Abstract
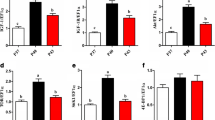
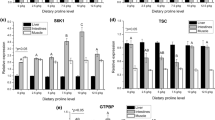
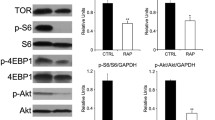
Commonly used aquatic feed naturally contains low-level or no hydroxyproline (Hyp). This study was conducted to evaluate the effects of dietary Hyp inclusion on growth performance, body composition, amino acid profiles, blood biochemistry, and the expression of target of rapamycin (TOR) pathway-related genes in juvenile Nibea diacanthus. Fish with similar size (initial body weight, 133.00 ± 2.14 g) were fed six isonitrogenous and isolipidic practical diets supplemented with graded levels of Hyp (0, 5, 10, 15, 20, and 25 g kg−1 of dry matter) for 8 weeks. The results indicated that growth performance and feed utilization were improved with increased levels of dietary Hyp (P < 0.05), and the optimum amount of dietary Hyp estimated from SGR as 16.6 g kg−1. The crude protein of whole body and swim bladder and the amino acid composition of muscle and swim bladder were significantly (P < 0.05) affected by the addition of dietary Hyp, which reflects the important role of feed composition in animal body composition. In addition, the expression levels of mammalian target of rapamycin (TOR) and ribosomal protein S6 kinase1 (S6K1) genes in the liver, muscle, and swim bladder increased with increasing Hyp content of diets, while the mRNA expression level of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein (4E-BP) gene in these tissues decreased. These results indicated that Hyp improved fish growth and the ability to synthesize proteins, most likely through the TOR pathway. It is suggested that dietary Hyp supplementation is particularly necessary for application in aquatic feed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksnes A, Mundheim H, Toppe J, Albrektsen S (2008) The effect of dietary hydroxyproline supplementation on salmon (Salmo salar L.) fed high plant protein diets. Aquaculture 275:242–249
Alam S, Watanabe WO, Carroll PM (2008) Dietary protein requirements of juvenile black sea bass (Centroperistis striata). J World Aquacult Soc 39:656–663
Albrektsen S, Sirnes E, Aksnes A, Hagen Ø (2010) Impacts of dietary hydroxyproline on growth, muscle firmness, collagen and PYD cross-links formation in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Program and Abstracts of the 14th international symposium on fish nutrition and feeding. P. 79
Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC) (1995) Official methods of analysis of Official Analytical Chemists International, 16th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington
Ban H, Shigemitsu K, Yamatsuji T, Haisa M, Haisa M, Takaoka M, Nobuhisa T, Gunduz M, Tanaka N, Naomoto Y (2004) Arginine and leucine regulate p70 S6 kinase and 4E-BP1 in intestinal epithelial cells. Int J Mol Med 13:537–543
Bulbul M, Kader MA, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Yokoyama S (2014) Effect of replacing fishmeal with canola meal on growth and nutrient utilization in kuruma shrimp Marsupenaeus japonicus (Bate). Aquac Res 45:848–858
Chen HD, Zheng JH, Shen ZK (2011) Technique for artificial breeding of spotted drum N. diacanthus. Fish Sci 30:501–504 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen GF, Feng L, Kuang SY, Liu Y, Jiang J, Hu K, Jiang WD, Li SH, Tang L, Zhou XQ (2012) Effect of dietary arginine on growth, intestinal enzyme activities and gene expression in muscle, hepatopancreas and intestine of juvenile Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var. Jian). Br J Nutr 108:195–207
Deng JM, Chen LQ, Mai KS, Mi HF, Zhang L (2017) Effects of replacing soybean meal with rubber seed meal on digestive enzyme activity, nutrient digestibility and retention in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus×Oreochromis aureus). Aquac Res 48:1767–1777
Gunasekera RM, Shim KF, Lam TJ (1997) Influence of dietary protein content on the distribution of amino acids in oocytes, serum and muscle of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.). Aquaculture 152:205–221
He Y, Chi S, Tan B, Dong X, Yang Q, Liu H, Zhang S, Han F, Liu D (2019) dl-Methionine supplementation in a low-fishmeal diet affects the TOR/S6K pathway by stimulating ASCT2 amino acid transporter and insulin-like growth factor-I in the dorsal muscle of juvenile cobia (Rachycentron canadum). Br J Nutr 122(7):734–744
Holz MK, Ballif BA, Gygi SP, Blenis J (2005) mTOR and S6K1 mediate assembly of the translation preinitiation complex through dynamic protein interchange and ordered phosphorylation events. Cell 123:569–580
Hou YQ, Wu G (2017) Nutritionally nonessential amino acids: a misnomer in nutritional sciences. Adv Nutr 8:137–139
Li P, Wu GY (2018) Roles of dietary glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline in collagen synthesis and animal growth. Amino Acids 50:29–38
Li P, Mai KS, Trushenski J, Wu GY (2009) New developments in fish amino acid nutrition: towards functional and environmentally oriented aquafeeds. Amino Acids 37:43–53
Li X, Wu X, Dong Y, Gao Y, Yao W, Zhou Z (2019) Effects of dietary lysine levels on growth, feed utilization and related gene expression of juvenile hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus♀× Epinephelus lanceolatus♂). Aquaculture 502:153–161
Liang H, Ren M, Habte-Tsion HM, Ge X, Xie J, Mi H, Xi B, Miao LH, Liu B, Zhou QL, Fang W (2016) Dietary arginine affects growth performance, plasma amino acid contents and gene expressions of the TOR signaling pathway in juvenile blunt snout bream, Megalobrama amblycephala. Aquaculture 461:1–8
Liang H, Mokrani A, Chisomo-Kasiya H, Ji K, Ge X, Ren M, Liu B, Xi B, Sun A (2019) Dietary leucine affects glucose metabolism and lipogenesis involved in TOR/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway for juvenile blunt snout bream Megalobrama amblycephala. Fish Physiol Biochem 45(2):719–732
Liao XH, Majithia A, Huang XL, Kimmel AR (2008) Growth control via TOR kinase signaling, an intracellular sensor of amino acids and energy availability, with crosstalk potential to proline metabolism. Amino Acids 35:761–770
Liu YZ, He G, Wang QC, Mai KS, Xu W, Zhou HH (2014) Hydroxyproline supplementation on the performances of high plant protein source based diets in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Aquaculture 433:476–480
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using realtime quantitative PCR and the 2(-ΔΔC(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Manor ML, Cleveland BM, Weber GM, Brett-Kenney P (2015) Effects of sexual maturation and feeding level on fatty acid metabolism gene expression in muscle, liver, and visceral adipose tissue of diploid and triploid rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B 179:17–26
Marine L, Stephane P, Elisabeth PJ, Karine D, Iban S, Sandrine SC (2011) L-leucine, L-methionine, and L-lysine are involved in the regulation of intermediary metabolism-related gene expression in rainbow trout hepatocytes. J Nutr 141:75–80
National Research Council (NRC) (2011) Nutrient requirement of fish and shrimp. National Academy Press, Washington, DC
Phang JM, Donald SP, Pandhare J, Liu YM (2008) The metabolism of proline, a stress substrate, modulates carcinogenic pathways. Amino Acids 35:681–690
Rong H, Zhang YL, Hao ML, Zou WG, Yu J, Yu CQ, Shi QC, Wen XB (2019) Effects of dietary hydroxyproline on collagen metabolism, proline 4-hydroxylase activity, and expression of related gene in swim bladder of juvenile Nibea diacanthus. Fish Physiol Biochem 45(6):1779–1790
Rong H, Zhang YL, Hao ML, Lin F, Zou WG, Zhang HR, Yu CQ, Yu J, Shi QC, Aweya JJ, Wen XB (2020) Effect of hydroxyproline supplementation on growth performance, body composition, amino acid profiles, blood-biochemistry and collagen synthesis of juvenile chu’s croaker (Nibea coibor). Aquac Res 51(3):1264–1275
Sanchez-Lozano NB, Martinez-Llorens S, Tomas-Vidal A, Cerda MJ (2011) Amino acid retention of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata, L.) fed with pea protein concentrate. Aquac Nutr 17:604–614
Seiliez I, Gabillard JC, Skiba-Cassy S, Garcia-Serrana D, Gutiérrez J, Kaushik S, Panserat S, Tesseraud S (2008) An in vivo and in vitro assessment of TOR signaling cascade in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Am J Phys Regul Integr Comp Phys 295:329–335
Silvia ML, Rosa BA, Silvia NM, Miguel JC, Ana TV (2012) Carob seed meal as a partial substitute in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) diets: amino acid retention, digestibility, gut and liver histology. Aquaculture 338–341:124–133
Tang L, Feng L, Sun CY, Chen GF, Jiang WD, Hu K, Liu Y, Jiang J, Li SH, Kuang SY, Zhou XQ (2013) Effect of tryptophan on growth, intestinal enzyme activities and TOR gene expression in juvenile Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var. Jian): Studies in vivo and in vitro. Aquaculture 412:23–33
Unnikrishnan U, Paulraj R (2010) Dietary protein requirement of giant mud crab (Scylla serrata) juveniles fed iso-energetic formulated diets having graded protein levels. Aquac Res 41:278–294
Wei ZH, Ma J, Pan XY, Mu H, Li J, Shentu J, Zhang WB, Mai KS (2016) Dietary hydroxyproline improves the growth and muscle quality of large yellow croaker Larimichthys crocea. Aquaculture 464:497–504
Wu GY (2013) Functional amino acids in nutrition and health. Amino Acids 45:407–411
Wu GY (2014) Dietary requirements of synthesizable amino acids by animals: a paradigm shift in protein nutrition. Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology 5(1):34
Wullschleger SS, Loewith RR, Hall MM (2006) TOR signaling in growth and metabolism. Cell 124:471–484
Zhang KK, Ai QH, Mai KS, Xu W, Liufu ZG, Zhang YJ, Peng M (2013) Effects of dietary hydroxyproline on growth performance, body composition, hydroxyproline and collagen concentrations in tissues in relation to prolyl 4-hydroxylase α(I) gene expression of juvenile turbot, Scophthalmus maximus L. fed high plant protein diets. Aquaculture 404:77–84
Zhang KK, Mai KS, Xu W, Zhou HH, Liufu ZG, Zhang YJ, Peng M, Ai QH (2015) Proline with or without hydroxyproline influences collagen concentration and regulates prolyl 4-hydroxylase α (I) Gene expression in juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). J Ocean Univ China 14:541–548
Zhou Z, Wang X, Wu X, Gao Y, Li X, Dong Y, Yao W (2019) Effects of dietary leucine levels on growth, feed utilization, neuro-endocrine growth axis and TOR-related signaling genes expression of juvenile hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus♀× Epinephelus lanceolatus♂). Aquaculture 504:172–181
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Zhuangping Expert Workstation and all our laboratory members for technical advice and valuable help during the feeding trial and sample analysis.
Funding
This research was supported by Grant No. A201005D06-1 from China Guangdong Oceanic and Fishery Science and Technology Foundation, Grant No. 2016ZR14 from Natural Science Youth Research Foundation of Yunnan Agricultural University, and Grant No. 2018FG001-044 and 2017FG001-021 from Yunnan Province Agricultural Basic Research Joint Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed by the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rong, H., Lin, F., Zhang, Y. et al. The TOR pathway participates in the regulation of growth development in juvenile spotted drum (Nibea diacanthus) under different dietary hydroxyproline supplementation. Fish Physiol Biochem 46, 2085–2099 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-020-00863-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-020-00863-z