Abstract
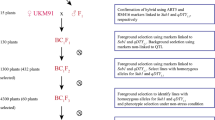
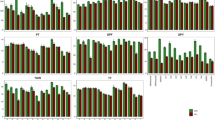
Drought regularly affects rainfed lowland and upland rice ecosystems in Malaysia. Three drought yield QTLs, viz qDTY 2.2 , qDTY 3.1 and qDTY 12.1 successfully pyramided into MRQ74 to increase its yield under reproductive stage drought stress (RS). Forty-eight genotypes comprising 39 pyramided lines (PLs) with different qDTYs combinations, four parents including MRQ74 (recipient) and five checks were evaluated for morpho-physiological traits under RS and non-stress (NS). This study aims to determine which traits influenced by individual qDTY and qDTY combinations and to gain better understanding of QTL interactions in enhancing grain yield (GY) under RS. Results showed plant height, number of panicles, root length, root weight, relative water content and 100-grain weight increased while chlorophyll content and GY decreased under RS compared to NS. No significant difference was observed in days to flowering, leaf rolling and grain length between selected PLs and MRQ74 under RS. Six PLs with yield advantage (YA) of 208.17–1751.63 kg ha−1 compared to MRQ74 in RS but yielded similar to MRQ74 under NS were further selected. Under RS, qDTY class analysis showed qDTY 12.1 individually and combination qDTY 12.1 + qDTY 2.2 produced the highest yield of 1521.77 and 1092.30 kg ha−1 respectively. qDTY 12.1 as single or combination with other qDTY is the best qDTY in stabilizing GY under RS. PL-77 with qDTY 12.1 is the best PL with YA of more than 1100 kg ha−1 compared to MRQ74 in both RS and NS conditions can be recommended for cultivation in normal and drought-prone areas.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernier J, Kumar A, Ramaiah V, Spaner D, Atlin G (2007) A large-effect QTL for grain yield under reproductive-stage drought stress in upland rice. Crop Sci 47(2):507. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2006.07.0495
Bernier J, Kumar A, Venuprasad R, Spaner D, Verulkar S, Mandal NP, Sinha PK, Peeraju P, Dongre PR, Mahto RN, Atlin G (2008) Characterization of the effect of a QTL for drought resistance in rice, qtl12.1, over a range of environments in the Philippines and eastern India. Euphytica 166(2):207–217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-008-9826-y
Bernier J, Serraj R, Kumar A, Venuprasad R, Impa S, Gowda RPV, Oane R, Spaner D, Atlin G (2009) The large-effect drought resistance QTL qtl12.1 increases water uptake in upland rice. Field Crops Res 110:139–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2008.07.010
Blum A (2011) Plant breeding for water-limited environments. Springer, New York
Chang TT, Somrith B, O’Toole JC (1979) Potential for improving drought resistance in rainfed lowland rice. In: International Rice Research Institute, Rainfed lowland rice: selected papers from the 1978 international rice research conference, International Rice Research Institute, Manila, pp 149–164
David CC (1991) The world rice economy: challenges ahead. In: Khush GS, Toenniessen GH (eds) Rice biotechnology. The Alden Press Ltd, Wallingford, pp 1–18
Department of Agriculture (2014) Perangkaan Padi Malaysia 2013. Department of Agriculture, Putrajaya
Department of Agriculture of Perak (2012) Sejarah jenis-jenis padi. http://pertanianmjg.perak.gov.my/bahasa/jenis_padi.htm. Accessed 7 Nov 2015
Dixit S, Singh A, Sta Cruz MT, Maturan PT, Amante M, Kumar A (2014) Multiple major QTL lead to stable yield performance of rice cultivars across varying drought intensities. BMC Genet 15(1):16–28
Dixit S, Kumar Biswal A, Min A, Henry A, Oane RH, Raorane ML, Longkumer T, Pabuayon IM, Mutte SK, Vardarajan AR, Miro B, Govindan G, Albano-Enriquez B, Pueffeld M, Sreenivasulu N, Slamet-Loedin I, Sundarvelpandian K, Tsai YC, Raghuvanshi S, Hsing YI, Kumar A, Kohli A (2015) Action of multiple intra-QTL genes concerted around a co-localized transcription factor underpins a large effect QTL. Sci Rep 5:15183. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep15183
Dixit S, Singh A, Sandhu N, Bhandari A, Vikram P, Kumar A (2017) Combining drought and submergence tolerance in rice: marker-assisted breeding and QTL combination effects. Mol Breed 37:143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-017-0737-2
Fen LL, Ismail MR, Zulkarami B, Abdul Rahman MS, Islam MR (2015) Physiological and molecular characterization of drought responses and screening of drought tolerant rice varieties. Biosci J 31(3):709–718
Fukai S, Pantuwan G, Jongdee B, Cooper M (1999) Screening for drought resistance in rainfed lowland rice. Field Crops Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-4290(99)00051-9
Gomez SM, Bhoopati NM, Kumar SS, Ramasubramaniam T, Chengsong Z, Jayaprakash P, Senthil A, Babu RC (2010) Molecular mapping and location of QTL for drought resistance traits in Indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) lines adapted to target environments. Acta Physiol Plant 32(2):355–364
Guo P, Li M (1996) Studies on photosynthetic characteristics in rice hybrid progenies and their parents. I. Chlorophyll content, chlorophyll-protein complex and chlorophyll fluorescence kinetics. J Trop Subtrop Bot 4:60–65
Ha PTT (2014) Physiological responses of rice seedlings under drought stress. J Sci Dev 12(5):635–640
Hasan MJ, Kulsum MU, Akter A, Masuduzzaman ASM, Ramesha MS (2011) Genetic variability and character association for agronomic traits in hybrid rice (Oryza sativa L.). Bangladesh J Plant Breed Genet 24(1):45–51
Henry A, Dixit S, Mandal NP, Anantha MS, Torres R, Kumar A (2014) Grain yield and physiological traits of rice lines with the drought yield QTL qDTY 12.1 showed different responses to drought and soil characteristics in upland environments. Funct Plant Biol 41(11):1066. https://doi.org/10.1071/fp13324
Henry A, Swamy BP, Dixit S, Torres RD, Batoto TC, Manalili M, Anantha MS, Mandal NP, Kumar A (2015) Physiological mechanisms contributing to the QTL-combination effects on improved performance of IR64 rice NILs under drought. J Exp Bot 66(7):1787–1799. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru506
Huke RE, Huke EH (1997) Rice area by type of culture: South, Southeast, and East Asia: a revised and updated data base. IRRI, Manila
IRRI (2013) Standard evaluation system for rice. IRRI, Los Banos
Jamal K, Kamarulzaman NH, Abdullah AM, Ismail MM, Hashim M (2014) Adoption of fragrant rice farming: the case of paddy farmers in the East Coast Malaysia. UMK Procedia 1:8–17
Kanjoo V, Punyawaew K, Lanceras J, Siangliw JL (2012) Evaluation of agronomic traits in chromosome segment substitution lines of KDML105 containing drought tolerance QTL under drought stress. Rice Sci 19(2):117–124
Kumar R, Venuprasad R, Atlin GN (2007) Genetic analysis of rainfed lowland rice drought tolerance under naturally-occurring stress in eastern India: heritability and QTL effects. Field Crops Res 103(1):42–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2007.04.013
Li G, Zhang J, Yang C, Song Y, Zheng C, Wang S, Liu Z, Ding Y (2014) Optimal yield-related attributes of irrigated rice for high yield potential based on path analysis and stability analysis. Crop J 2(4):235–243
Li X, Guo Z, Lv Y, Cen X, Ding X, Wu H, Li X, Huang J, Xiong L (2017) Genetic control of the root system in rice under normal and drought stress conditions by genome-wide association study. PLoS Genet 13(7):e1006889. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1006889
Luo L, Zhang Q (2000) The status and strategy on drought resistance of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Zhongguo Shuidao Kexue 15(3):209–214
Maisura CMA, Lubis I, Junaedinand A, Ehara H (2014) Some physiological character responses of rice under drought conditions in a paddy system. J Int Soc Southeast Asian Agric Sci 20(1):104–114
Meteorological Department of Malaysia (2017) Buletin Cuaca Bulanan. http://www.met.gov.my/iklim/laporanringkasan/buletincuacabulanan. Accessed 16 Oct 2017
Mishra KK, Vikram P, Yadaw RB, Swamy BPM, Dixit S, Cruz MTS, Maturan P (2013) qDTY12.1: a locus with a consistent effect on grain yield under drought in rice. BMC Genet 14:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2156-14-12
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucl Acids Res 8(19):4321–4325. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/8.19.4321
Mustafa MA, Elsheikh MAY (2007) Variability, correlation and path co-efficient analysis for yield and its components in rice. Afr Crop Sci J 15(4):183–189
Panaud O, Chen X, McCouch S (1996) Development of microsatellite markers and characterization of simple sequence length polymorphism (SSLP) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Gen Genet 252:597–607
Pandey V, Shukla A (2015) Acclimation and tolerance strategies of rice under drought stress. Rice Sci 22(4):147–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsci.2015.04.001
Pantuwan G, Fukai S, Cooper M, Rajatasereekul S, O’Toole JC (2002a) Yield response of rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes to different types of drought under rainfed lowlands. I. Grain yield and yield components. Field Crops Res 73:153–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-4290(01)00187-3
Pantuwan G, Fukai S, Cooper M, Rajatasereekul S, O’Toole JC (2002b) Yield response of rice (Oryza sativa L.) to drought under rainfed lowlands: 2. Selection for drought resistance genotypes. Field Crops Res 73:169–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4290(01)00195-2
Poorter L, Markersteijn L (2008) Seedling traits determining drought tolerance of tropical tree species. Biotropica 40:321–331. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7429.2007.00380.x
Raorane ML, Pabuayon IM, Varadarajan AR, Mutte SK, Kumar A, Treumann A, Kohli A (2015) Proteomic insights into the role of the large-effect QTL qDTY 12.1 for rice yield under drought. Mol Breed 35:139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-015-0321-6
Romyen P, Hanviriyapant P, Rajatasereekul S, Khunthasuvon S, Fukai S, Basnayake J, Skulkhu E (1998) Lowland rice improvement in northern and northeast Thailand. 2. Cultivar differences. Field Crops Res 59:109–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4290(98)00110-5
Shaaban AJB, Sing LK (2003) Drought in Malaysia: a look at its characteristics, impacts, related policies and management strategies. Paper presented at the water and drainage 2003 conference, Kuala Lumpur
Shamsudin NAA, Swamy BPM, Ratnam W, Sta Cruz MT, Raman A, Kumar A (2016a) Marker assisted pyramiding of drought yield QTLs into a popular Malaysian rice cultivar, MR219. BMC Genet 17:30. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-016-0334-0
Shamsudin NAA, Swamy BPM, Ratnam W, Sta Cruz MT, Sandhu N, Raman AK, Kumar A (2016b) Pyramiding of drought yield QTLs into a high quality Malaysian rice cultivar MRQ74 improves yield under reproductive stage drought. Rice 9(1):21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-016-0093-6
Shao HB, Chu LY, Shao MA, Jaleel CA, Mi HM (2008) Higher plant antioxidants and redox signaling under environmental stresses. CR Biol 331(6):433–441
Sikuku P, Onyango J (2012) Physiological and biochemical responses of five nerica rice varieties (Oryza sativa L.) to water deficit at vegetative and reproductive stage. Agric Biol J N Am 3(3):93–104. https://doi.org/10.5251/abjna.2012.3.3.93.104
Suralta RR, Inukai Y, Yamauchi A (2008) Genotypic variations in responses of lateral root development to transient moisture stresses in rice cultivars. Plant Prod Sci 11:324–335. https://doi.org/10.1626/pps.11.324
Swamy BPM, Kumar A (2012) Sustainable rice yield in water-short drought-prone environments: conventional and molecular approaches. In: Lee TS (ed) Irrig Syst Pract Chall Environ. InTech, Shanghai, pp 149–168
Swamy BPM, Kumar A (2013) Genomics-based precision breeding approaches to improve drought tolerance in rice. Biotechnol Adv 31(8):1308–1318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.05.004
Taiz L, Zeiger E (2006) Plant physiology, 4th edn. Sinauer Associates Inc. Publishers, Massachusetts
Venuprasad R, Shashidhar H, Hittalmani S, Hemamalini G (2002) Tagging quantitative trait loci associated with grain yield and root morphological traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under contrasting moisture regimes. Euphytica 128(3):293–300. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:102128142
Venuprasad R, Dalid CO, Del Valle M, Zhao D, Espiritu M, Sta Cruz MT, Amante M, Kumar A, Atlin GN (2009) Identification and characterization of large-effect quantitative trait loci for grain yield under lowland drought stress in rice using bulk-segregant analysis. Theor Appl Genet 120(1):177–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-1168-1
Venuprasad R, Bool ME, Quiatchon L, Atlin GN (2012) A QTL for rice grain yield in aerobic environments with large effects in three genetic backgrounds. Theor Appl Genet 124(2):323–332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-011-1707-4
Visscher PM, Hill WG, Wray NR (2008) Heritability in the genomics era—concepts and misconceptions. Nat Rev Genet 9:255–266. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2322
Wei H, Chen C, Ma X, Zhang Y, Han J, Mei H, Yu S (2017) Comparative analysis of expression profiles of panicle development among tolerant and sensitive rice in response to drought stress. Front Plant Sci 8:437. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00437
Wopereis M, Kropff M, Maligaya A, Tuong T (1996) Drought-stress responses of two lowland rice cultivars to soil water status. Field Crops Res 46(1):21–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-4290(95)00084-4
Wu W, Cheng S (2014) Root genetic research, an opportunity and challenge to rice improvement. Field Crop Res 165:111–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2014.04.013
Yano K, Yamamoto E, Aya K, Takeuchi H, Lo PC, Hu L, Yamasaki M, Yoshida S, Kitano H, Hirano K, Matsuoka M (2016) Genome-wide association study using whole-genome sequencing rapidly identifies new genes influencing agronomic traits in rice. Nat Genet 48(8):927–934. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3596
Zhao X, Qin Y, Sohn JK (2010) Identification of main effects, epistatic effects and their environmental interactions of QTLs for yield traits in rice. Genes Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-010-0786-y
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Faculty of Science and Technology (FST) for the facilities provided, to International Rice Research Institute (IRRI), to Prof. Dr. Wickneswari Ratnam for ideas and encouragement, to all staffs of the laboratories, glasshouse and field. We gratefully acknowledged UKM for the Young Researchers Encouragement Grant (GGPM-2015-008), Centre for Research and Instrumentation (CRIM) and Centre for Collaborative Innovation (PIK) for Economic Transformation Program Research Fund (ETP-2015-002). The first author also would like to thank Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia for Zamalah Yayasan Canselor scheme scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohd Ikmal, A., Nurasyikin, Z., Kumar, A. et al. Evaluation of morpho-physiological traits of MRQ74 pyramided lines with drought yield QTLs. Euphytica 214, 98 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-018-2178-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-018-2178-3