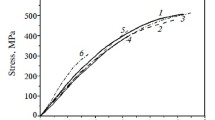
Abstract
The change in the mechanical properties of high-strength, high-modulus carbocyclic and heterocyclic para-aramids exposed to high (250, 275, 300°C) temperatures for up to 100 h was investigated. It was found that the change in the strength characteristics and elongation at break after prolonged thermal effects is diminishing in character. A small increase in the elongation, probably caused by predominance of the effect of structural transformations over degradation processes, was only observed in the fibres based on CpPABI in the initial period at 250 and 275°C. The data on the change in the strength and elongation at break as a function of the duration of the thermal effect are described by exponential dependences: second order for the elongation at break of Rusar and Armos fibres at 250 and 275°C and first-order in the other cases. The values of the coefficients in these dependences were found. The data obtained and curves approximating them describe the change in the strength and elongation at break of para-aramid fibres in the time range of up to 100 h and can be used to approximately predict the change in them over a longer period. The results of the study of the effect of high temperatures on the mechanical properties of high-strength, high-modulus para-aramid fibres can be used to determine the temperature boundaries of use of articles made from them. It follows from the data obtained that these articles can be used for a long time at 250 and even 275°C and briefly up to 300°C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. V. Avrorova, A. V. Volokhina, et al., Khim. Volokna, No. 4, 21–26 (1989).
G. I. Kudryavtsev, V. Ya. Varshavskii, et al., Reinforcing Chemical Fibres for Composite Materials [in Russian], Khimiya, Moscow (1992).
K. E. Perepelkin, Ros. Khim. Zh., 46, No. 1, 31–48 (2002).
K. E. Perepelkin, in: High-Performance Fibres, J. W. S. Hearle (ed.), Woodhead, Cambridge (2001), pp. 115–132; 146–154.
K. E. Perepelkin, N. N. Machalaba, and V. A. Kvaratskheliya, Khim. Volokna, No. 2, 22–29 (2001).
K. E. Perepelkin, N. N. Machalaba, et al., Vestn. Sankt-Peterburg. Gos. Univ. Tekhnol. Dizaina, No. 4, 64–83 (2000).
K. E. Perepelkin and N. N. Matchalaba, Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst., Ser. Sci. Technol., 354, 275–286 (2000).
L. P. Kobets, in: Thermal Stability of Construction Plastics [in Russian], E. B. Trostyanskaya (ed.), Khimiya, Moscow (1980), pp. 107–135.
K. E. Perepelkin, S. A. Baranova, et al., Tekst. Prom-st’, No. 4–5, 28–30 (1995).
K. E. Perepelkin, S. A. Baranova, and E. Yu. Gurova, Khim. Volokna, No. 1, 34–37 (1995).
K. E. Perepelkin, I. V. Andreeva, et al., Khim. Volokna, No. 4, 22–26 (2003).
K. E. Perepelkin, O. B. Malan’ina, et al., Khim. Volokna, No. 5, 45–48 (2004).
K. E. Perepelkin, E. A. Pakshver, et al., Khim. Volokna, No. 5, 27–31 (2005).
I. N. Pavlov, Aging of Plastics in Natural and Artificial Conditions [in Russian], Khimiya, Moscow (1982).
I. N. Pavlov, V. A. Sade, and G. A. Kudryavtseva, Plast. Massy, No. 3, 52–54 (1974).
K. E. Perepelkin, I. Yu. Morgoeva, et al., Khim. Volokna, No. 1, 45–49 (2001).
B. D. Goikhman, Plast. Massy, No. 2, 56–58 (1971).
B. D. Goikhman, Usp. Khim., 49, No. 5, 1554–1566 (1980).
B. D. Goikhman and S. V. Kuznetsov, Plast. Massy, No. 7, 47–48 (1985).
B. M. Kovarskaya, A. V. Blyumenfel’d, and I. I. Levantovskaya, Thermal Stability of Heterochain Polymers [in Russian], Khimiya, Moscow (1977).
A. A. Askadskii, Structure and Properties of Thermostable Polymers [in Russian], Khimiya, Moscow (1981).
Yu. I. Matveev, V. V. Askadskii, et al., Vysokomolek. Soedin., 18, No. 9, 2013 (1981).
K. Yu. Byuller, Thermostable and Heat-Resistant Polymers [in Russian], Khimiya, Moscow (1984).
A. T. Kalashnik, Khim. Volokna, No. 4, 22–26 (1987).
L. S. Efros and L. E. Utevskii, Vysokomolek. Soedin., Ser. B, No. 4, 309–313 (1975).
K. E. Perepelkin and A. E. Gal’, Thermal Properties of Chemical Fibres [in Russian], NIITEKhim, Moscow (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
__________
Translated from Khimicheskie Volokna, No. 5, pp. 44–49, September–October, 2006.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perepelkin, K.E., Andreeva, I.V., Meshcheryakova, G.P. et al. Change in the mechanical properties of para-aramid fibres in thermal aging. Fibre Chem 38, 400–405 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10692-006-0099-8
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10692-006-0099-8