Abstract
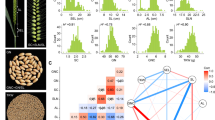
Rice grain size directly affects grain yield and is an important quantitative trait target. Many genes regulating grain size have been mapped and cloned in recent years. These genes not only play a single role on grain size regulation but have mutual interactive effect on grain size. Mining key allele combinations of grain-size regulating genes will favorite the pyramiding of favorable alleles in rice varieties with desired grain size and shape that meet people’s preferences. Here, we studied the effect of seven major grain-size regulating genes (GS3, GS5, GW8/OsSPL16, BG2, GS6, GS2 and TGW3) and their allele combinations on grain size-related traits (grain length, grain width, grain length width ratio, thousand grain weight), and established multiple regression equations to predict rice grain size. We found that alleles of seven genes displayed significant differences in rice grain size. Among the seven genes, GS3 gene played the most important effect in regulating grain size, pyramiding GS3 alleles with other alleles such as GS6-II/III allele could significantly enhance grain size or grain weight. Specific allele combination of GS3-A, GS2-ZH11, GS5-Zhenshan97, GS6-II/III, BG2-9311 and GW8-HJX74 can produce rice varieties with slender grains; allele combination of GS3-A, GS6-I, BG2-Nipponbare and TGW3-CW23 produce grains with higher grain weight. The regression equation model developed in this study provided a useful tool to predict rice grain size. These results would help in breeding rice varieties with ideal traits and high yield by pyramiding favorable alleles.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data is enclosed either in the main text or as supplementary data.
References
Calingacion M, Laborte A, Nelson A, Resurreccion A, Concepcion JC, Daygon VD, Mumm R, Reinke R, Dipti S, Bassinello PZ, Manful J, Sophany S, Lara KC, Bao J, Xie L, Loaiza K, El-hissewy A, Gayin J, Sharma N, Rajeswari S, Manonmani S, Rani NS, Kota S, Indrasari SD, Habibi F, Hosseini M, Tavasoli F, Suzuki K, Umemoto T, Boualaphanh C, Lee HH, Hung YP, Ramli A, Aung PP, Ahmad R, Wattoo JI, Bandonill E, Romero M, Brites CM, Hafeel R, Lur HS, Cheaupun K, Jongdee S, Blanco P, Bryant R, Thi Lang N, Hall RD, Fitzgerald M (2014) Diversity of global rice markets and the science required for consumer-targeted rice breeding. PLoS ONE 9(1):e85106. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0085106
Chen N, Luo YK, Zhu ZW, Zhang BP, Zhen YC, Xie LH (1997) Correlation between eating quality and phisco-chemical properties of high grain quality rice. Chin J Rice Sci 2(02):70–76. https://doi.org/10.16819/j.1001-7216.1997.02.002
Chen K, Lyskowski A, Jaremko L, Jaremko M (2021) Genetic and molecular factors determining grain weight in rice. Front Plant Sci 12:605799. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.605799
Fan C, Xing Y, Mao H, Lu T, Han B, Xu C, Li X, Zhang Q (2006) GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein. Theor Appl Genet 112(6):1164–1171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0218-1
Fan C, Yu S, Wang C, Xing Y (2009) A causal C-A mutation in the second exon of GS3 highly associated with rice grain length and validated as a functional marker. Theor Appl Genet 118(3):465–472. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-008-0913-1
Gao X, Zhang X, Lan H, Huang J, Wang J, Zhang H (2015) The additive effects of GS3 and qGL3 on rice grain length regulation revealed by genetic and transcriptome comparisons. BMC Plant Biol 15:156. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-015-0515-4
Gull S, Haider Z, Gu H, Raza Khan RA, Miao J, Wenchen T, Uddin S, Ahmad I, Liang G (2019) InDel marker based estimation of multi-gene allele contribution and genetic variations for grain size and weight in Rice (Oryza sativa L). Int J Mol Sci 20(19):4824. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194824
Haghshenas H, Soltani A, Ghanbari Malidarreh A, Ajam Norouzi H, Dastan S (2019) Selecting the ideotype of improved rice cultivars using multiple regression and multivariate models. Arch Agron Soil Sci 66(8):1134–1153. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2019.1658866
Hu ZJ, Lu SJ, Wang MJ, He HH, Sun L, Wang HR, Liu XH, Jiang L, Sun JL, Xin XY, Kong W, Chu CC, Xue HW, Yang JS, Luo XJ, Liu JX (2018) A novel QTL qTGW3 encodes the GSK3/SHAGGY-Like kinase OsGSK5/OsSK41 that interacts with OsARF4 to negatively regulate grain size and weight in Rice. Mol Plant 11(5):736–749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2018.03.005
Hu J, Wang YX, Fang YX, Zeng LJ, Xu J, Yu HP, Shi ZY, Pan JJ, Zhang D, Kang SJ, Zhu L, Dong GJ, Guo LB, Zeng DL, Zhang GH, Xie LH, Xiong GS, Li JY, Qian Q (2015) A rare allele of GS2 enhances grain size and grain yield in Rice. Mol Plant 8(10):1455–1465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2015.07.002
Huang H, Ye Y, Song W, Li Q, Han R, Wu C, Wang S, Yu J, Liu X, Fu X, Liu Q, Wu K (2022) Modulating the C-terminus of DEP1 synergistically enhances grain quality and yield in rice. J Genet Genomics 49(5):506–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgg.2022.01.009
Lee CM, Park J, Kim B, Seo J, Lee G, Jang S, Koh HJ (2015) Influence of multi-gene allele combinations on grain size of rice and development of a regression equation model to predict grain parameters. Rice (N Y) 8(1):33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-015-0066-1
Lei H, Wenhua L, Jiang H, Chunfang Z, Shu Y, Tao C, Zhen Z, Qingyong Z, Kai L, Ling Z, Lihui Z, Qian Q, Cailin W, Yadong Z (2023) Additive effects of QTLs/genes on rice grain size traits revealed by genetic comparisons. Rice Sci 30(3):171–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsci.2023.03.001
Lestari P, Ham TH, Lee HH, Woo MO, Jiang WZ, Chu SH, Kwon SW, Ma K, Lee JH, Cho YC, Koh HJ (2009) PCR marker-based evaluation of the eating quality of Japonica Rice (Oryza sativa L). J Agric Food Chem 57(7):2754–2762. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf803804k
Li YB, Fan CC, Xing YZ, Jiang YH, Luo LJ, Sun L, Shao D, Xu CJ, Li XH, Xiao JH, He YQ, Zhang QF (2011) Natural variation in GS5 plays an important role in regulating grain size and yield in rice. Nat Genet 43(12):1266. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.977
Li N, Xu R, Duan P, Li Y (2018) Control of grain size in rice. Plant Reprod 31(3):237–251. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00497-018-0333-6
Makino A, Kaneta Y, Obara M, Ishiyama K, Kanno K, Kondo E, Suzuki Y, Mae T (2020) High yielding ability of a large-grain rice cultivar, Akita 63. Sci Rep-Uk. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-69289-0
Muthayya S, Sugimoto JD, Montgomery S, Maberly GF (2014) An overview of global rice production, supply, trade, and consumption. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1324:7–14. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.12540
Ngangkham U, Samantaray S, Yadav MK, Kumar A, Chidambaranathan P, Katara JL (2018) Effect of multiple allelic combinations of genes on regulating grain size in rice. PLoS ONE 13(1):e0190684. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0190684
Obara M, Kaneta Y, Kodama I, Matsumoto S, Kawamoto T, Ishiyama K, Mae T, Makino A (2022) Contribution of the grain size QTL GS3 to yield properties and physiological nitrogen-use efficiency in the large-grain rice cultivar ‘Akita 63.’ Breed Sci. https://doi.org/10.1270/jsbbs.21043
Ring K (2014) The 3,000 rice genomes project. GigaScience 3 (7) 2047. https://doi.org/10.1186/2047-217X-3-7
Sakamoto T, Matsuoka M (2008) Identifying and exploiting grain yield genes in rice. Curr Opin Plant Biol 11(2):209–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2008.01.009
Song Y, Zou G, Li S, Wang H, Liu H, Zhai G, Peng G, Song H, Yan C, Tao Y (2011) Seed size is determined by the combinations of the genes controlling different seed characteristics in rice. Theor Appl Genet 123(7):1173–1181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-011-1657-x
Sun LJ, Li XJ, Fu YC, Zhu ZF, Tan LB, Liu FX, Sun XY, Sun XW, Sun CQ (2013) GS6, a Member of the GRAS gene family, negatively regulates grain size in rice. J Integr Plant Biol 55(10):938–949. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12062
Sun SY, Wang L, Mao HL, Shao L, Li XH, Xiao JH, Ouyang YD, Zhang QF (2018) A G-protein pathway determines grain size in rice. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03141-y
Takano-Kai N, Doi K, Yoshimura A (2011) GS3 participates in stigma exsertion as well as seed length in rice. Breed Sci 61(3):244–250. https://doi.org/10.1270/jsbbs.61.244
Takano-Kai N, Jiang H, Kubo T, Sweeney M, Matsumoto T, Kanamori H, Padhukasahasram B, Bustamante C, Yoshimura A, Doi K, McCouch S (2009) Evolutionary history of GS3, a gene conferring grain length in rice. Genetics 182(4):1323–1334. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.109.103002
Wang SK, Wu K, Yuan QB, Liu XY, Liu ZB, Lin XY, Zeng RZ, Zhu HT, Dong GJ, Qian Q, Zhang GQ, Fu XD (2012) Control of grain size, shape and quality by OsSPL16 in rice. Nat Genet 44(8):950. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2327
Wu L, Wang X, Yu Z, Cui X, Xu Q (2022) Simultaneous improvement of grain yield and quality through manipulating two type C G protein gamma subunits in rice. Int J Mol Sci 23(3):1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031463
Wu K, Xu XP, Zhong N, Huang HX, Yu JP, Ye YF, Wu YJ, Fu XD (2018) The rational design of multiple molecular module-based assemblies for simultaneously improving rice yield and grain quality. J Genet Genomics 45(6):337–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgg.2018.03.007
Xia D, Zhou H, Liu R, Dan W, Li P, Wu B, Chen J, Wang L, Gao G, Zhang Q, He Y (2018) GL3.3, a novel QTL encoding a GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase, Epistatically interacts with GS3 to produce extra-long grains in Rice. Mol Plant 11(5):754–756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2018.03.006
Xu Z, Chen W, Ma D, Lu Y, Zhou S, Liu L (2004) Correlations between Rice Grain shapes and Main qualitative characteristics. ACTA Agron SINICA 30(09):894–900
Xu F, Fang J, Ou SJ, Gao SP, Zhang FX, Du L, Xiao YH, Wang HR, Sun XH, Chu JF, Wang GD, Chu CC (2015) Variations in CYP78A13 coding region influence grain size and yield in rice. Plant Cell Environ 38(4):800–811. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12452
Yang T, Gu H, Yang W, Liu B, Liang S, Zhao J (2023) Artificially selected grain shape gene combinations in Guangdong Simiao varieties of Rice (Oryza sativa L). Rice (NY) 16(1):3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-023-00620-9
Yoon DK, Suganami M, Ishiyama K, Kagawa T, Tanaka M, Nagao R, Takagi D, Ishida H, Suzuki Y, Mae T, Makino A, Obara M (2022) The gs3 allele from a large-grain rice cultivar, Akita 63, increases yield and improves nitrogen-use efficiency. Plant Direct 6(7):e417
Zhang H, Yu F, Xie P, Sun S, Qiao X, Tang S, Chen C, Yang S, Mei C, Yang D, Wu Y, Xia R, Li X, Lu J, Liu Y, Xie X, Ma D, Xu X, Liang Z, Feng Z, Huang X, Yu H, Liu G, Wang Y, Li J, Zhang Q, Chen C, Ouyang Y, Xie Q (2023) A ggamma protein regulates alkaline sensitivity in crops. Science 379(6638):eade8416. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.ade8416
Zhong H, Liu C, Kong W, Zhang Y, Zhao G, Sun T, Li Y (2020) Effect of multi-allele combination on rice grain size based on prediction of regression equation model. Mol Genet Genomics 295(2):465–474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-019-01627-y
Zuo J, Li J (2014) Molecular genetic dissection of quantitative trait loci regulating rice grain size. Annu Rev Genet 48:99–118. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genet-120213-092138
Acknowledgements
Financial support for this research was supported by Research Fund of Maoming Branch, Guangdong Laboratory for Lingnan Modern Agriculture (No. 2022KF003). The author thanks the researchers that constructed the RFGB dataset which provide genotype and phenotype information of Rice 3 K.
Funding
This work was supported by Research Fund of Maoming Branch, Guangdong Laboratory for Lingnan Modern Agriculture (2022KF003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GY and HL designed the project and revised the manuscript. SZ and JZ performed all the experiments, analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. YZ helped revise the manuscript. HL, YL and YZ assisted in conducting experiments. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Zhang, J., Zhang, Y. et al. Mining and effect evaluation and prediction of natural allele combinations of rice grain-size regulating genes. Euphytica 219, 123 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-023-03254-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-023-03254-6