Abstract
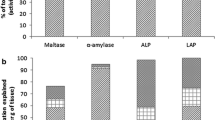
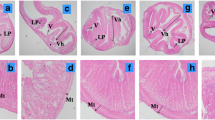
An 87-day feeding trial was carried out to assess the use of dehulled and defatted sesame seed meal (SM) as a partial dietary replacement for soybean meal (SBM) at 0%, 15%, 30% and 45% (SM0, SM1, SM2 and SM3, respectively) in juvenile sea bass stocked in 12 tanks (0.5 m3) and with an initial weight of 24 ± 0.50 g. All diets were isonitrogenous (~ 47% crude protein), isoenergetic (~ 22 MJ/kg) and tested in triplicate. The lowest growth and feed utilization efficacy were detected in fish fed the SM3 diet; moreover, diets with a lower SM content did not have significant effects relative to the CTR diet. Fish biochemical analysis indicated a gradual decrease in carcass protein content coinciding with an increase in lipid deposition and viscerosomatic index values as the SM level in the diet increased. The macroelements’ (P, Na and K) fish contents did not differ significantly among groups. The SM3 group had the lowest Ca and highest Mg contents among the experimental groups. The fish amino acid profile indicated slight alterations in essential amino acid percentages among groups. Haematological analysis and serum biochemistry indicated that using SM at a content of up to 30% had limited negative impacts on fish health. Liver histological inspection indicated that higher levels of SM led to severe hepatocyte infiltration with slight signs of necrosis in fish fed SM3 diet. Intestinal histological examinations indicated that the distal portion of the intestine was the portion most affected by SBM replacement with SM with signs of intestinal inflammation in SM3 group.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abboudi T, Mambrini M, Larondelle Y, Rollin X (2009) The effect of dispensable amino acids on nitrogen and amino acid losses in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L) fry fed a protein-free diet. Aquaculture 289:327–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2009.01.031
Alam MS, Teshima S, Yaniharto D, Koshio S, Ishikawa M (2002) Influence of different amino acid patterns on growth and body composition juvenile Japanese flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Aquaculture 210:359–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(01)00892-4
AOAC (1995) Official methods of analysis of AOAC international. 6th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington, VA, USA pp 1141
APHA (1995) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (19th edn). Author, Washington, DC., USA. https://doi.org/10.3996/082016-JFWM-068.S6
APHA, AWWA and WPCF (1999) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington
Ashri A (1989) Sesame. In: Downey RGR, Ashri A (eds) Oil Crops of the World. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 375–387
Atamanalp M, Yilmaz M, Haliloğlu HI (2003) Comparing serum cholesterol types and levels of three trout species (Salvelinus alpinus, Salmo trutta fario and Oncorhynchus mykiss). J Appl Anim Res 23:223–226. https://doi.org/10.1080/09712119.2003.9706425
Bergmayer H U (1963) Methods of enzymatic analysis. Verlag Chemie G.m.b.H., Weinheim/Bergstr. (Germany) and academic press, New York and London. https://doi.org/10.1002/star.19630150713
Bonaldo A, Roem AJ, Fagioli P et al (2008) Influence of dietary levels of soybean meal on the performance and gut histology of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) and European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.). Aquac Res 39:970–978. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2008.01958.x
Booman M, Forster L, Vederas JC et al (2018) Soybean meal-induced enteritis in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) and Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) but not in pink salmon (O. gorbuscha). Aquaculture 483:238–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2017.10.025
Chawla R (2003) Practical clinical biochemistry: methods and interpretations, 3th edn. Jaypee Brothers, New Delhi
Coz-Rakovac R, Strunjak-Perovic I, Hacmanjek M et al (2005) Blood chemistry and histological properties of wild and cultured sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) in the North Adriatic Sea. Vet Res Commun 29:677–687
Cui X, Wang Y, She X (2010) Determination of Ca, K, Mg and Fe in four fish species by FAASJ. Ocean Univ China 9:235–238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-010-1758-1
Das P, Ghosh K (2015) Improvement of nutritive value of sesame oil cake in formulated diets for rohu, Labeo rohita (Hamilton) after bio-processing through solid state fermentation by a phytase-producing fish gut bacterium. Int J Aquat Biol 3(2):89–101
Dernekbaş S, Karayücel I (2017) Partial replacement of soybean meal by peanut and sesame seed meals in practical diets for rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. J Aquac Mar Biol 6(1):00146. https://doi.org/10.15406/jamb.2017.06.00146
Dernekbaş S, Karayücel I, Akyüz AP (2017) Evaluation of sesame (Sesamum indicum) seed meal as a replacer for soybean meal in the diets of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum, 1792). Ege J Fish Aquat Sci 34(1):31–39. https://doi.org/10.12714/egejfas.2017.34.1.05
Di Marco P, Priori A, Finoia G et al (2008) Physiological responses of European sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax to different stocking densities and acute stress challenge. Aquaculture 275:319–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.12.012
Doumas BT, Biggs HG (1972) Standard methods of clinical chemistry, vol 7. Academic Press, New York, 175 pp
El-Saidy DMS, Samy HM, Mostafa AE et al (2009) Nutrition evaluation of sesame seed meal, Sesamum indicum (L.) as alternative protein source in diets of juvenile mono-sex Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Egypt J Aquat Biolol Fish 13(1):93–106. https://doi.org/10.21608/ejabf.2009.2026
Emadi H, Mokhayer B, Faal M (2014) Alternative role of sesame seed replacing fish meal in the diet of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fingerlings. Iran J Fish Sci 13(3):608–620
Enyidi UD, Pirhonen J, Vielma J (2014) Effects of sesame seed meal and bambara nut meal on growth, feed utilization and body composition of juvenile African catfish Clarias gariepinus. Iran J Fish Sci 13(4):998–1013
Erkan N, Ozden O (2007) Proximate composition and mineral contents in aquacultured sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax), sea bream (Sparus aurata) analyzed by ICP-MS. Food Chem 102:721–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.06.004
Fagbenro OA, Adeparusi EO, Jimoh WA (2010) Nutritional evaluation of sunflower and sesame seed meal in Clarias gariepinus: an assessment by growth performance and nutrient utilization. Afr J Agric Res 5(22):3096–3101
Falayi BA, Sadiku SOE, Ogedengbe JO (2013) Effects of substituting fish meal with sesame seed cake on growth and feed utilization of African mud fish Clarias gariepinus. Adv Res Biol Sci 1(3):31–35
FAO (Food and Agricultural Organization) (2012) Food and agriculture in national and international settings, pp 1–4
Fazio F, Ferrantelli V, Piccione G et al (2018) Biochemical and hematological parameters in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax Linnaeus, 1758) and Gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata Linnaeus, 1758) in relation to temperature. Veterinarski Arhiv 88(3):397–411. https://doi.org/10.24099/vet.arhiv.170406c
Filiciotto F, Fazio F, Marafioti S et al (2012) Assessment of haematological parameters range values using an automatic method in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.). Natura Rerum 1:29–36
Forsythe WA (1995) Soy protein, thyroid regulation and cholesterol metabolism. J Nutr 125(3):619S–623S. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/125.3_Suppl.619S
Francis G, Makkar HP, Becker K (2001) Antinutritional factors present in plant-derived alternate fish feed ingredients and their effects in fish. Aquaculture 199:197–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(01)00526-9
Fuentes-Quesada JP, Viana MT, Rombenso AN (2018) Enteritis induction by soybean meal in Totoaba macdonaldi diets: effects on growth performance, digestive capacity, immune response and distal intestine integrity. Aquaculture 495:78–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.05.025
Goda A, Omar EA, Srour TM et al (2018) Effect of diets supplemented with feed additives on growth, feed utilization, survival, body composition and intestinal bacterial load of early weaning European seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax post-larvae. Aquac Int 26(1):169–183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-017-0200-8
Grove TH (1979) Effect of reagent pH on determination of HDL cholesterol by precipitation with sodium phosphotungstate-magnesium. Clin Chem 25(4):560–561
Guo Y, Dong X, Tan B et al (2011) Partial replacement of soybean meal by sesame meal in diets of juvenile Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus L. Aquac Res 42:1298–1307. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2010.02718.x
Henry RJ, Cannon DC, Winkelman JW (1974) Clinical chemistry: principles and techniques, 11th edn. Harper and Row Publishers, New York 1629 pp
Hu L, Yun B, Xue M et al (2013) Effects of fish meal quality and fish meal substitution by animal protein blend on growth performance, flesh quality and liver histology of Japanese seabass (Lateolabrax japonicus). Aquaculture 372–375:52–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2012.10.025
Huang F, Wang L, Zhang C et al (2017) Replacement of fishmeal with soybean meal and mineral supplements in diets of Litopenaeus vannamei reared in low-salinity water. Aquaculture 473:172–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2017.02.011
Jahanbakhshi A, Imanpuor M, Taghizadeh V et al (2012) Effects of replacing fish meal with plant protein (sesame oil cake and corn gluten) on growth performance, survival and carcass quality of juvenile beluga (Huso huso). World J Fish Mar Sci 4(4):422–425. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.wjfms.2012.04.04.63107
Jimoh WA, Aroyehun HT (2011) Evaluation of cooked and mechanically defatted sesame (Sesamum indicum) seed meal as a replacer for soybean meal in the diet of African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Turk J Fish Aquat Sci 11:185–190. https://doi.org/10.4194/trjfas.2011.0202
Jimoh WA, Fagbenro OA, Adeparusi EO (2011) Effect of processing on some minerals, anti-nutrients and nutritional composition of sesame (Sesamum indicum) seed meals. EJEAFChe 10(1):1858–1864
Jimoh WA, Fagbenro OA, Adeparusi EO (2014) Response of African catfish, Clarias gariepinus (Burchell 1822), fingerlings fed diets containing differently timed wet-heat-treated sesame (Sesamum indicum) seed meal. Agric Sci 5:1159–1117. https://doi.org/10.4236/as.2014.512126
Kaushik SJ, Cravedi JP, Lalles JP et al (1995) Partial or total replacement of fish meal by soya protein on growth, protein utilization, potential estrogenic or antigenic effects, cholesterolemia and flesh quality in rainbow trout. Aquaculture 133:257–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/0044-8486(94)00403-B
Kavadias S, Castritsi-Catharios J, Dessypris A (2003) Annual cycles of growth rate, feeding rate, food conversion, plasma glucose and plasma lipids in the population of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) farmed in floating marine cages. J Appl Ichthyol 19:29–34. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1439-0426.2003.00346.x
Lall SP (2002) The minerals. In: Halver JE, Hardy RW (eds) Fish Nutrition, 3rd edn. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 259–308
Lawal MO, Aderlu AZ, Aarode OO et al (2016) Evaluation of soybean meal replacement with sesame seed meal using activated charcoal as an additive in the diet of African catfish juveniles, Clarias gariepinus. Int J Aquat Biol 4(1):43–50
Lim C, Akiyama DM (1992) Full-fat soybean meal utilization by fish. Asian Fish Sci 5:181–197
Lin S, Mai K, Tan B et al (2010) Effects of four vegetable protein supplementation on growth, digestive enzyme activities, and liver functions of juvenile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus × Oreochromis aureus. J World Aquacult Soc 41(4):583–593. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-7345.2010.00398.x
Maita M (2007) Fish health assessment. In: Nakagawa H, Sato M, Gatlin DM (eds) Dietary supplements for the health and quality of cultured fish. CAB International Publishing, Washington, pp 10–34
Njinkoue JM, Gouado I, Tchoumbougnang F et al (2016) Proximate composition, mineral content and fatty acid profile of two marine fishes from Cameroonian coast: Pseudotolithus typus (Bleeker, 1863) and Pseudotolithus elongatus (Bowdich, 1825). NFS J 4:27–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nfs.2016.07.002
NRC (2011) Nutrient requirements of fish and shrimp. National Academies Press, Washington
Olude O, George F, Alegbeleye W (2016) Utilization of autoclaved and fermented sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) seed meal in diets for Til-aqua natural male tilapia. Anim Nutr 2(4):339–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aninu.2016.09.001
Peres H, Santos S, Oliva-Teles A (2014) Blood chemistry profile as indicator of nutritional status in European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Fish Physiol Biochem 40(5):1339–1347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-014-9928-5
Reigh RC (2008) Underutilized and unconventional plant protein supplements. In: Lim C, Webster CD, Lee C-S (eds) Alternatives Protein Sources in Aquaculture Diets. The Howarth Press, New-York, pp 433–474
Saleh NE, Wassef EA, Shalaby SM (2018) The role of dietary astaxanthin in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) growth, immunity, antioxidant competence and stress tolerance. Egypt J Aquat Biol Fish 22(5):189–200. https://doi.org/10.21608/EJABF.2018.21044
Saraiva A, Costa J, Serrão J et al (2015) A histology-based fish health assessment of farmed seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.). Aquaculture 448:375–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.06.028
Schulz C, Knaus U, Wirth M et al (2005) Effects of varying dietary fatty acid profile on growth performance, fatty acid, body and tissue composition of juvenile pike perch, Sander lucioperca. Aquac Nutr 11(6):403–413. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2095.2005.00369.x
Shimeno S, Masumoto T, Hujita T et al (1993) Alternative protein sources for fish meal in diets of young yellowtail. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 59(1):137–143. https://doi.org/10.2331/suisan.59.137
Siano F, Bilotto S, Nazzaro M et al (2017) Effects of conventional and organic feed on the mineral composition of cultured European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Aquac Nutr 23(4):796–804. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12446
Siddhuraju P, Becker K (2001) Preliminary nutritional evaluation of mucuna seed meal (Mucuna pruriens var. utilis) in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.), an assessment by growth performance and feed utilization. Aquaculture 196:105–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(00)00577-9
Simpson RJ, Neuberger MR, Liu T-Y (1976) Complete amino acid analysis of proteins from a single analysis. J Biol Chem 251(7):1936–1940
Song J-Y, Zhang C-X, Wang L et al (2017) Effect of dietary calcium levels on growth and tissue mineralization in Japanese seabass, Lateolabrax japonicas. Aquac Nutr 23:637–648. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12431
Thu TTN, Bodin N, De Saeger S et al (2011) Substitution of fishmeal by sesame oil cake (Sesamum indica L.) in the diet of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss W.). Aquac Nutr 17:80–89. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2095.2009.00732.x
Tibaldi E, Kaushik SJ (2005) Amino acid requirements of Mediterranean fish species. Cah Options Mediterr 63:59–65
Tietz NW, Fiereck EA (1966) A specific method for serum lipase determination. Clin Chem Acta 13(3):352–358
Wassef EA, Abdel-Momen SA, Saleh NE et al (2017) Is sodium diformate a beneficial feed supplement for European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax)? Effect on growth performance and health status. Egypt J Aquat Res 43:229–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejar.2017.09.005
Xu QY, Wang CA, Zhao ZG, Luo L (2012) Effects of replacement of fish meal by soy protein isolate on the growth, digestive enzyme activity and serum biochemical parameters for juvenile Amur sturgeon (Acipenser schrenckii). Asian Australas J Anim Sci 25(11):1588–1594. https://doi.org/10.5713/ajas.2012.12192
Yaghoubi M, Mansour TM, Marammazi JG et al (2016) Dietary replacement of fish meal by soy products (soybean meal and isolated soy protein) in silvery-black porgy juveniles (Sparidentex hasta). Aquaculture 464:50–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2016.06.002
Yamamoto T, Unuma T, Akiyama T (2000) The influence of dietary protein and fat levels on tissue amino acid levels of fingerling rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 182:353–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(99)00277-X
Yasothai R (2014) Chemical composition of sesame oil cake – review. Int J Sci Environ Tech 3(3):827–835
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank the Egyptian Knowledge Bank for help in providing professional English language editing. Also, thanks to my colleagues, Prof. Ghada Farouk, Dr. Rania Fahmy, Dr. Hossam Saleh and Dr. Heba Abdel-mohsen (NIOF) for help in the practical part of the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable national and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed by the author.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saleh, N.E. Assessment of sesame meal as a soybean meal replacement in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) diets based on aspects of growth, amino acid profiles, haematology, intestinal and hepatic integrity and macroelement contents. Fish Physiol Biochem 46, 861–879 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-019-00756-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-019-00756-w