Abstract
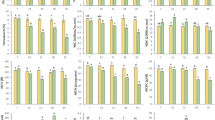
Stress in fish can be assessed by means of a bioenergetic approach, based on the evaluation of changes in their physiological parameters. The objective of this study was to determine the impact of sublethal water-borne cadmium (Cd) on the energetic balance of juvenile Cyprinus carpio under laboratory conditions after a short-term exposure. Fish were exposed to a concentration of Cd (0.15 mg Cd l−1) for 2 weeks. This concentration is environmentally realistic since it is usually found, even at higher values, in heavily polluted periurban water bodies of Argentina. No mortality was recorded among the animals used in the experiments. Food intake, food assimilation and assimilation efficiency, fecal production, liver glycogen content, oxygen consumption, oxygen extraction efficiency, specific metabolic rate, ammonia excretion and ammonia quotient (AQ), condition factor, and liver somatic index were determined. The overall balance was expressed as the scope for growth (SFG). The morphological indices and the liver glycogen content of Cd-exposed fish showed no significant differences when compared to those of controls. There was a significant decrease in the food intake, fecal production, and food assimilation rates as well as in AQ; the SFG exhibited a highly significant decrease. The remaining parameters (assimilation efficiency, oxygen consumption, oxygen extraction efficiency, specific metabolic rate, and ammonia excretion) increased after the exposure to Cd. We concluded that the sub-chronic exposure of Cyprinus carpio to a sublethal concentration of Cd causes important alterations in the energy-related homeostasis of fish. Most of the responses are indicative of physiological adaptations to compensate an increased energy requirement due to the impairments caused by the metal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abel PD, Papoutsoglou SE (1986) Lethal toxicity of cadmium to Cyprinus carpio and Tilapia aurea. Bull Env Contam Toxicol 37:382–386
Alcaraz G, Espina S (1997) Scope for growth of juvenile Grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella exposed to nitrite. Comp Biochem Physiol 116:85–88
Allin CJ, Wilson RW (1999) Behavioural and metabolic effects of chronic exposure to sublethal cadmium in acidic soft water in juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Can J Fish Aquat Sci 56:670–673
Almeida JA, Novelli ELB, Dal Pai Silva M, Alves Júnior R (2001) Environmental cadmium exposure and metabolic responses of the Nile tilapia. Oreochromis niloticus Environm Pollut 114:169–175
Alves LC, Glover CN, Wood CM (2006) Dietary Pb accumulation in juvenile freshwater rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 51:615–625
Asagba SO, Eriyamremu GE, Igberaese ME (2008) Bioaccumulation of cadmium and its biochemical effect on selected tissues of the catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Fish Physiol Biochem 34:61–69
Battaglini P, Andreozzi G, Antonucci R, Arcamone N, De Girolamo P, Ferrara L, Gargiulo G (1993) The effects of cadmium on the gills of the goldfish Carassius auratus L.: metal uptake and histochemical changes. Comp Biochem Physiol 104C:239–247
Bentley PJ (1991) Accumulation of cadmium by channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus): influx from environmental solutions. Comp Biochem Physiol 99C:527–529
Carrier R, Beitinger TL (1988) Resistance of temperature tolerance ability of green sunfish to cadmium exposure. Bull Env Contam Toxicol 40:475–480
Couture P, Kumar PR (2003) Impairment of metabolic capacities in copper and cadmium contaminated wild yellow perch (Perca flavescens). Aquat Toxicol 64:107–120
Datta DK, Sinha GM (1990) Comparative static bioassay of cadmium toxicity for two Indian freshwater teleosts. J Freshwater Biol 2:313–321
De Boeck G, De Smet H, Blust R (1995) The effect of sublethal levels of copper on oxygen consumption and ammonia excretion in the common carp, Cyprinus carpio. Aquat Toxicol 32:127–141
De Boeck G, Vlaeminck A, Van der Linden A, Blust R (2000) The energy metabolism of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) when exposed to salt stress: an increase in energy expenditure or effects of starvation? Physiol Biochem Zool 73:102–111
De Boeck G, van der Ven K, Hattink J, Blust R (2006) Swimming performance and energy metabolism of rainbow trout, common carp and gibel carp respond differently to sublethal copper exposure. Aquat Toxicol 80:92–100
de la Torre FR (2001) Estudio integrado de la contaminación acuática mediante bioensayos y parámetros fisiológicos y bioquímicos indicadores de estrés ambiental. Doctoral Dissertation, Faculty of Exact and Natural Sciences, University of Buenos Aires
de la Torre FR, Ferrari L, Salibián A (1999) Enzyme activities as biomarkers of freshwater pollution: response of fish branchial Na+ K-ATPase and liver transaminases. Environ Toxicol 14:313–319
de la Torre F, Ferrari L, Salibián A (2000) Long-term in situ water toxicity bioassays in the Reconquista river (Argentina) with Cyprinus carpio as sentinel organism. Water Air Soil Pollut 121:205–215
De Smet H, Blust R (2001) Stress responses and changes in protein metabolism in carp Cyprinus carpio during cadmium exposure. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 48:255–262
Eastwood S, Couture P (2002) Seasonal variations in condition and liver metal concentrations of yellow perch (Perca flavescens) from a metal-contaminated environment. Aquat Toxicol 58:43–56
Eissa BL (2009) Biomarcadores comportamentales, fisiológicos y morfológicos de exposición al Cadmio en peces pampeanos. Doctoral Dissertation, Faculty of Exact and Natural Sciences, University of Buenos Aires
Eissa BL, Salibián A, Ferrari L (2006) Behavioral alterations in juvenile Cyprinus carpio exposed to sublethal waterborne cadmium. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 77:931–937
Eissa BL, Ossana NA, Salibián A, Ferrari L, Pérez RH (2009) Cambios en la velocidad de nado como indicador del efecto tóxico del Cadmio en Astyanax fasciatus y Australoheros facetum. Biología Acuática 26:83–90
Eissa BL, Osanna NA, Ferrari L, Salibián A (2010) Quantitative behavioral parameters as toxicity biomarkers: fish responses to waterborne cadmium. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 58:1032–1039
Elliott JM, Davison W (1975) Energy equivalents of oxygen consumption in animal energetics. Oecologia 19:195–201
Espina S, Díaz F, Rosas C, Rosas I (1986). Influencia del detergente en el balance energético de Ctenopharyngodon idclla a través de un bioensayo crónico Contam Ambient 2:25–37
Espina S, Salibián A, Díaz F (2000) Influence of cadmium on the respiratory function of the grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idella. Water Air Soil Pollut 119:1–4
Evans DH, Piermarini PM, Choe KP (2005) The multifunctional fish gill: dominant site of gas exchange, osmoregulation, acid-base regulation, and excretion of nitrogenous waste. Physiol Revs 85:97–177
Fangue NA, Mandic M, Richards JG, Schulte PM (2008) Swimming performance and energetics as a function of temperature in killifish Fundulus heteroclitus. Physiol Biochem Zool 81:389–401
Ferrari L, Eissa BL, Ossana N, Salibián A (2005) Efectos de la exposición a cadmio subletal sobre la morfología de las branquias de Cyprinus carpio. Acta Toxicol Argent 13(Suppl):18–19
Ferrari L, Eissa BL, Salibián A, Borgnia M. (2006) Análisis de parámetros morfológicos y fisiológicos como biomarcadores de contaminación por Cadmio en juveniles de Cyprinus carpio. In: Herkovits J (ed) Salud ambiental y humana: una visión holistica, SETAC-Buenos Aires. pp 106–108
Ferrari L, Eissa BL, Ossana NA, Salibián A (2009) Effects of sublethal waterbone cadmium on gills in three teleosteans species: scanning electron microscope study. Internat J Environ Health 3:410–426
Giesy JP, Graney RL (1989) Recent developments in the intercomparisons of acute and chronic bioassays and bioindicators. Hydrobiologia 188(189):21–60
Goering PL, Waalkes MP, Klaassen CD (1995) Toxicology of cadmium. In: Goyer RA, Cherian MG (eds) Toxicology of metals—biochemical aspects. Springer, Berlin, pp 189–214
Handy R, Depledge MH (1999) Physiological responses: their measurement and use as environmental biomarkers in Ecotoxicology. Ecotoxicology 8:329–349
Hashemi S, Blust R, De Boeck G (2008) Combined effects of different food rations and sublethal cooper exposure on growth and energy metabolism in common carp. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 54:318–324
Hellawell JM (1986) Biological indicators of freshwater pollution and environmental management. Elsevier Applied Science Publishers, London, p 546
Jezierska B, Witeska M (2001) Metal toxicity to fish. Wydawnictwo Akademii Podlaskiej, Siedlce, p 318
Kunwar PS, Tudorache C, Eyckmans M, Blust R, De Boeck G (2009) Influence of food ration, copper exposure and exercise on the energy metabolism of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Comp Biochem Physiol 149C:113–119
Kuroshima R, Kimura S, Date K, Yamamoto Y (1993) Kinetic analysis of cadmium toxicity to red sea bream, Pagrus major. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 25:300–314
Kutty MN (1978) Ammonia quotient in sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka). J Fish Res Bd Can 35:1003–1005
Morrow MD, Higgs D, Kennedy CJ (2004) The effects of diet composition and ration on biotransformation enzymes and stress parameters in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Comp Biochem Physiol 137C:143–154
Moza U, De Silva SS, Mitchell BM (1995) Effect of sub-lethal concentrations of cadmium on food intake, growth and digestibility in the goldfish, Carassius auratus L. J Environ Biol 16:253–264
Navarro I, Gutiérrez J (1995) Fasting and starvation. In: Hochachka PW, Mommsen TP (eds) Biochemistry and molecular biology of fishes, vol 4. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 393–434
Newman MC, Clements WH (2008) Ecotoxicology. A comprehensive treatment. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Ossana NA, Eissa BL, Salibián A (2009) Cadmium bioconcentration and genotoxicity in the common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Internat J Environ Health 3:302–309
Owen SF, Houlihan DF, Rennie MJ, van Weerd JH (1998) Bioenergetics and nitrogen balance of the European eel (Anguila anguila) fed at high and low ration levels. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 55:2365–2375
Peters G (1982) The effect of stress on the stomach of the European eel, Anguilla anguilla. J Fish Physiol 21:497–512
Pistole DH, Peles JD, Taylor K (2008) Influence of metal concentrations, percent salinity and length of exposure on the metabolic rate of fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas). Comp Biochem Physiol 148C:48–52
Pottinger TG, Calder GM (1995) Physiological stress in fish during toxicologicl procedures: a potentally confounding factor. Environ Toxicol Water Qual 10:135–146
Roast SD, Widdows J, Jones MB (1999) Scope for growth of the estuarine mysid Neomysis integer (Peracarida: Mysidacea): effects of the organophosphate pesticide chlorpyrifos. Mar Ecol Progr Ser 191:233–241
Salibián A (2006) Ecotoxicological assessment of the highly polluted Reconquista River of Argentina. In: Ware GW (ed) Rev Environm Contam Toxicol, vol 185, pp 35–65
Sanchez W, Porcher JM (2009) Fish biomarkers for environmental monitoring within the water framework directive of the European Union. Trends Anal Chem 28:150–158
Sancho E, Ferrando MD, Fernádez C, Andreu E (1998) Liver energy metabolism of anguilla after exposure to fenitrothion. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 41:168–175
Schelenk D, Handy R, Steinert S, Depledge MH, Benson W (2008) Biomarkers. In: Di Giulio RT, Hinton DE (eds) The toxicology of fishes. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 683–731
Scott GS, Sloman KA (2004) The effects of environmental pollutants on complex fish behavior: integrating behavioral and physiological indicators of toxicity. Aquat Toxicol 38:369–392
Seifter S, Dayton S, Novic B, Montwyler E (1950) The estimation of glycogen with the anthrone reagent. Arch Biochem 25:191–200
Seyle H (1973) The evolution of the stress concept. Am Sci 61:692–699
Sibly RM, Calow P (1986) Physiological ecology of animals. An evolutionary approach. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford
Sloman KA, Wilson RW (2006) Anthropogenic impacts upon behaviour and physiology. In: Sloman KA, Wilson RW, Balshine S (eds) Behaviour and physiology of fish. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 413–458
Smolders R, Bervoets L, De Boeck G (2002) Integrated condition indices as measure of whole effluent toxicity in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Toxicol Chem 21:87–93
Soengas JL, Agra-Lago MJ, Carballo B, Andrés MD, Veira JAR (1996) Effect of acute exposure to sublethal concentrations of cadmium on liver carbohydrate metabolism of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 57:625–631
Strand A, Magnhagen C, Alanara A (2007) Effects of repeated disturbances on feed intake, growth rates and energy expenditures of juvenile perch, Perca fluviatilis. Aquaculture 265:163–168
Suresh A, Sivaramakrishna B, Radhakrishnaiah K (1993) Effect of lethal and sublethal concentrations of cadmium on energetics in the gills of fry and fingerlings of Cyprinus carpio. Bull Env Contam Toxicol 51:920–926
van der Oost R, Beyer J, Vermeulen NPE (2003) Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: a review. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 13:57–149
Watson CF, Benson WH (1987) Comparative activity of gill ATPase in three freshwater teleosts exposed to cadmium. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 14:252–259
Wendelaar Bonga SE (1997) The stress response in fish. Physiol Rev 77:591–625
Widdows J, Donkin P (1991) Role of physiological energetics in ecotoxicology. Comp Biochem Physiol 100C:69–75
Widdows J, Salkeld PN (1993) Practical procedures for the measurement of scope for growth. MAP Teach Rep Ser 71:147–172
Wilson RW, Bergman HL, Wood CM (1994) Metabolic costs and physiological consequences of acclimation to aluminum in juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss).1: acclimation specificity, resting physiology, feeding and growth. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 51:527–535
Witeska M, Jezierska B, Wolnicki J (2006) Respiratory and hematological response of tench, Tinca tinca (L.) to a short-term cadmium exposure. Aquacult Internat 14:141–152
Wright DA, Welbourn PM (1994) Cadmium in the aquatic environment: a review of ecological, physiological, and toxicological effects on biota. Environ Rev 2:187–214
Zar JH (2010) Biostatistical analysis. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Acknowledgments
Authors wish to thank Mr. J. Perez (CIC) for cadmium measurements, Eng C. Marchesich for the determination of analytical composition of fish food, Dr. Mariela Borgnia for her help during experiments and to the reviewers’ valuables comments and suggestions that helped them to improve the original text of the manuscript This work was supported by grants from the National University of Lujan (Basic Sciences Department) and the Scientific Research Commission of Buenos Aires (CIC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferrari, L., Eissa, B.L. & Salibián, A. Energy balance of juvenile Cyprinus carpio after a short-term exposure to sublethal water-borne cadmium. Fish Physiol Biochem 37, 853–862 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-011-9483-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-011-9483-2