Abstract
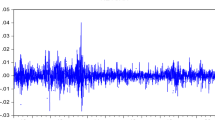
The paper is concerned with time series modelling of foreign exchange rate of an important emerging economy, viz., India, with due consideration to possible sources of misspecification of the conditional mean like serial correlation, parameter instability, omitted time series variables and nonlinear dependences. Since structural change is pervasive in economic time series relationships, the paper first studies this aspect of the exchange rate series in detail and finds the existence of four structural breaks. Accordingly, the entire sample period is divided into five sub-periods of stable parameters each, and then the appropriate mean specification for each of these sub-periods is determined by incorporating functions of recursive residuals. Thereafter, the GARCH and EGARCH models are considered to capture the volatility contained in the data. The estimated models thus obtained suggest that return on Indian exchange rate series is marked by instabilities and that the appropriate volatility model is EGARCH. Further, out-of-sample forecasting performance of the model has been studied by standard forecasting criteria, and then compared with that of an AR model only to find that the findings are quite favorable for the former.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalla, I. S. A., & Murinde, V. (1997). Exchange rate and stock price interactions in emerging financial markets: Evidence on India, Korea, Pakistan and the Philippines. Applied Financial Economics, 7, 25–35.
Aggarwal, R. (1981). Exchange rates and stock prices: A study of the US capital markets under floating exchange rates. Akron Business and Economic Review, 12, 7–12.
Ajayi, R. A., & Mougoue, M. (1996). On the dynamic relation between stock prices and exchange rates. Journal of Financial Research, 19, 193–207.
Ajayi, R. A., Friedman, J., & Mehdian, S. M. (1998). On the relationship between stock returns and exchange rates: Test of granger causality. Global Finance Journal, V9(2, Fall/Spring), 241–251.
Andrews, D. W. K. (1993). Tests for parameter instability and structural change with unknown change point. Econometrica, 61(4), 821–856.
Andrews, D. W. K. (2003). Tests for parameter instability and structural change with unknown change point: A corrrigendum. Econometrica, 71(1), 395–397.
Andrews, D. W. K., & Ploberger, W. (1994). Optimal tests when a nuisance parameter is present only under the alternative. Econometrica, 62(6), 1383–1414.
Backus, D. (1984). Empirical models of the exchange rate: Separating the wheat from the chaff. Canadian Journal of Economics, 17, 824–846.
Bai, J. (1994). Least squares estimation of a shift in linear processes. Journal of Time Series Analysis, 15(5), 453–472.
Bai, J. (1997a). Estimation of a change point in multiple regression models. Review of Economics and Statistics, 79(4), 551–563.
Bai, J. (1997b). Estimating multiple breaks once at a time. Econometric Theory, 13(3), 315–352.
Bai, J., & Perron, P. (1998). Estimating and testing linear models with multiple structural changes. Econometrica, 66(1), 271–287.
Baillie, R. T., & Bollerslev, T. (1989). The message in daily exchange rates: A conditional-variance tale. Journal of Business and Economic Statistics, 7, 297–305.
Bekaert, G. (1992). The time-variation of expected returns and volatility in foreign exchange markets, Mimeo, Northwestern University.
Bhaumik, S. K., & Mukhopadhyay, H. (2000). RBI’s intervention in foreign exchange market. An␣econometric analysis. Economic and Political Weekly, 35(5), 373–376.
Bollen, N. P. B., Gray, S. F., & Whaley, R. (2000). Regime switching in foreign exchange rates: Evidence from currency option prices. Journal of Econometrics, 94, 239–276.
Bollerslev, T. (1986). Generalised autoregressive conditional heteroskedasticity. Journal of Econometrics, 31, 307–327.
Bollerlev, T. (1990). Modelling the coherence in short-run nominal exchange rates: A multivariate generalized ARCH approach. Review of Economics and Statistics, 72, 498–505.
Brooks, C. (2002). Introductory econometrics for finance. Cambridge University Press.
Boughton, J. (1988). The monetary approach to exchange rates: What now remains? Essays in International Finance, Vol. 171. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University.
Chong, T. T.-L. (1995). Partial parameter consistency in a misspecified structural change model. Economics Letters, 49(4), 351–357.
Chow, G. C. (1960). Tests of equality between sets of coefficients in two linear regressions. Econometrica, 28(3), 591–605.
Diebold, F. X. (1988). Empirical modelling of exchange rate dynamics. New York: Springer Verlag.
Dornbusch, R. (1976). Expectations and exchange rate dynamics. Journal of Political Economy, 84, 1161–1176.
Dornbusch, R. (1987). Flexible exchange rates 1986. Economic Journal, 1, 1–18.
De Gooijer, J. G., & Kumar, K. (1992). Some recent developments in non-linear time series modelling, testing and forecasting. International Journal of Forecasting, 8, 135–156.
Engle, R. F. (1982). Autoregressive conditional heteroskedasticity with estimates of the variance of U.K. inflation. Econometrica, 55, 252–276.
Fuller, W. A. (1976). Introduction to statistical time series. New York.
Frankel, J. A. (1993). Monetary and portfolio-balance models of the determination of exchange rates. On exchange rates. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Gerlow, M. E., Irwin, S. H., & Liu, T. R. (1993). Economic evaluation of commodity price forecasting models. International Journal of Forecasting, 9, 387–397.
Ghosh, S. K. (2002). RBI intervention in the forex market: Results from a tobit and logit model using daily data. Economic and Political Weekly, 37(24), 2333–2348.
Golub, S. (1989). Foreign-currency government debt, asset markets, and the balance of payments. Journal of International Money and Finance, 8, 285–294.
Grilli, V., & Kaminsky, G. (1991). Nominal exchange rates regimes and the real exchange rate. Journal of Monetary Economics, 27,191–212.
Guilkey, D. K., & Schmidt, P. (1989). Extended tabulations for Dickey–Fuller tests. Economic Letters, 31, 355–357.
Hall, A. (1994). Testing for a unit root in time series with pretest data-based model selection. Journal of Business and Economic Statistics, 12, 461–470.
Hansen, B. E. (1997). Approximate asymptotic P values for structural-change tests. Journal of␣Business and Economic Statistics, 15(1), 60–67.
Hansen, B. E. (2001). The new econometrics of structural change: Dating breaks in U.S. labor productivity. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 15, 117–128.
Hooper, P., & Morton, J. (1982). Fluctuations in the dollar: A model of nominal and real exchange rate determination. Journal of International Money and Finance, 1, 39–56.
Hsieh, D. A. (1989). Modelling heteroscedasticity in daily foreign-exchange rates. Journal of␣Business and Economics Statistics 7(3), 307–317.
Huizinga, J. (1987). An empirical investigation of the long-run behavior of real exchange rates. Carnegie-Rochester Conference series on Public Policy, Vol 27, pp. 149–214.
Joshi, H., & Saggar, M. (1998). Excess returns, risk premia and efficiency of the foreign exchange market: Indian experience in the post-liberalisation period. Reserve Bank of India, Occasional Papers Issue, June 1998.
Kenen, P. (1988). Managing exchange rates. New York: The Royal Institute of International affairs, Council on Foreign Relations Press.
Kim, Ki ho (2003). Dollar exchange rate and stock price: Evidence from multivariate cointegration and error correction model. Review of Financial Economics, 12, 301–313.
Kim, S., & Roubini, N. (2000). Exchange rate anomalies in the industrial countries: A solution with a structural VAR approach. Journal of Monetary Economics, 45, 561–586.
Kohli, R. (2000). Aspects of exchange rate behaviour and management in India 1993–98. Economic and Political Weekly, 35(5), 365–371.
Kohli, R. (2002). Real exchange rate stationarity in managed floats: Evidence from India. Economic and Political Weekly, 37(5), 475–482.
Lumsdaine, R. L., & Ng, S. (1999). Testing for ARCH in the presence of a possibly misspecified conditional mean. Journal of Econometrics, 93, 257–279.
MacDonald, R. (1990a). Are exchange market forecasters ‘rational’: Some survey-based tests. The Manchester School of Economic and Social Studies, 58, 229–241.
MacDonald, R. (1990b). Exchange rate economics: An empirical perspective. In G. Bird (Ed.), The international financial regime (pp. 91–144). London: Academic Press Ltd.
MacDonald, R., & Taylor, M. P. (1989). Economic analysis of foreign exchange markets: An expository survey. In R. MacDonald & M. P. Taylor (Eds.), Exchange rates and open economy macroeconomics (pp. 1–108). Oxford, UK: Basil Blackwell.
MacDonald, R., & Taylor, M. P. (1992). Exchange rate economics. International Monetary Fund Staff Papers, 39, 1–57.
MacDonald, R., & Taylor, M. P. (1993). Exchange rate behavior under alternative exchange rate arrangements. International Monetary Fund: mimeo
MacKinnon, J. G. (1994). Approximate asymptotic distribution functions for unit root and cointegration tests. Journal of Business and Economic Statistics, American Statistical Association, 12(2), 167–176.
Malik, A. K. (2005). European exchange rate volatility dynamics: An empirical investigation. Journal of Empirical Finance, 12, 187–215.
Meese, R. A. (1990). Currency fluctuations in the post-Bretton Woods era. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 4, 117–134.
Meese, R. A., & Rogoff, K. (1983a). Empirical exchange rate models of the seventies: Do they fit out in sample? Journal of International Economics, 14, 3–24.
Meese, R. A., & Rogoff, K. (1983b). The out-of-sample failure of empirical exchange rate models: Sampling error or misspecification? Exchange rates and International Macroeconomics published by the University of Chicago Press.
Milhoj, A. (1987). A conditional variance model of daily observations of an exchange rate. Journal of Business and Economic Statistics, 5, 99–103.
Mussa, M. (1990). Exchange rates in theory and in reality. Essays in International Finance No. 179. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University.
Nelson, D. B. (1991). Conditional heteroskedasticity in asset returns: A new approach. Econometrica, 59, 347–370.
Nelson, D. B., & Cao, C.Q. (1992). Inequality constraints in the univariate GARCH model. Journal of Business and Economic Statistics, 10, 229–235.
Nieh, C.-C., & Lee, C.-F. (2001). Dynamic relationship between stock prices and exchange rates for G-7 countries. Quarterly Review of Economics and Finance, 41(4), 477–490.
Pattanaik, S., & Mitra, A. K. (2001). Interest rate defence of exchange rate, tale of the Indian Rupee. Economic and Political Weekly, 36(46,47), 4418–4427.
Pattnaik, R. K., Kapur, M., & Dhal, S. C. (2003). Exchange rate policy and management: The Indian experience. Economic and Political Weekly, 38(22), 2139–2154.
Phylaktis, K., & Ravazzolo, F. (2005). Stock prices and exchange rate dynamics. Journal of␣International Money and Finance, 24, 1031–1053.
Quandt, R. (1960). Tests of the hypothesis that a linear regression obeys two separate regimes. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 55, 324–330.
Ramsey, J. B. (1969). Tests for specification error in classical linear least squares analysis. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B, 31, 350–371.
Ramsey, J. B., & Schmidt, P. (1976). Some further results on the use of OLS and BLUS residuals in sprecification error tests. Journal of American Statistical Association, 71, 389–390.
Rao, M. (2000). On predicting exchange rates. Economic and Political Weekly, 35(5) (January 29).
Sarkar, N., & Mukhopadhyay, D. (2005). Testing predictability and non-linear dependence in Indian stock market. Emerging Markets Finance and Trade, 41(6), 7–44.
Unnikrishnan, N. K., & Ravi Mohan, P. R. (2001). Exchange rate dynamics: An Indian perspective. Reserve Bank of India Occasional Papers, 22(1), 2–3.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank two anonymous referees for their useful suggestions on the first draft of this paper. The responsibility of remaining errors, if any, lies with the authors only.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kar, R., Sarkar, N. Mean and volatility dynamics of Indian rupee/US dollar exchange rate series: an empirical investigation. Asia-Pacific Finan Markets 13, 41–69 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10690-007-9034-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10690-007-9034-0