Abstract
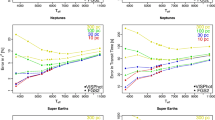
The absolute stability of the PACS bolometer response over the entire mission lifetime without applying any corrections is about 0.5 % (standard deviation) or about 8 % peak-to-peak. This fantastic stability allows us to calibrate all scientific measurements by a fixed and time-independent response file, without using any information from the PACS internal calibration sources. However, the analysis of calibration block observations revealed clear correlations of the internal source signals with the evaporator temperature and a signal drift during the first half hour after the cooler recycling. These effects are small, but can be seen in repeated measurements of standard stars. From our analysis we established corrections for both effects which push the stability of the PACS bolometer response to about 0.2 % (stdev) or 2 % in the blue, 3 % in the green and 5 % in the red channel (peak-to-peak). After both corrections we still see a correlation of the signals with PACS FPU temperatures, possibly caused by parasitic heat influences via the Kevlar wires which connect the bolometers with the PACS Focal Plane Unit. No aging effect or degradation of the photometric system during the mission lifetime has been found.











Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Applying IDL’s biweight_mean routine that uses Tukey’s biweight method for robust moment estimation.
References
Balog, Z., Müller, T., Nielbock, M., Altieri, B., Klaas, U., Linz, H., Lutz, D., Moór, A., Billot, N., Sauvage, M., Okomura, K.: The Herschel-PACS photometer calibration: point-source flux calibration. Exp. Astron. this issue (2013)
Billot, N., Sauvage, M., Rodriguez, L., et al.: CEA bolometer arrays: the first year in space. SPIE 7741, 1 (2010)
Klaas, U., Nielbock, M.: PACS Performance Verification Phase Plan, Issue 1.6, PICC-MA-PL-001, available from http://pacs.ster.kuleuven.be/Documents/WBS/CAL/014/010/PICC-MA-PL-001_PACS-PV-Plan_v1p6.pdf (2009)
Müller, T.: Pacs FM (ILT, IST, TVTB, CoP) Full Functional Test: 413 Thermal Behaviour in Photometry, available from http://pacs.ster.kuleuven.be/Documents/WBS/FlightReports/012/001/tb_phot_v20090703.pdf (2009)
Nielbock, N., Müller, T., Balog, Z., Klaas, U., Linz, H.: The Herschel PACS photometer calibration: a time dependent flux calibration for the PACS chopped photometry AOT mode. Exp. Astron. this issue (2013)
Pilbratt, G.L., Riedinger, J.R., Passvogel, T., et al.: Herschel space observatory. An ESA facility for far-infrared and submillimetre astronomy. A&A 518, L1 (2010)
Poglitsch, A., Waelkens, C., Geis, N., et al.: The Herschel photodetector array camera & pectrometer (PACS): design and in-flight operation and scientific performance. A&A 518, L2 (2010)
Acknowledgments
We thank our anonymous referee whose comments significantly improved the manuscript. This research has been supported by the PECS programme of the Hungarian Space Office and the European Space Agency (contact number: 98073). CK and AM acknowledge the support of the Hungarian Research Fund (OTKA K-104607) and that of the Bolyai Research Fellowship of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moór, A., Müller, T.G., Kiss, C. et al. PACS photometer calibration block analysis. Exp Astron 37, 225–238 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10686-013-9360-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10686-013-9360-3