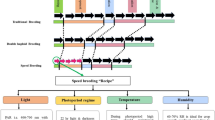
Abstract
Pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum [L.] R. Br., 2n = 2x = 14) is a nutrient-dense and climate-resilient crop widely cultivated in the dry regions of Africa and Asia. In Burkina Faso, the actual mean yield of the crop is < 1 ton/ha compared with a potential yield of 3 tons/ha. Several constraints, including cultivar susceptibility to the noxious weed Striga hermonthica (Del.) Bentham (Sh) and severe and recurrent drought stress limit the potential productivity of the crop. Therefore, this study aimed to determine the combining ability effects and degree of heterosis for agronomic traits and resistance to Sh among complementary pearl millet genotypes to select promising parental lines and hybrids to develop and deploy farmer-preferred varieties. The narrow-and broad-sense heritability were relatively higher for Striga-resistance (≥ 70%) and low (≤ 23%) for grain yield. The general combining ability and specific combining ability ratios were less than unity for agronomic traits and Striga reaction indicating the predominance of non-additive gene action conditioning the assessed traits. The new experimental hybrids such as IP-11358 × ICMB177111, IP-11358 × IKMB18002, IP-10579 × ICMB177002 and IP-9242 × ICMB177002 are recommended for multi-environment evaluation and production in Sh-infested pearl millet cultivation agro-ecologies in Burkina Faso or similar agro-ecologies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Acharya ZR, Khanapara M, Chaudhari V, Dobaria JD (2017) Exploitation of heterosis in pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum [L.] R. Br.) for yield and its component traits by using male sterile line. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 6(12):750–759. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.612.079
Acquaah G (2012) Principles of plant genetics and breeding, 2nd edn. Wiley, Hoboken, p 740
Baker R (1978) Issues in diallel crosses. Crop Sci 18(4):533–536
Balami G, Izge AU, Sabo M, Buba U, Fagam A (2022) Combining ability analysis for Striga tolerance among pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum [L.] R. Br.) inbreds in a line × tester cross. Direct Res J Agric Food Sci 10(1):1–10
Barathi MB, Lakshmi BV, Reddy PS, Umar SN (2020) Heterosis and combining ability studies in indigenous collection of pearl millet germplasm (Pennisetum glaucum [L.] R. Br.). Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 9(10):2648–2660
Boussim I, Yonli D, Guinko S, Sallé G (2011) Infestation status, endogenous knowledge and systematic approach to species of the genus Striga in Burkina Faso. Int J Biol Chem Sci 5(4):1374–1386
Burgarella C, Cubry P, Kane NA, Varshney RK, Mariac C, Liu X, Shi C, Thudi M, Couderc M, Xu X, Chitikineni A, Scarcelli N, Barnaud A, Rhoné B, Dupuy C, François O, Berthouly-Salazar C, Vigouroux Y (2018) A western Sahara centre of domestication inferred from pearl millet genomes. Nat Ecol Evol 2(9):1377–1380. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-018-0643-y
Chittora K, Patel J (2017) Estimation of heterosis for grain yield and yield components in pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum [L.] R. Br.). Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 6(3):412–418. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.603.047
Dawud MA (2018) Genetic studies of pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum [L.] R. Br.)for resistance to Striga hermonthica. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Ghana, p 168. http://ugspace.ug.edu.gh
De Mendiburu F, de Mendiburu MF (2019) Package ‘agricolae’. R Package, version, 1(3)
Divya B, Biswas A, Robin S, Rabindran R, Joel AJ (2014) Gene interactions and genetics of blast resistance and yield attributes in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Genet 93:415–424
Drabo I (2016) Breeding pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum [L.] R. BR.) for downy mildew resistance and improved yield in Burkina Faso. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Ghana, p 154. http://ugspace.ug.edu.gh
Drabo I, Zangre RG, Danquah EY, Ofori K, Witcombe JR, Hash C (2018) Identifying farmers’ preferences and constraints to pearl millet production in the Sahel and North-Sudan zones of Burkina Faso. Exp Agric 55(5):765–775. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0014479718000352
ECOWAS-UEMOA-CILSS (2021) Regional catalogue of plant species and varieties, p 38
Falconer DS, Mackay TF (1996) Introduction to quantitative genetics. Pearson Education India, p 371
FAOSTAT (2022) FAOSTAT online database 2022: Rome Italy. https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL
Ghatak A, Chaturvedi P, Nagler M, Roustan V, Lyon D, Bachmann G, Postl W, Schröfl A, Desai N, Varshneyd RK, Weckwerth W (2016) Comprehensive tissue-specific proteome analysis of drought stress responses in Pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum [L.] R. Br.). J Proteomics 143:122–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2016.02.032
Gupta V, Singh AP, Gupta N (2022) Importance of pearl millet and its health benefits. Just Agric Multidiscip Newsl 2(7):1–3
Haussmann BI, Hess DE, Welz HG, Geiger HH (2000) Improved methodologies for breeding Striga-resistant sorghums. Field Crop Res 66(3):195–211
INERA (2000) Bilan de 10 années de recherche. 1988–1998. CNRST/INERA/CTA. Burkina Faso, p 114
Jeeterwal R, Sharma L, Nehra A (2018) Genetic component analysis of grain yield and iron and zinc content in pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum [L.] R. Br.) under varying environmental conditions. Ann Plant Soil Res 20(3):294–297
Kanampiu F, Makumbi D, Mageto E, Omanya G, Waruingi S, Musyoka P, Ransom J (2018) Assessment of management options on Striga infestation and maize grain yield in Kenya. Weed Sci 66(4):516–524. https://doi.org/10.1017/wsc.2018.4
Karaya H, Njoroge K, Mugo SN, Ariga ES, Kanampiu F, Nderitu J (2014) Combining ability of maize (Zea mays) inbred lines resistant to Striga hermonthica (Del.) Benth evaluated under artificial Striga infestation. Afr J Agric Res 9(16):1287–1295
Kempthorne O (1957) An introduction to genetic statistics, 1st edn. Wiley, New York, p 545
Kountche BA, Al-Babili S, Haussmann BIG (2016) Striga: a persistent problem on millets. Biotic stress resistance in millets. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 173–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-804549-7.00006-8
Kumawat KR, Gupta PC, Sharma NK (2019) Combining ability and gene action studies in pearl millet using line × tester analysis under arid conditions. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 8(04):976–984
Lobulu J, Shimelis H, Laing MD, Mushongi AA, Shayanowako AI (2023) Progeny testing of maize (Zea mays) genotypes for grain yield and yield components Striga-resistance and Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Strigae compatibility. Plant Breed 142(3):284–299
MARAH (2022) Agro-sylvopastoral statistics yearbook 2021, pp 573
Nduwumuremyi A, Tongoona P, Habimana S (2013) Mating design: helpful tool for quantitative plant breeding analysis. J Plant Breed Genet 1(3):117–129
Parker C (2009) Observations on the current status of Orobanche and Striga problems worldwide. Pest Manag Sci 65(5):453–459. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.1713
Parker C (2012) Parasitic weeds: a world challenge. Weed Sci 60(2):269–276. https://doi.org/10.1614/WS-D-11-00068.1
R Core Team (2021) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. URL https://www.R-project.org/
Rattunde HF (1988) Mass selection strategies for pearl millet improvement. Ph.D. thesis, Iowa State University, pp 118
Rodrı́guez F, Alvarado G, Pacheco A, Crossa J, Burgueño J (2015) Analysis of genetic designs with r for windows (AGD-r) version 5.0. In: Biometrics and statistical unit. CIMMYT, El Batań, Mexico
Rouamba A, Shimelis H, Drabo I, Laing M, Gangashetty P, Mathew I, Mrema E, Shayanowako AIT (2021) Constraints to pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum [L.] R. Br.) production and farmers’ approaches to Striga hermonthica management in Burkina Faso. Sustainability 13(15):8460
Sangaré S, Menkir A, Ofori K, Gracen V (2018) Combining ability for grain yield, agronomic traits and Striga hermonthica resistance of yellow endosperm maize. J Plant Genet Breed 2:107
Sanghera GS, Hussain W (2012) Heterosis and combining ability estimates using line × tester analysis to develop rice hybrids for temperate conditions. Not Scientia Biologicae 4(3):131–142
Santosh T, Sadhana K, Reddy GA, Patil HT (2018) Assessment of combining ability and gene action in pearl millet (Pennisetum Glaucum [L.] R. Br.) using line × tester analysis. Indian J Pure Appl Biosci 6(2):172–177. https://doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.5057
Sharma R, Singh J (2019) Combining ability and gene action studies for yield and component traits in pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum [L.] R. Br.). J Agric for Meteorol Res 2(1):63–72
Shivhare R, Lata C (2017) Exploration of genetic and genomic resources for abiotic and biotic stress tolerance in pearl millet. Front Plant Sci 7:2069. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.02069
Sumathi P, Revathi S (2017) Heterosis and variability studies for yield and yield components traits in pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum [L.] R. Br.). Electron J Plant Breed 8(2):528–533. https://doi.org/10.5958/0975-928X.2017.00079.5
Sumit S, Wali MC (2016) Heterosis for yield and yield related components using diverse restorer lines in pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum [L.] R. Br.). J Farm Sci 29(4):436–438
Yehia W, El-Hashash E (2019) Combining ability effects and heterosis estimates through line × tester analysis for yield, yield components and fiber traits in Egyptian cotton. J Agron Technol Eng Manag 2(2):248–262
Yoder JI, Scholes JD (2010) Host plant resistance to parasitic weeds; recent progress and bottlenecks. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13(4):478–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2010.04.011
Zebire D, Menkir A, Adetimirin V, Mengesha W, Meseka S, Gedil M (2020) Effectiveness of yellow maize testers with varying resistance reactions to Striga hermonthica for evaluating the combining ability of maize inbred lines. Agronomy 10(9):1276. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10091276
Zebire D, Menkir A, Adetimirin V, Mengesha W, Meseka S, Gedil M (2021) Identifying suitable tester for evaluating Striga-resistant lines using DArTseq markers and agronomic traits. PLoS ONE 16(6):e0253481. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0253481
Acknowledgements
The African Centre for Crop Improvement (ACCI) is acknowledged for the administration work that facilitated the first author’s study. The authors would furthermore like to thank the International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) and International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT).
Funding
The research was funded by the International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) through the ‘Harnessing Opportunities for Productivity Enhancement (HOPE II) for Sorghum and Millets in sub-Saharan Africa’ project (OPP1198373), funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AR: Methodology, data collection, data analysis, and Writing of the manuscript draft. HS: Supervision, writing conceptualization, review, and editing. ID: Guided experiment designing, writing, reviewing and editing. EM: Reviewing and editing. JM: Reviewing and editing. LM: Reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent to participate
All authors agreed to participate in this work willingly.
Consent for publication
All authors agreed to have this paper published in this journal by open access.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rouamba, A., Shimelis, H., Drabo, I. et al. Combining ability and hybrid breeding in pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum [L.] R. Br.) for agronomic traits and resistance to Striga hermonthica. Euphytica 220, 62 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-024-03320-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-024-03320-7