Abstract
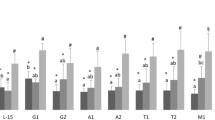
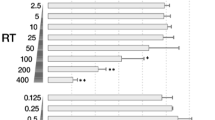
The in vitro and in vivo effect of prolactin (PRL) on kidney macrophages from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) was investigated under the assumption that PRL stimulates immune innate response in mammals. Kidney macrophages were treated two ways: first, cultured in RPMI 1640 medium containing 10, 25, 50 and 100 ng/mL of PRL and second, isolated from a fish with a PRL-injected dose of 100 ng/Kg. Reduced nitro blue tetrazolium (formazan) was used to produce intracellular superoxide anion. Phagocytic activity of PRL was determined in treated cells by optical microscopy observation of phagocytized Congo red-stained yeast. Kidney lysozyme activity was measured in PRL-injected fish. In vitro and in vivo macrophages treated with PRL presented an enhanced superoxide anion production, elevated phagocytic index and increased phagocytic activity. Treated fish showed higher levels of lysozyme activity in the head kidney compared to the control. These results indicate that PRL-stimulated innate immune response in Atlantic salmon and future studies will allow us to assess the possibility of using PRL as an immunostimulant in the Chilean salmon industry.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida A, Rehder J, Dalge S, Martins-Filho J, Newburger P, Condino-Neto P (2005) The effect of IFN-γ and TNF-α on the NADPH oxidase system of human colostrum macrophages, blood monocytes, and THP-1 Cells. J Interferon Cytokine Res 25:540–546
Andersen Ø, Skibeli V, Gautvik K (1989) Purification and characterization of Atlantic salmon prolactin. Gen Comp Endocrinol 73(3):354–360
Aquaculture, Fisheries and Aquaculture Department, FAO (2010). www.fao.org/fishery/aquaculture/en. Accessed 13 Apr 2010
Bagni M, Romano N, Finoia M, Abelli L, Scapigliati G (2005) Short- and long-term effects of a dietary yeast beta-glucan (Macrogard) and alginic acid (Ergosan) preparation on immune response in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Fish Shellfish Immunol 18:311–325
Bai N, Zhang W, Mai K, Wang X, Xu W, Ma H (2010) Effects of discontinuous administration of β-glucan and glycyrrhizin on the growth and immunity of white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 306:218–224
Bole-Feysot H, Goffin V, Edery M, Binart N, Kelly P (1998) Prolactin and its receptor: actions, signal transduction pathways and phenotypes observed in PRL receptor knockout mice. Endocr Rev 19(3):225–268
Bonaldo A, Thompson K, Manfrin A, Adams A, Murano E, Mordenti A, Gatta P (2009) The influence of dietary β-glucans on the adaptive and innate immune responses of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) vaccinated against vibriosis. Italian J Animal Sci 6(2):151–164
Boutet I, Lorin-Nebel J, Lorgeril De, Guinand B (2007) Molecular characterisation of prolactin and analysis of extrapituitary expression in the European sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax under various salinity conditions. Comp Biochem Physiol D: Genomics Proteomics 2(1):74–83
Cabello F (2004) Antibióticos y acuicultura en Chile: consecuencias para la salud humana y animal. Revista Médica de Chile 132:1001–1006
Cabello F (2006) Heavy use of prophylactic antibiotics in aquaculture: a growing problem for human and animal health and for the environment. Environ Microbiol 8:1137–1144
Chen D, Ainsworth A (1992) Glucan administration potentiates immune defence mechanisms of channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus Rafinesque. J Fish Dis 15:295–304
Chen Y, Johnson A (1993) In vivo activation of macrophages by prolactin from young and aging mice. Int J Immunopharmacol 15:39–43
Clevenger C, Freier D, Kline J (1998) Prolactin receptor signal transduction in cells of the immune system. J Endocrinol 157:187–197
Cook M, Hayball P, Hutchinson W, Nowak B, Hayball J (2003) Administration of a commercial immunostimulant preparation, EcoActiva™, as a feed supplement enhances macrophage respiratory burst and the growth rate of snapper (Pagrus auratus) in winter. Fish Shellfish Immunol 14:333–345
Dimitrov T, Lange H, Fehm L, Born J (2004) A regulatory role for prolactin, growth hormone and corticosteroids for human T cell production of cytokines. Brain Behav Immun 18:368–374
Engstad R, Robertsen B, Frivold E (1992) Yeast glucan induces increase in lysozyme and complement-mediated haemolytic activity in Atlantic salmon blood. Fish Shellfish Immunol 2(4):287–297
Giacomini E, Iona E, Ferroni L (2001) Infection of human macrophages and dendritic cells with Mycobacterium tuberculosis induces a differential cytokine gene expression that modulates T cell response. J Immunol 166:7033–7040
Hoffman O, Olson E, Limper A (1993) Fungal β-glucans modulate macrophage release of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Immunol Lett 37:19–25
Jeney G, Anderson D (1993) Glucan injection or bath exposure given alone or in combination with bacterin enhance the non-specific defence mechanism in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 116:315–329
Miranda C, Zemelman R (2002) Antimicrobial multiresistance in bacteria isolated from freshwater Chilean salmon farms. Sci Total Environ 293:207–218
Murtaugh P, Foss D (2002) Inflammatory cytokines and antigen presenting cell activation. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 87:109–114
Narnaware Y, Kelly S, Woo Y (1998) Stimulation of macrophage phagocytosis and lymphocyte count by exogenous prolactin administration in silver sea bream (Sparus sarba) adapted to hyper- and hypo-osmotic salinities. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 61:387–391
Olavarria V, Sepulcre M, Figueroa J, Mulero V (2010) Prolactin-induced production of reactive oxygen species and IL-1β in leukocytes from the bony fish gilthead seabream involves Jak/Stat and NF-κB signaling pathways. J Immunol 185:3873–3883
Olavarria V, Figueroa F, Mulero V (2012) Prolactin-induced activation of phagocyte NADPH oxidase in the teleost fish gilthead seabream involves the phosphorylation of p47phox by protein kinase C. Dev Comp Immunol 36:216–221
Ortega E, Forner A, Barriga C (1996) Effect of prolactin on the in vitro phagocytic capacity of macrophages. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 19:139–146
Pal D, Joardar S, Roy B (2007) Immunostimulatory effects of a yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) cell wall feed supplement on rohu (Labeo rohita), an Indian major carp. Israeli J Aquacu–Bamidgeh 59:175–181
Parry R Jr, Camden R, Shahani K (1965) A rapid and sensitive assay of muramidase. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 119:384–386
Paulsen S, Engstad E, Robertsen B (2000) Enhanced lysozyme production in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) macrophages treated with yeast β-glucan and bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Fish Shellfish Immunol 11:23–37
Peeva E, Venkatesh J, Michael D, Diamond B (2004) Prolactin as a modulator of B cell function: implications for SLE. Biomedecine Pharmacother 58:310–319
Sakai M, Kobayashi M, Kawauchi H (1996a) Mitogenic effect of growth hormone and prolactin on chum salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) leukocytes in vitro. Veterinay. Immunol Immunopathol 53:185–189
Sakai M, Kobayashi M, Kawauchi H (1996b) In vitro activation of fish phagocytic cells by GH, prolactin and somatolactin. J Endocrinol 151:113–118
Szekanecz Z, Koch A (2007) Macrophages and their products in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 19:289–295
Taylor P, Martinez-Pomares L, Stacey M, Lin H, Brown G, Gordon S (2005) Macrophage receptors and immune recognition. Annu Rev Immunol 23:901–944
Tripathi A, Sodhi A (2008) Prolactin induced production of cytokines involves Jak/Stat and JNK MAP kinase pathways. Int Immunol 20:326–327
Wandurska-Nowak E (2004) The role of nitric oxide (NO) in parasitic infections. Wiad Parasytol 50:665–678
Yada T, Nagae M, Moriyama S, Azuma T (1999) Effects of prolactin and growth hormone on plasma immunoglobulin M levels of hypophysectomized rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Gen Comp Endocrinol 115:46–52
Yada T, Uchida K, Kajimura S, Azuma T, Hirano T, Grau E (2002) Immunomodulatory effects of prolactin and growth hormone in the tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus. J Endocrinol 173:483–492
Yada T, Misumi I, Muto K, Azuma T, Schreck C (2004) Effects of prolactin and growth hormone on proliferation and survival of cultured trout leucocytes. Gen Comp Endocrinol 136:298–306
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by FONDECYT grant 1040073 and DID-Doctorado grant 2005–07 from the Universidad Austral de Chile.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paredes, M., Gonzalez, K., Figueroa, J. et al. Immunomodulatory effect of prolactin on Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) macrophage function. Fish Physiol Biochem 39, 1215–1221 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-013-9777-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-013-9777-7