Abstract
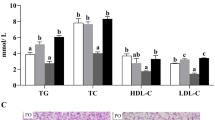
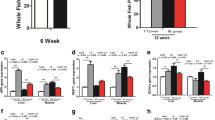
Many metabolic diseases in fish are often associated with lowered peroxisomal fatty acid (FA) β-oxidation. However, the physiological role of peroxisomal FA oxidation in lipid metabolism in fish still remains unclear. In the present study, a specific peroxisomal FA β-oxidation inhibitor, 10,12-tricosadiynoic acid (TDYA), was used to investigate the effects of impaired peroxisomal β-oxidation on growth performance, health status, and lipid metabolism in Nile tilapia. The results showed that the dietary TDYA treatment did not affect weight gain, but significantly decreased peroxisomal β-oxidation in the liver, and increased body fat accumulation. The fish with impaired peroxisomal β-oxidation exhibited higher contents of serum lipid and peroxidation products, and alanine aminotransferase activity, and significantly lowered hepatic activities of superoxide dismutase and catalase. The inhibited peroxisomal β-oxidation did not enhance mitochondrial β-oxidation activity, but compensatorily upregulated FA β-oxidation-related gene expression, and downregulated the gene expressions in lipolysis and lipogenesis. Taken together, TDYA treatment markedly induced lipid accumulation and hepatic oxidative damage via systemically depressing lipid catabolism and antioxidant capacity. Our findings reveal the pivotal roles of peroxisomal β-oxidation in maintaining health and lipid homeostasis in fish, and could be helpful in understanding metabolic diseases in fish.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cipolla CM, Lodhi IJ (2017) Peroxisomal dysfunction in age-related diseases. Trends Endocrinol Metab 28:297–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2016.12.003
Córdoba J, O’Riordan K, Dupuis J, Borensztajn J, Blei AT (1998) Diurnal variation of serum alanine transaminase activity in chronic liver disease. Hepatology 28:1724–1725. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.510280640
Crockett EL, Sidell BD (1993) Peroxisomal β–oxidation is a significant pathway for catabolism of fatty acids in a marine teleost. Am J Phys 264:R1004–R1009. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.1993.264.5.R1004
Du ZY, Demizieux L, Degrace P, Gresti J, Moindrot B, Liu YJ, Tian LX, Cao JM, Clouet P (2004) Alteration of 20:5n-3 and 22:6n-3 fat contents and liver peroxisomal activities in fenofibrate-treated rainbow trout. Lipids 39:849–855. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-004-1306-3
Du ZY, Clouet P, Zheng WH, Degrace P, Tian LX, Liu YJ (2006) Biochemical hepatic alterations and body lipid composition in the herbivorous grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) fed high-fat diets. Br J Nutr 95:905–915. https://doi.org/10.1079/BJN20061733
Du ZY, Clouet P, Degrace P, Zheng WH, Frøyland L, Tian LX, Liu YJ (2008a) Hypolipidaemic effects of fenofibrate and fasting in the herbivorous grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) fed a high-fat diet. Br J Nutr 100:1200–1212. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114508986840
Du ZY, Clouet P, Huang LM, Degrace P, Zheng WH, He JG, Tian LX, Liu YJ (2008b) Utilization of different dietary lipid sources at high level in herbivorous grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella): mechanism related to hepatic fatty acid oxidation. Aquac Nutr 14:77–92. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2095.2007.00507.x
Du ZY, Ma T, Liaset B, Keenan AH, Araujo P, Lock EJ, Demizieux L, Degrace P, Frøyland L, Kristiansen K, Madsen L (2013) Dietary eicosapentaenoic acid supplementation accentuates hepatic triglyceride accumulation in mice with impaired fatty acid oxidation capacity. Biochim Biophys Acta 1831:291–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2012.10.002
Guyon R, Rakotomanga M, Azzouzi N, Coutanceau JP, Bonillo C, D’Cotta H, Pepey E, Soler L, Rodier-Goud M, D’Hont A, Conte MA, van Bers NEM, Penman DJ, Hitte C, Crooijmans RPMA, Kocher TD, Ozouf-Costaz C, Baroiller JF, Galibert F (2012) A high-resolution map of the Nile tilapia genome: a resource for studying cichlids and other percomorphs. BMC Genomics 13:222. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-222
Han SL, Wang J, Zhang YX, Qiao F, Chen LQ, Zhang ML, Du ZY (2019) Inhibited autophagy impairs systemic nutrient metabolism in Nile tilapia. Comp Biochem Physiol Part A Mol Integr Physiol 236:110521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2019.06.021
Huang JS, Jia YZ, Fu T, Viswakarma N, Bai L, Rao MS, Zhu YJ, Borensztajn J, Reddy JK (2011a) Sustained activation of PPARα by endogenous ligands increases hepatic fatty acid oxidation and prevents obesity in ob/ob mice. FASEB J 26:628–638. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.11-194019
Huang JS, Viswakarma N, Yu ST, Jia YZ, Bai L, Vluggens A, Cherkaoui-Malki M, Khan M, Singh I, Yang G, Rao MS, Borensztajn J, Reddy JK (2011b) Progressive endoplasmic reticulum stress contributes to hepatocarcinogenesis in fatty acyl-coa oxidase 1–deficient mice. Am J Pathol 179:703–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.04.030
Hwang I, Lee J, Huh JY, Park J, Lee HB, Ho YS, Ha H (2012) Catalase deficiency accelerates diabetic renal injury through peroxisomal dysfunction. Diabetes 61:728–738. https://doi.org/10.2337/db11-0584
Kim S, Sohn I, Ahn JI, Lee KH, Lee YS, Lee YS (2004) Hepatic gene expression profiles in a long-term high-fat diet-induced obesity mouse model. Gene 340:99–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2004.06.015
Kim WR, Flamm SL, Di Bisceglie AM, Bodenheimer HC (2008) Serum activity of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) as an indicator of health and disease. Hepatology 47:1363–1370. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.22109
Koepke JI, Nakrieko KA, Wood CS, Boucher KK, Terlecky LJ, Walton PA, Terlecky SR (2007) Restoration of peroxisomal catalase import in a model of human cellular aging. Traffic 8:1590–1600. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0854.2007.00633.x
Kreeft AJ, Moen CJA, Porter G, Kasanmoentalib S, Sverdlov R, van Gorp PJ, Havekes LM, Frants RR, Hofker MH (2005) Genomic analysis of the response of mouse models to high-fat feeding shows a major role of nuclear receptors in the simultaneous regulation of lipid and inflammatory genes. Atherosclerosis 182:249–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2005.01.049
Lee CH, Olson P, Evans RM (2003) Minireview: lipid metabolism, metabolic diseases, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Endocrinology 144:2201–2207. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2003-0288
Li JM, Li LY, Qin X, Degrace P, Demizieux L, Limbu SM, Wang X, Zhang ML, Li DL, Du ZY (2018) Inhibited carnitine synthesis causes systemic alteration of nutrient metabolism in zebrafish. Front Physiol 9:509–509. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.00509
Li JM, Li LY, Zhang YX, Jiang ZY, Limbu SM, Qiao F, Degrace P, Chen LQ, Zhang ML, Du ZY (2019) Functional differences between L- and D-carnitine in metabolic regulation evaluated using a low-carnitine Nile tilapia model. Br J Nutr 122:625–638. https://doi.org/10.1017/S000711451900148X
Lin D, Mao YQ, Cai FS (1990) Nutritional lipid liver disease of grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idullus (C. et V.). Chin J Oceanol Limnol 8:363–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02849682
Liu Y, Wen JJ, Ning LJ, Jiao JG, Qiao F, Chen LQ, Zhang ML, Du ZY (2019) Comparison of effects of dietary-specific fatty acids on growth and lipid metabolism in Nile tilapia. Aquac Nutr 25:862–872. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12906
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lu KL, Xu WN, Li XF, Liu WB, Wang LN, Zhang CN (2013) Hepatic triacylglycerol secretion, lipid transport and tissue lipid uptake in blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) fed high-fat diet. Aquaculture 408-409:160–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2013.06.003
Lu KL, Xu WN, Wang LN, Zhang DD, Zhang CN, Liu WB (2014) Hepatic β-oxidation and regulation of carnitine palmitoyltransferase (CPT) I in blunt snout bream Megalobrama amblycephala fed a high fat diet. PLoS One 9:e93135. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0093135
Montagner A, Polizzi A, Fouché E, Ducheix S, Lippi Y, Lasserre F, Barquissau V, Régnier M, Lukowicz C, Benhamed F, Iroz A, Bertrand-Michel J, Al Saati T, Cano P, Mselli-Lakhal L, Mithieux G, Rajas F, Lagarrigue S, Pineau T, Loiseau N, Postic C, Langin D, Wahli W, Guillou H (2016) Liver PPARα is crucial for whole-body fatty acid homeostasis and is protective against NAFLD. Gut 65:1202–1214. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2015-310798
Moyes CD, Buck LT, Hochachka PW (1990) Mitochondrial and peroxisomal fatty acid oxidation in elasmobranchs. Am J Phys 258:R756–R762. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.1990.258.3.R756
Muoio DM, Neufer PD (2012) Lipid-induced mitochondrial stress and insulin action in muscle. Cell Metab 15:595–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2012.04.010
Ning LJ, He AY, Li JM, Lu DL, Jiao JG, Li LY, Li DL, Zhang ML, Chen LQ, Du ZY (2016) Mechanisms and metabolic regulation of PPARα activation in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Biochim Biophys Acta 1861:1036–1048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2016.06.005
Nordgren M, Fransen M (2014) Peroxisomal metabolism and oxidative stress. Biochimie 98:56–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2013.07.026
Pan H, Li LY, Li JM, Wang WL, Limbu SM, Degrace P, Li DL, Du ZY (2017) Inhibited fatty acid β-oxidation impairs stress resistance ability in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol 68:500–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2017.07.058
Pascual-Ahuir A, Manzanares-Estreder S, Proft M (2017) Pro- and antioxidant functions of the peroxisome-mitochondria connection and its impact on aging and disease. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2017:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9860841
Poirier Y, Antonenkov VD, Glumoff T, Hiltunen JK (2006) Peroxisomal β-oxidation--a metabolic pathway with multiple functions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1763:1413–1426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.08.034
Raas Q, Saih FE, Gondcaille C, Trompier D, Hamon Y, Leoni V, Caccia C, Nasser B, Jadot M, Ménétrier F, Lizard G, Cherkaoui-Malki M, Andreoletti P, Savary S (2019) A microglial cell model for acyl-CoA oxidase 1 deficiency. Biochim Biophys Acta 1864:567–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2018.10.005
Veerkamp JH, van Moerkerk HTB, Glatz JFC, van Hinsbergh VWM (1983) Incomplete palmitate oxidation in cell-free systems of rat and human muscles. Biochim Biophys Acta 753:399–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2760(83)90064-4
Vluggens A, Andreoletti P, Viswakarma N, Jia Y, Matsumoto K, Kulik W, Khan M, Huang J, Guo D, Yu S, Sarkar J, Singh I, Rao MS, Wanders RJ, Reddy JK, Cherkaoui-Malki M (2010) Functional significance of the two ACOX1 isoforms and their crosstalks with PPARα and RXRα. Lab Investig 90:696–708. https://doi.org/10.1038/labinvest.2010.46
Walton PA, Pizzitelli M (2012) Effects of peroxisomal catalase inhibition on mitochondrial function. Front Physiol 3:108–108. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2012.00108
Wanders RJA, Ruiter JPN, Ijlst L, Waterham HR, Houten SM (2010) The enzymology of mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation and its application to follow-up analysis of positive neonatal screening results. J Inherit Metab Dis 33:479–494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-010-9104-8
Wang RY, Monuki ES, Powers J, Schwartz PH, Watkins PA, Shi Y, Moser A, Shrier DA, Waterham HR, Nugent DJ, Abdenur JE (2014) Effects of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation on acyl-CoA oxidase deficiency: a sibling comparison study. J Inherit Metab Dis 37:791–799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-014-9698-3
Wang ZX, Hou L, Huang LH, Guo J, Zhou XL (2017) Exenatide improves liver mitochondrial dysfunction and insulin resistance by reducing oxidative stress in high fat diet-induced obese mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 486:116–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.03.010
Wang J, Han SL, Li LY, Lu DL, McHele Limbu S, Li DL, Zhang ML, Du ZY (2018) Lipophagy is essential for lipid metabolism in fish. Sci Bull 63:879–882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2018.05.026
Yan J, Liao K, Wang TJ, Mai KS, Xu W, Ai QH (2015) Dietary lipid levels influence lipid deposition in the liver of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) by regulating lipoprotein receptors, fatty acid uptake and triacylglycerol synthesis and catabolism at the transcriptional level. PLoS One 10:e0129937. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0129937
Zeng J, Deng GS, Li D (2006) Intrinsic enoyl-CoA isomerase activity of rat acyl-CoA oxidase I. Biochim Biophys Acta 1760:78–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2005.09.010
Zeng J, Wu L, Zhang XJ, Liu YD, Deng GS, Li D (2008) Oct-2-en-4-ynoyl-CoA as a specific inhibitor of acyl-CoA oxidase. Org Lett 10:4287–4290. https://doi.org/10.1021/ol801571n
Zeng J, Deng SW, Wang YP, Li P, Tang L, Pang YF (2017) Specific inhibition of acyl-CoA oxidase-1 by an acetylenic acid improves hepatic lipid and reactive oxygen species (ROS) metabolism in rats fed a high fat diet. J Biol Chem 292:3800–3809. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.763532
Zhang DY, Christianson J, Liu ZX, Tian LQ, Choi CS, Neschen S, Dong JY, Wood PA, Shulman GI (2010) Resistance to high-fat diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance in mice with very long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. Cell Metab 11:402–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2010.03.012
Funding
This study received financial support given by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31830102) and Program of Shanghai Academic Research Leader (19XD1421200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The care and use of animals and all experimental procedures involving animals were approved by the Committee on the Ethics of Animals Experiments of East China Normal University and followed the Guidance of the Care and Usage of Laboratory Animals in China.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Han, SL., Luo, Y. et al. Impaired peroxisomal fat oxidation induces hepatic lipid accumulation and oxidative damage in Nile tilapia. Fish Physiol Biochem 46, 1229–1242 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-020-00785-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-020-00785-w