5(4):237–243
Francis G, Makkar HP, Becker K (2001) Antinutritional factors present in plant-derived alternate fish feed ingredients and their effects in fish. Aquaculture 199(3-4):197–227
Hemre GI, Waagbø R, Hjeltnes B, Aksnes A (1996) Effect of gelatinized wheat and maize in diets for large Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) on glycogen retention, plasma glucose and fish health. Aquac Nutr 2(1):33–39
Houston AH (1997) Are the classical hematological variables acceptable indicators of fish health? Trans Am Fish Soc 126:879–894
Jahanbakhshi A, Imanpoor MR, Taghizadeh V, Shabani A (2013) Hematological and serum biochemical indices changes induced by replacing fish meal with plant protein (sesame oil cake and corn gluten) in the Great sturgeon (Huso huso). Comp Clin Pathol 22:1087–1092
Jiang N, Tan NS, Ho B, Ding JL (2007) Respiratory protein-generated reactive oxygen species as an antimicrobial strategy. Nat Immun 8:1114–1122
Jones JI, Clemmons DR (1995) Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins: biological actions. Endocr Rev 16(1):3–34
Kumar V, Sinha A, Makkar H, De Boeck G, Becker K (2012) Phytate and phytase in fish nutrition. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr 96:335–364
Kumar S, Sahu NP, Gupta S, Deo AD, Shamna N, Ranjan A (2017) Inclusion level of Deoiled Rice Bran (DORB) in the diet of Labeo rohita (Hamilton, 1882) Fingerlings: effect on growth and gene expression of IGF-I and IGF-II. Aquaculture 481:211–217
Kumar S, Sahu NP, Shamna N, Ranjan A (2018a) Feeding higher level of de-oiled rice bran causes stress to Labeo rohita fingerlings. Aquaculture 484:184–190
Kumar S, Sahu NP, Ranjan A (2018b) Feeding de-oiled rice bran (DORB) to Rohu, Labeo rohita: effect of varying dietary protein and lipid level on growth, body composition, and insulin like growth factor (IGF) expression. Aquaculture 492:59–66
Kumar S, Sahu NP, Ranjan A, Gupta S, Sardar P, Kumar M, Gupta G (2019) Optimization of de-oiled rice bran inclusion level in the diet of Labeo rohita: effect on growth performance, nutrient utilization, insulin-like growth factors I and II gene expression. Aquac Nutr 25:477–485. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12873
Lin S, Mai K, Tan B (2007) Effects of exogenous enzyme supplementation in diets on growth and feed utilization in tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus x O. aureus. Aquac Res 38:1645–1653
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using realtime quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Mutch DM, Wahli W, Williamson G (2005) Nutrigenomics and nutrigenetics: the emerging faces of nutrition. FASEB J 19:1602–1616
NRC (National Research Council) (1993) Nutrient Requirements of Fish. National Academic Press, Washington DC, p 114
Ramakrishna R, Shipton TA, Hasan MR (2013) Feeding and feed management of Indian major carps in Andhra Pradesh, India. In: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper No. 578. FAO, Rome, p 90
Rambhaskar B, Srinivasa Rao K (1986) Comparative haematology of ten species of marine fish from Visakhapatnam Coast. J Fish Biol 30:59–66
Ramos LR, Pedrosa VF, Mori A, Andrade CFD, Romano LA, Abreu PC, Tesser MB (2017) Exogenous enzyme complex prevents intestinal soybean meal-induced enteritis in Mugil liza (Valenciennes, 1836) juvenile. An Acad Bras Cienc 89(1):341–353
Ranjan A, Sahu NP, Deo AD, Kumar HS, Kumar S, Jain KK (2017) Xylanase and phytase supplementation in the de-oiled rice bran (DORB) based diet improves the growth performance of Labeo rohita. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 6(6):1493–1503
Ranjan A, Sahu NP, Deo AD, Kumar HS, Kumar S, Jain KK (2018a) Comparative evaluation of fermented and non-fermented de-oiled rice bran with or without exogenous enzymes supplementation in the diet of Labeo rohita (Hamilton, 1822). Fish Physiol Biochem 44:1037–1049
Ranjan A, Sahu NP, Deo AD, Kumar S (2018b) Comparative growth performance, in vivo digestibility and enzyme activities of Labeo rohita fed with DORB based formulated diet and commercial carp feed. Turk J Fish Aquat Sci 18(9):1025–1036
Ranjan A, Sahu NP, Deo AD, Kumar S (2019) Solid state fermentation of de-oiled rice bran: Effect on in vitro protein digestibility, fatty acid profile and anti-nutritional factors. Food Res Int 119:1–5
Roberts RJ, Rodger HD (2012) The pathophysiology and systematic pathology of teleosts. Fish pathology 62–143.
Shah SL, Altindağ A (2004) Hematological parameters of tench (Tinca tinca L.) after acute and chronic exposure to lethal and sublethal mercury treatments. Bull Environ Contam. Toxicol 73:911–918
Uchida K, Kajimura S, Riley LG, Hirano T, Aida K, Grau EG (2003) Effects of fasting on growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor I axis in the tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus. Comp Biochem Physiol 134A:429–439
Wilson R, Taylor E (1993) The physiological responses of freshwater rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, during acutely lethal copper exposure. J Comp Physiol 163(B):38–47
Wood AW, Duan C, Bern HA (2005) Insulin-like growth factor signalling in fish. Int Rev Cytol 243:215–285
Zamini A, Kanani HG, azam Esmaeili A, Ramezani S, Zoriezahra SJ (2014) Effects of two dietary exogenous multi-enzyme supplementation, Natuzyme® and beta-mannanase (Hemicell®), on growth and blood parameters of Caspian salmon (Salmo trutta caspius). Comp Clin Pathol 23:187–192
Zhou X, Li M, Abbas K, Wang W (2009) Comparison of haematology and serum biochemistry of cultured and wild Dojo loach Misgurnus anguillicaudatus. Fish Physiol Biochem 35:435–441
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Director, ICAR-Central Institute of Fisheries Education, Mumbai, for providing all the required facilities and infrastructure to carry out this research. The authors sincerely acknowledge the support of Vaighai Agro Products Limited, Tamil Nadu, for supplying DORB and AB Vista, India, for arranging enzymes free of cost for the successful completion of this research work. The financial support provided by ICAR-Central Institute of Fisheries Education, Mumbai, for successful completion of this research work is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Amit Ranjan performed the experiment, collected and analysed data and written the draft of the manuscript. Sarvendra Kumar has performed the gene expression study and analysis. Narottam Prasad Sahu has supervised the first author, designed the experiment and corrected the draft of the manuscript. Kamal Kant Jain has helped in the analysis and correction of the draft of the manuscript. Ashutosh Dharmendra Deo has helped in the analysis and interpretation of data and correction of the draft of the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ranjan, A., Kumar, S., Sahu, N.P. et al. Exogenous phytase and xylanase supplementation of formulated diets for rohu (Labeo rohita): impact on haematology, histology and IGF I gene expression. Fish Physiol Biochem 47, 49–58 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-020-00893-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-020-00893-7