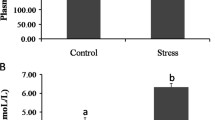
Abstract
MS-222 (tricaine methanesulfonate) and eugenol are the two frequently used fish anesthetics. This study intends to analyze the regulation of these anesthetics in Chinese sea bass, Lateolabrax maculatus, through transcriptomic analysis. L. maculatus were exposed to MS-222 or eugenol, and those without any treatments were regarded as controls. Gills and livers were extracted for transcriptomic analysis after recovery in fresh water for 6 h. Identified genes were assigned to NR, COG, SWISS, GO, and KEGG database for predicting gene functions. A FDR ≤ 0.05 and |log2(FC)| ≥ 1 were applied to determined differentially expressed gene (DEG). A total of 45,626 unigenes were annotated using at least one database. The eugenol-treated liver group presented less DEGs compared with that treated by MS-222. Both the MS-222- and eugenol-treated liver groups presented notable DEGs that participated in human disease and metabolism pathways. The eugenol group showed more pathways related to detoxification activity and xenobiotics biodegradation, and those from the MS-222 group were related to organismal system such as reproduction. By comparing gill and liver samples using the same drug, the enriched pathways were generally consistent among the three comparisons. In conclusion, eugenol and MS-222 could change the pathways related to metabolism and immunity in L. maculatus. MS-222 may trigger more damages on the fish liver and reproduction.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aluru N, Vijayan MM (2007) Hepatic transcriptome response to glucocorticoid receptor activation in rainbow trout. Physiol Genomics 31:483–491. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00118.2007
Berg H, Modig C, Olsson PE (2004) 17beta-estradiol induced vitellogenesis is inhibited by cortisol at the post-transcriptional level in Arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus). Reprod Biol Endocrinol 2:62. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7827-2-62
Bolasina S, De Azevedo A, Petry A (2017) Comparative efficacy of benzocaine, tricaine methanesulfonate and eugenol as anesthetic agents in the guppy Poecilia vivipara. 6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2017.04.002
Duan Y, Zhang Y, Dong H, Zhang J (2016) Effect of desiccation on oxidative stress and antioxidant response of the black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon. Fish Shellfish Immunol 58:10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2016.09.004
Endo T, Ogishima K, Tanaka H, Ohshima S (1972) Studies on the anesthetic effect of eugenol in some fresh water fishes. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 38:761–767. https://doi.org/10.2331/suisan.38.761
Fischer IU, von Unruh GE, Dengler HJ (1990) The metabolism of eugenol in man. Xenobiotica; the fate of foreign compounds in biological systems. 20:209–222. https://doi.org/10.3109/00498259009047156
Fujimoto RY, Pereira DM, Silva JCS, de Oliveira LCA, Inoue LAKA, Hamoy M, de Mello VJ, Torres MF, Barbas LALet al. (2018) Clove oil induces anaesthesia and blunts muscle contraction power in three Amazon fish species. Fish Physiol Biochem 44:245–256 doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-017-0430-8
Gil HW, Ko MG, Lee TH, Park IS, Kim DS (2016) Anesthetic effect and physiological response in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) to clove oil in a simulated transport experiment. Dev Reprod 20:255–266. https://doi.org/10.12717/dr.2016.20.3.255
Gomes LC, Chippari-Gomes AR, Lopes NP, Roubach R, Araujo-Lima CARM (2001) Efficacy of benzocaine as an anesthetic in juvenile tambaqui Colossoma macropomum. J World Aquacult Soc 32:426–431. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-7345.2001.tb00470.x
Gressler L et al (2014) Silver catfish Rhamdia quelen immersion anaesthesia with essential oil of Aloysia triphylla (L'Hérit) Britton or tricaine methanesulfonate: effect on stress response and antioxidant status. Aquac Res 45:1061–1072. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.12043
Guo F-C, Teo L-H, Chen T-W (1995) Effects of anaesthetics on the water parameters in a simulated transport experiment of platyfish, Xiphophorus maculatus (Günther). Aquac Res 26:265–271. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.1995.tb00911.x
Jerez-Cepa I, Fernandez-Castro M, Del Santo O'Neill TJ, Martos-Sitcha JA, Martinez-Rodriguez G, Mancera JM, Ruiz-Jarabo I (2019) Transport and recovery of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.) sedated with clove oil and MS-222: effects on stress axis regulation and intermediary metabolism. Front Physiol 10:612. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.00612
Le Q et al (2019) Transcriptomic and cortisol analysis reveals differences in stress alleviation by different methods of anesthesia in crucian carp (Carassius auratus). Fish Shellfish Immunol 84:1170–1179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.10.061
Lethimonier C, Flouriot G, Valotaire Y, Kah O, Ducouret B (2000) Transcriptional interference between glucocorticoid receptor and estradiol receptor mediates the inhibitory effect of cortisol on fish vitellogenesis. Biol Reprod 62:1763–1771
Liu JX, Gao TX, Yokogawa K, Zhang YP (2006) Differential population structuring and demographic history of two closely related fish species, Japanese sea bass (Lateolabrax japonicus) and spotted sea bass (Lateolabrax maculatus) in Northwestern Pacific. Mol Phylogenet Evol 39:799–811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2006.01.009
Mitjana O, Bonastre C, Insua D, Victoria Falceto M, Esteban J, Josa A, Espinosa E (2014) The efficacy and effect of repeated exposure to 2-phenoxyethanol, clove oil and tricaine methanesulphonate as anesthetic agents on juvenile angelfish (Pterophyllum scalare). 433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2014.07.013
Mommsen T, Vijayan M, Moon T (1999) Cortisol in teleost dynamics, mechanisms of action, and metabolic regulation. 9. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008924418720
Narnaware YK, Baker BI (1996) Evidence that cortisol may protect against the immediate effects of stress on circulating leukocytes in the trout. Gen Comp Endocrinol 103:359–366. https://doi.org/10.1006/gcen.1996.0131
Pagniello KB, Bols NC, Lee LE (2002) Effect of corticosteroids on viability and proliferation of the rainbow trout monocyte/macrophage cell line, RTS11. Fish Shellfish Immunol 13:199–214
Park IS, Gil HW, Lee TH, Nam YK, Lim SG, Kim DS (2017) Effects of clove oil and lidocaine-HCl anesthesia on water parameter during simulated transportation in the marine medaka, Oryzias dancena. Dev Reprod 21:19–33. https://doi.org/10.12717/dr.2017.21.1.019
Pawar H, Sanaye S, Rayadurga S, Venkatakrishnan H, Suryavanshi U, Tanu, Za A (2011) Comparative efficacy of four anaesthetic agents in the yellow seahorse, Hippocampus kuda (Bleeker, 1852). 311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2010.12.007
Rajakumar DV, Rao MN (1993) Dehydrozingerone and isoeugenol as inhibitors of lipid peroxidation and as free radical scavengers. Biochem Pharmacol 46:2067–2072
Roubach R, Gomes L, Fonseca F, Val A (2005) Eugenol as an efficacious anesthetic for tambaqui, Colossoma macropomum (Cuvier). 36. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2005.01319.x
Saeij JP, Verburg-van Kemenade LB, van Muiswinkel WB, Wiegertjes GF (2003) Daily handling stress reduces resistance of carp to Trypanoplasma borreli: in vitro modulatory effects of cortisol on leukocyte function and apoptosis. Dev Comp Immunol 27:233–245
Schreck C, Contreras-Sánchez W, Fitzpatrick SM (2001) Effects of stress on fish reproduction, gamete quality, and progeny. 197. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(01)00580-4
Sneddon L (2012) Clinical Anesthesia and Analgesia in Fish. 21. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jepm.2011.11.009
Soltanian S, Hoseinifar SH, Gholamhosseini A (2018) Modulation of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) cutaneous mucosal immune responses following anesthesia: a comparative study on different anesthetic agents. Fish Shellfish Immunol 80:319–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.06.032
Storey KB (1996) Oxidative stress: animal adaptations in nature. Braz J Med Biol Res 29:1715–1733
Stringhetta GR, Barbas LAL, Maltez LC, Sampaio LA, Monserrat JM, Garcia LO (2017) Oxidative stress responses of juvenile tambaqui Colossoma macropomum after short-term anesthesia with benzocaine and MS-222. An Acad Bras Cienc 89:2209–2218. https://doi.org/10.1590/0001-3765201720160823
Teles M, Oliveira M, Jerez-Cepa I, Franco-Martinez L, Tvarijonaviciute A, Tort L, Mancera JM (2019) Transport and recovery of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) sedated with clove oil and MS222: effects on oxidative stress status. Front Physiol 10:523. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.00523
Topic Popovic N, Strunjak-Perovic I, Coz-Rakovac R, Barisic J, Jadan M, Persin Berakovic A, Sauerborn Klobučar R (2012) Tricaine methane-sulfonate (MS-222) application in fish anaesthesia. 28. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0426.2012.01950.x
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (1997) Freedom of information summary for NADA 200–226
Velisek J, Stara A, Li Z-H, Silovska S, Turek J (2011) Comparison of the effects of four anaesthetics on blood biochemical profiles and oxidative stress biomarkers in rainbow trout. Aquaculture 310:369–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2010.11.010
Vera LM, Montoya A, Sanchez-Vazquez FJ (2013) Effectiveness of the anaesthetic MS-222 in gilthead seabream, Sparus aurata: effect of feeding time and day-night variations in plasma MS-222 concentration and GST activity. Physiol Behav 110-111:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2012.12.012
Wang W et al (2018) The efficacy of eugenol and tricaine methanesulphonate as anaesthetics for juvenile Chinese sea bass (Lateolabrax maculatus) during simulated transport. J Appl Ichthyol 35. https://doi.org/10.1111/jai.13844
Weber R, Peleteiro JB, García Martín LO, Aldegunde M (2009) The efficacy of 2-phenoxyethanol, metomidate, clove oil and MS-222 as anaesthetic agents in the Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis Kaup 1858). 288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2008.11.024
Weyts FA, Verburg-van Kemenade BM, Flik G, Lambert JG, Wendelaar Bonga SE (1997) Conservation of apoptosis as an immune regulatory mechanism: effects of cortisol and cortisone on carp lymphocytes. Brain Behav Immun 11:95–105. https://doi.org/10.1006/brbi.1997.0484
Wiseman S, Osachoff H, Bassett E, Malhotra J, Bruno J, Vanaggelen G, Mommsen TP, Vijayan MMet al. (2007) Gene expression pattern in the liver during recovery from an acute stressor in rainbow trout. Comp Biochem Physiol Part D Genomics Proteomics 2:234–244 doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbd.2007.04.005
Yokogawa K, Seki S (1995) Morphological and genetic differences between Japanese and Chinese sea bass of the genus Lateolabrax. Jpn J Ichthyol 41:437–445. https://doi.org/10.11369/jji1950.41.437
Zhao Y, Jiang X, Kong X, Di G, Nie G, Li X (2015) Effects of hypoxia on lysozyme activity and antioxidant defences in the kidney and spleen of Carassius auratus. Aquac Res 48. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.12876
Funding
This study was funded by the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute (2017YB15); The Funding of Key Laboratory of South China Sea Fishery Resources Exploration & Utilization, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs (FREU2018-02), and The Funding of Guangzhou Science and technology Planning Project (201904010169).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Fig. S1
SNP detection of Lateolabrax maculatus with and without anesthetics treatment. CL: control liver; CG: control gill; EL: eugenol-treated liver; EG: eugenol-treated gill; ML: MS-222-treated liver; MG: MS-222-treated gill. (JPG 3281 kb)
Fig. S2
SRR detection of Lateolabrax maculatus with and without anesthetics treatment (JPG 680 kb)
ESM 1
(DOCX 32 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, H., Wang, W., Duan, Y. et al. Transcriptomic analysis of juvenile Chinese sea bass (Lateolabrax maculatus) anesthetized by MS-222 (tricaine methanesulfonate) and eugenol. Fish Physiol Biochem 46, 909–920 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-019-00755-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-019-00755-x