Abstract
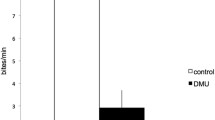
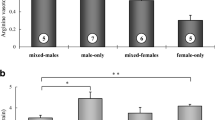
In this study, relationships between circulating androgens, aggressive behaviour and breeding tubercles in males of common bream Abramis brama were examined in an aquarium environment. The breeding tubercles of fish were counted, the number of attacks was quantified by male status and circulating rates of testosterone and 11-ketotestosterone from blood plasma were analysed using radioimmunoassay procedures. The results revealed that no significant differences were found between circulating testosterone and 11-ketotestosterone in territorial and nonterritorial males. Furthermore, no significant correlations were found between circulating androgens, androgens and aggression, androgens and tubercles and breeding tubercles and aggression in common bream by male status. However, territorial fish displayed a significantly higher level of aggressive behaviour and breeding tubercles than nonterritorial fish. In natural environments, the occurrence of breeding tubercles during the spawning season could contribute to identifying the behavioural status of common bream males.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adkins-Regan E (2005) Hormones and animal social behavior, vol 310. Princeton University Press (Monographs in Behavior and Ecology) Reviewed in Science, p 1905
Ahnelt H, Keckeis H (1994) Breeding tubercles and spawning behaviour in Chondrostoma nasus (Teleostei: Cyprinidea): a correlation? Ichtyol Explor Freshw 5:321–330
Balthazart J (1983) Hormonal correlates of behavior. Avian Biol 70:221–365
Bisazza A, Marconato A (1988) Female mate choice, male-male competition and parental care in the river bullhead Cottus gobio L. (Pisces, Cottidae) Anim Behav 36:1352–1360
Borg B (1994) Androgens in teleost fishes. Comp Biochem Physiol 109C:219–245
Cardwell JR, Liley NR (1991) Androgen control of social status in males of a wild population of Stoplight parrotfish, Sparisoma viride (Scaridae). Horm Behav 25:1–18
Elofsson UE, Mayer I, Damsgard B, Winberg S (2000) Intermale competition in sexually mature arctic charr: effects on brain monoamines, endocrine stress responses, sex hormone levels and behaviour. Gen Comp Endocrinol 118:450–460
Fostier A, Jalabert B (1985) Steroidogenesis in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) at various preovulatory stages: changes in plasma hormone levels and in vivo and in vitro response of the ovary to salmo gonadotropin. Fish Physiol Biochem 2:87–89
Gazola R, Borella MI (1997) Plasma testosterone and 11-ketotestosterone levels of male pacu Piaractus mesopotamicus (Cypriniformes, Characidae). Braz J Med Biol Res 30:1485–1487
Grand TC, Grant JWA (1994) Spatial predictability of food influences its monopolisation and defence by juvenile convict cichlids. Anim Behav 47:91–100
Jessop TS, Fitzsimmons N, Limpus CJ, Whitter JM (1999) Interactions between behaviour and plasma steroids within the scramble mating system of the promiscuous green turtle, Chelonia mydas. Horm Behav 36:86–97
Jobling M (1995) Environmental biology of fish. Fish and Fisheries series 16. Chapman & Hall, London, p 455
Kobayashi M, Sorensen PW, Stacey NE (2002) Hormonal and pheronomal control of spawning behavior in the goldfish. Fish Physiol Biochem 26:71–84
Kortet R, Taskinen J (2004) Parasitism, condition and number of front head breeding tubercles in roach (Rutilus rutilus L.). Ecol Freshw Fish 13:119–124
Kortet R, Vainikka A, Rantala MJ, Jokinen I, Taskinen J (2003) Sexual ornamentation, androgens and papillomatosis in male roach (Rutilus rutilus). Evol Ecol Res 5:411–419
Kortet R, Taskinen J, Vainikka A, Ylonen H (2004) Breeding tubercles, papillomatosis and dominance behaviour of male roach (Rutilus rutilus) during the spawning period. Ethology 110:591–601
Kozlovskij SV (1991) Observations of roach and bream spawning behaviour in the saratov reservoir. Vopr Ikhtiol 31:876–878
Liley NR, Stacey NE (1983) Hormones, pheromones, and reproductive behavior in fish. In: Hoar WS, Randall DJ, Donaldson EM (eds) Fish physiology, vo1 9 reproduction, part B: behavior and fertility control. Academic Press, New York, pp 1–63
Mackeretha RW, Noakesa DLG, Ridgway MS (1999) Size-based variation in somatic energy reserves and parental expenditure by male smallmouth bass, Micropterus dolomieu. Environ Biol Fish 56:263–275
Müller G, Ward PI (1995) Parasitism and heterozygosity influence the secondary sexual characters of the European minnow, Phoxinus phoxinus (L.) (Cyprinidae). Ethology 100:309–319
Nakagawa S (2004) A farewell to Bonferroni: the problems of low statistical power and publication bias. Behav Ecol 15:1044–1045
Nzau Matondo B, Ovidio M, Poncin P, Kakesa TA, Wamuini LS, Philippart JC (2007) Hybridization success of three common European cyprinid species, Rutilus rutilus, Blicca bjoerkna and Abramis brama and larval resistance to stress. Fish Sci 73:1136–1145
Nzau Matondo B, Ovidio M, Philippart JC, Poncin P (2009) Hybridization behaviour between two common European cyprinid fish species–silver bream, Blicca bjoerkna and common bream, Abramis brama–in a controlled environment. Anim Biol 59:97–108
Oliveira RF, Canario AVM (2001) Hormones and social behavior of cichlid fishes: a case study in the Mozambique tilapia. J Aquaricult Aquat Sci 9:187–207
Oliveira RF, Hirschenhauser K, Carneiro LA, Canario AVM (2002) Social modulation of androgen levels in male teleost fish. Comp Biochem Physiol 132B:203–215
Ota K, Kohda M (2006) Nest use by territorial males in a shell-brooding cichlid: the effect of reproductive parasitism. J Ethol 24:91–95
Pankhurst NW (1995) Hormones and reproductive behaviour in male damselfish. Bull Mar Sci 57:569–581
Parikh VN, Tricia SC, Russell DF (2006) Androgen level and male social status in the African cichlid, Astatotilapia burtoni. Beh Brain Res 166:291–295
Philippart JC (1981) Ecologie d’une population de vandoises, Leuciscus leuciscus (L.) dans la rivière Ourthe (Bassin de la Meuse, Belgique). Annls Limnol 17:41–62
Poncin P, Philippart JC, Ruwet JC (1996) Territorial and non territorial spawning behaviour in the bream. J Fish Biol 49:622–626
Poncin P, Binda O, Termol C, Chenuil A, Rinchard J, Kestemont P, Berriberi P, Ruwet JC (2000) Spawning tactics and reproductive success in two European cyprinids, the barbel (Barbus meridionalis) and the bream (Abramis brama): an overview. In: Proceedings of the 6th international symposium on the reproductive physiology of fish. Bergen, pp 132–134
Pottle RA, Green JM (1979) Territorial behaviour of the north temperate labrid, Tautogolabrus adspersus. Can J Zool 57:2337–2347
Ryer CH, Olla BL (1995) The influence of food distribution upon the development of aggressive and competitive behaviour in juvenile chum salmon, Oncorhynchus keta. J Fish Biol 46:264–272
Sabat AM (1994) Costs and benefits of parental effort in a brood-guarding fish (Ambloplites rupestris, Centrarchidae). Behav Ecol 5:195–201
Spillman CJ (1961) Faune de France, n° 65. Poissons d’eau douce Paul Le Chevalier, Paris 303p
Taborsky M (2001) The evolution of bourgeois, parasitic, and cooperative reproductive behaviours in fishes. J Hered 92:100–110
Takahashi D, Kohda M, Yanagisawa Y (2001) Male–male competition for large nests as a determinant of male mating success in a Japanese stream goby, Rhinogogius sp. DA. Ichthol Res 48:91–95
Vainikka A, Kortet R, Taskinen J (2004) Epizootic cutaneous papillomatosis, cortisol and male ornamentation during and after breeding in the roach Rutilus rutilus. Dis Aquat Organ 60:189–195
Vladykov VD, Renaud CB, Laframboise S (1985) Breeding tubercles in three species of Gadus (cods). Can J Fish Aquat Sci 42:608–615
Wiley ML, Collette BB (1970) Breeding tubercules and contact organs in fishes: their occurrence, structure, and significance. Bull Am Mus Nat Hist 143:143–216
Wingfield JC (1994) Hormone–behavior interactions and mating systems in male and female birds. In: Short RV, Balaban E (eds) The differences between the sexes. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 303–330
Wingfield JC, Lewis DM (1993) Hormonal and behavioural responses to simulated territorial intrusion in the cooperatively breeding white-browed sparrow weaver, Plocepasser mahali. Anim Behav 45:1–11
Witkowski A, Rogowska MW (1991) Breeding tubercles in some European cyprinid fishes (Osteichthyes, Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae). Zool Abhandlungen 9:129–155
Acknowledgements
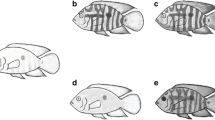
We thank A. Massin for drawing the picture and two anonymous referees for valuable comments on this manuscript. The correction of English has been funded by the project of FNRS (Fonds National de la Recherche Scientifique) N°1482.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poncin, P., Matondo, B.N., Termol, C. et al. Relationships between circulating androgens, aggressive behaviour and breeding tubercles in males of the common bream Abramis brama L. in an aquarium environment. Fish Physiol Biochem 37, 533–542 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-010-9455-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-010-9455-y