Abstract
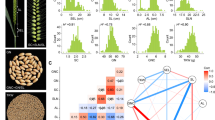
Soybean yield components and agronomic traits are connected through physiological pathways that impose tradeoffs through genetic and environmental constraints. Our primary aim is to assess the interdependence of soybean traits by using unsupervised machine learning techniques to divide phenotypic associations into environmental and genetic associations. This study was performed on large scale, jointly analyzing 14 quantitative traits in a large multi-parental population designed for genetic studies. We collected phenotypes from 2012 to 2015 from a soybean nested association panel with 40 families of approximately 140 individuals each. Pearson and Spearman correlations measured phenotypic associations. A multivariate mixed linear model provided genotypic and environmental correlations. To evaluate relationships among traits, the study used principal component and undirected graphical models from phenotypic, genotypic, and environmental correlation matrices. Results indicate that high phenotypic correlation occurs when traits display both genetic and environmental correlations. In genetic terms, length of reproductive period, node number, and canopy coverage play important roles in determining yield potential. Optimal grain yield production occurs when the growing environment favors faster canopy closure and extended reproductive length. Environmental associations found among yield components give insight into the nature of yield component compensation. The use of unsupervised learning methods provides a good framework for investigating interactions among various quantitative traits and defining target traits for breeding.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DAP:
-
Days after planting
- LASSO:
-
Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator
- MG:
-
Maturity group
- NAM:
-
Nested association mapping
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait loci
- RIL:
-
Recombinant inbred line
- SNP:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism
References
Ali F, Kanwal N, Ahsan M, Ali Q, Bibi I, Niazi NK (2015) Multivariate analysis of grain yield and its attributing traits in different maize hybrids grown under heat and drought stress. Scientifica 2015:1–6
Ball RA, Purcell LC, Vories ED (2000) Short-season soybean yield compensation in response to population and water regime. Crop Sci 40(4):1070–1078
Board JE (2000) Light interception efficiency and light quality affect yield compensation of soybean at low plant populations. Crop Sci 40(5):1285–1294
Board JE, Hall W (1984) Premature flowering in soybean yield reductions at nonoptimal planting dates as influenced by temperature and photoperiod. Agron J 76(4):700–704
Board JE, Harville BG (1993) Soybean yield component responses to a light interception gradient during the reproductive period. Crop Sci 33(4):772–777
Board JE, Kahlon CS (2011) Soybean yield formation: what controls it and how it can be improved? Soybean Physiol Biochem. doi:10.5772/17596
Board JE, Kahlon CS (2012) A proposed method for stress analysis and yield prediction in soybean using light interception and developmental timing. Crop Management 11(1):22
Board JE, Tan Q (1995) Assimilatory capacity effects on soybean yield components and pod number. Crop Sci 35(3):846–851
Board JE, Kamal M, Harville BG (1992) Temporal importance of greater light interception to increased yield in narrow-row soybean. Agron J 84(4):575–579
Board JE, Kang MS, Harville BG (1997) Path analyses of the yield formation process for late-planted soybean. Agron J 91(1):128–135
Borrás L, Slafer GA, Otegui ME (2004) Seed dry weight response to source-sink manipulations in wheat, maize and soybean: a quantitative reappraisal. Field Crops Res 86(2):131–146
Carpenter AC, Board JE (1997) Branch yield components controlling soybean yield stability across plant populations. Crop Sci 37(3):885–891
Chung J, Babka HL, Graef GL, Staswick PE, Lee DJ, Cregan PB, Specht JE (2003) The seed protein, oil, and yield QTL on soybean linkage group I. Crop Sci 43(3):1053–1067
Cober ER, Stewart DW, Voldeng HD (2001) Photoperiod and temperature responses in early-maturing, near-isogenic soybean lines. Crop Sci 41(3):721–727
Concibido V, LaVallee B, Mclaird P, Pineda N, Meyer J, Hummel L, Wang J, Wu K, Delannay X (2003) Introgression of a quantitative trait locus for yield from Glycine soja into commercial soybean cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 106(4):575–582
Crabbe JC, Phillips TJ, Kosobud A, Belknap JK (1990) Estimation of genetic correlation: interpretation of experiments using selectively bred and inbred animals. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 14(2):141–151
Cui S, He X, Fu S, Meng Q, Gai J, Yu D (2008) Genetic dissection of the relationship of apparent biological yield and apparent harvest index with seed yield and yield related traits in soybean. Crop Pasture Sci 59:86–93
DeBruin JL, Pedersen P (2008) Soybean seed yield response to planting date and seeding rate in the Upper Midwest. Agron J 100(3):696–703
DeJong G, VanNoordwijk AJ (1992) Acquisition and allocation of resources: genetic (co) variances, selection, and life histories. Am Nat 139(4):749–770
Diers, B.W., 2014. SoyNAM Project Update. Soybean Breeders Workshop, St. Louis MO. http://soybase.org/meeting_presentations/soybean_breeders_workshop/SBW_2014/presentations/Diers_SBW2014.pdf
Dinkins RD, Keim KR, Farno L, Edwards LH (2002) Expression of the narrow leaflet gene for yield and agronomic traits in soybean. J Hered 93(5):346–351
Dornhoff GM, Shibles RM (1970) Varietal differences in net photosynthesis of soybean leaves. Crop Sci 10(1):42–45
Ecochard R, Ravelomanantsoa Y (1982) Genetic correlations derived from Full-sib relationships in soybean (Glycine max Merr.). Theor Appl Gen 63(1):9–15
Edwards JT, Purcell LC (2005) Soybean yield and biomass responses to increasing plant population among diverse maturity groups. Crop Sci 45(5):1770–1777
Egli DB (1993) Cultivar maturity and potential yield of soybean. Field Crops Res 32(1):147–158
El-Mohsen AAA, Mahmoud GO, Safina SA (2013) Agronomical evaluation of six soybean cultivars using correlation and regression analysis under different irrigation regime conditions. J Plant Breed Crop Sci 5(5):91–102
Elmore RW (1990) Soybean cultivar response to tillage systems and planting date. Agron J 82(1):69–73
Epler M, Staggenborg S (2008) Soybean yield and yield component response to plant density in narrow row systems. Crop Manag. doi:10.1094/CM-2008-0925-01-RS
Falconer DS (1952) The problem of environment and selection. Am Nat 86(830):293–298
Fehr WR, Caviness CE, Burmood DT, Pennington JS (1971) Stage of development descriptions for soybeans, Glycine max (L. Merrill). Crop Sci 11(6):929–931
Fehr WR, Burris JS, Gilman NA (1973) Soybean emergence under field conditions. Agron J 65(5):740–742
Frederick JR, Alm DM, Hesketh JD (1989) Leaf photosynthetic rates, stomatal resistances, and internal CO2 concentrations of soybean cultivars under drought stress. Photosynthetica 23(4):575–584
Frederick JR, Camp CR, Bauer PJ (2001) Drought-stress effects on branch and mainstem seed yield and yield components of determinate soybean. Crop Sci 41(3):759–763
Gay S, Egli DB, Reicosky DA (1980) Physiological aspects of yield improvement in soybeans. Agron J 72(2):387–391
Ghanem ME, Marrou H, Sinclair TR (2014) Physiological phenotyping of plants for crop improvement. Trends Plant Sci 20:139–144
Giglioti ÉA, Sumida CH, Canteri MG (2015) Disease phenomics. Phenomics. Springer, Berlin, pp 101–123
Hall B (2015) Quantitative characterization of canopy coverage in the genetically diverse soybean population. M.Sc. Thesis, Department of Agronomy, Purdue University
Hastie T, Tibshirani R, Friedman J, Franklin J (2005) The elements of statistical learning: data mining, inference and prediction. Math Intell 27(2):83–85
Hazel LN (1943) The genetic basis for constructing selection indexes. Genetics 28(6):476–490
Herbert SJ, Litchfield GV (1982) Partitioning soybean seed yield components. Crop Sci 22(5):1074–1079
Hu G, Liu C, Jiang H, Wang J, Chen Q, Qi Z (2011) Integration of major QTLs of important agronomic traits in soybean. INTECH, Rijeka
James G, Witten D, Hastie T, Tibshirani R (2013) An introduction to statistical learning. Springer, New York
Jin J, Liu X, Wang G, Mi L, Shen Z, Chen X, Herbert SJ (2010) Agronomic and physiological contributions to the yield improvement of soybean cultivars released from 1950 to 2006 in Northeast China. Field Crops Res 115(1):116–123
Johnson HW, Robinson HF, Comstock RE (1955) Estimates of genetic and environmental variability in soybeans. Agron J 47(7):314–318
Jombart T, Devillard S, Balloux F (2010) Discriminant analysis of principal components: a new method for the analysis of genetically structured populations. BMC Genet 11(1):94
Kahlon CS, Board JE (2012) Growth dynamic factors explaining yield improvement in new versus old soybean cultivars. J Crop Improv 26(2):282–299
Koester RP, Skoneczka JA, Cary TR, Diers BW, Ainsworth EA (2014) Historical gains in soybean (Glycine max Merr.) seed yield are driven by linear increases in light interception, energy conversion, and partitioning efficiencies. J Exp Bot 65(12):3311–3321
Kwon SH, Torrie JH (1964) Heritability of and interrelationships among traits of two soybean populations. Crop Sci 4(2):196
Larson EM, Hesketh JD, Woolley JT, Peters DB (1981) Seasonal variations in apparent photosynthesis among plant stands of different soybean cultivars. Photosynth Res 2(1):3–20
Lee SH, Bailey MA, Mian MAR, Carter TE, Ashley DA, Hussey RS, Parrott WA, Boerma HR (1996a) Molecular markers associated with soybean plant height, lodging, and maturity across locations. Crop Sci 36(3):728–735
Lee SH, Bailey MA, Mian MAR, Shipe ER, Ashley DA, Parrott WA, Hussey RS, Boerma HR (1996b) Identification of quantitative trait loci for plant height, lodging, and maturity in a soybean population segregating for growth habit. Theor Appl Genet 92(5):516–523
Lesoing GW, Francis CA (1999) Strip intercropping effects on yield and yield components of corn, grain sorghum, and soybean. Agron J 91(5):807–813
Lynch M, Walsh B (1998) Genetics and analysis of quantitative traits, vol 1. Sinauer, Sunderland
Malausa T, Guillemaud T, Lapchin L (2005) Combining genetic variation and phenotypic plasticity in tradeoff modelling. Oikos 110(2):330–338
Mandl FA, Buss GR (1981) Comparison of narrow and broad leaflet isolines of soybean. Crop Sci 21(1):25–27
Mansur LM, Lark KG, Kross H, Oliveira A (1993) Interval mapping of quantitative trait loci for reproductive, morphological, and seed traits of soybean (Glycine max L.). Theor Appl Genet 86(8):907–913
Mansur LM, Orf JH, Chase K, Jarvik T, Cregan PB, Lark KG (1996) Genetic mapping of agronomic traits using recombinant inbred lines of soybean. Crop Sci 36(5):1327–1336
Meinshausen N, Bühlmann P (2006) High-dimensional graphs and variable selection with the lasso. Ann Stat 34:1436–1462
Misztal I, Tsuruta S, Strabel T, Auvray B, Druet T, Lee DH (2002) BLUPF90 and related programs (BGF90). In: Proceedings of the 7th World Congress on Genetics Applied to Livestock Production, August, 2002. Session 28. Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique (INRA), Montpellier, France, pp 1–2
Ordas B, Malvar RA, Hill WG (2008) Genetic variation and quantitative trait loci associated with developmental stability and the environmental correlation between traits in maize. Genet Res 90(5):385
Palomeque L, Li-Jun L, Li W, Hedges B, Cober ER, Rajcan I (2009a) QTL in mega-environments: I. Universal and specific seed yield QTL detected in a population derived from a cross of high-yielding adapted x high-yielding exotic soybean lines. Theor Appl Genet 119(3):417–427
Palomeque L, Li-Jun L, Li W, Hedges B, Cober ER, Rajcan I (2009b) QTL in mega-environments: II. Agronomic trait QTL co-localized with seed yield QTL detected in a population derived from a cross of high-yielding adapted × high-yielding exotic soybean lines. Theor Appl Genet 119(3):429–436
Panthee DR, Pantalone VR, West DR, Saxton AM, Sams CE (2005) Quantitative trait loci for seed protein and oil concentration, and seed size in soybean. Crop Sci 45(5):2015–2022
Paterson AH (1995) Molecular dissection of quantitative traits: progress and prospects. Genome Res 5(4):321–333
Pedersen P, Lauer JG (2004) Response of soybean yield components to management system and planting date. Agron J 96(5):1372–1381
Peirson BE (2015) Plasticity, stability, and yield: the origins of Anthony David Bradshaw’s model of adaptive phenotypic plasticity. Stud Hist Philos Sci C 50:51–66
Pellet JP, Elisseeff A (2008) Using Markov blankets for causal structure learning. J Mach Learn Res 9:1295–1342
Piepho HP, Möhring J, Melchinger AE, Büchse A (2008) BLUP for phenotypic selection in plant breeding and variety testing. Euphytica 161(1–2):209–228
Purcell LC (2000) Soybean canopy coverage and light interception measurements using digital imagery. Crop Sci 40(3):834–837
R Core Team (2016) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org/
Ramachandra D, Madappa S, Phillips J, Loida P, Karunanandaa B (2015) Breeding and biotech approaches towards improving yield in soybean. In: Davey MR, Daniell H, Azhakanandam K, Silverstone A (eds) Recent advancements in gene expression and enabling technologies in crop plants. Springer, New York, pp 131–192
Recker JR, Burton JW, Cardinal A, Miranda L (2013) Analysis of quantitative traits in two long-term randomly mated soybean populations: I. Genetic Variances. Crop Sci 53(4):1375–1383
Recker JR, Burton JW, Cardinal A, Miranda L (2014) Genetic and phenotypic correlations of quantitative traits in two long-term, randomly mated soybean populations. Crop Sci 54(3):939–943
Richards RA (2000) Selectable traits to increase crop photosynthesis and yield of grain crops. J Exp Bot 51(suppl 1):447–458
Rincker K, Nelson R, Specht J, Sleper D, Cary T, Cianzio SR, Diers B (2014) Genetic improvement of US soybean in maturity groups II, III, and IV. Crop Sci 54(4):1419–1432
Rowntree SC, Suhre JJ, Weidenbenner NH, Wilson EW, Davis VM, Naeve SL, Casteel SN, Diers BW, Esker PD, Specht JE, Conley SP (2013) Genetic gain x management interactions in soybean: I. Planting date. Crop Sci 53(3):1128–1138
Rue H, Held L (2005) Gaussian Markov random fields: theory and applications. CRC Press, Baco Raton
Searle SR (1961) Phenotypic, genetic and environmental correlations. Biometrics 17(3):474–480
Simpson AM, Wilcox JR (1983) Genetic and phenotypic associations of agronomic characteristics in four high protein soybean populations. Crop Sci 23(6):1077–1081
Soares MM, Oliveira GL, Soriano PE, Sekita MC, Sediyama T (2013) Performance of soybean plants as function of seed size: II. Nutritional stress. J Seed Sci 35(4):419–427
Song Q, Yan L, Quigley C, Jordan BD, Fickus E, Schroeder S, Song BH, Charles An YQ, Hyten D, Nelson R, Rainey KM, Beavis WD, Specht JE, Diers BW, Cregan P (2017) Genetic characterization of the soybean nested association mapping population. Plant Genome 10(2):1–14
Sorensen D, Gianola D (2002) Likelihood, Bayesian, and MCMC methods in quantitative genetics. Springer, New York
Spear JD, Fehr WR (2007) Genetic improvement of seedling emergence of soybean lines with low phytate. Crop Sci 47(4):1354–1360
Specht JE, Hume DJ, Kumudini SV (1999) Soybean yield potential: a genetic and physiological perspective. Crop Sci 39(6):1560–1570
Steinsland I, Jensen H (2010) Utilizing Gaussian Markov random field properties of Bayesian animal models. Biometrics 66(3):763–771
Sudaric A, Vrataric M, Duvnjak T (2002) Quantitative genetic analysis of yield components and grain yield for soybean cultivars. Poljoprivreda 2(8):11–15
Swoboda C, Pedersen P (2009) Effect of fungicide on soybean growth and yield. Agron J 101(2):352–356
Ustun A, Allen FL, English BC (2001) Genetic progress in soybean of the US Midsouth. Crop Sci 41(4):993–998
VanRaden PM (2008) Efficient methods to compute genomic predictions. J Dairy Sci 91(11):4414–4423
Vieira SR, Paz-Gonzalez A (2003) Analysis of the spatial variability of crop yield and soil properties in small agricultural plots. Bragantia 62(1):127–138
Wells R (1991) Soybean growth response to plant density: relationships among canopy photosynthesis, leaf area, and light interception. Crop Sci 31(3):755–761
Wilcox JR, Sediyama T (1981) Interrelationships among height, lodging and yield in determinate and indeterminate soybeans. Euphytica 30(2):323–326
Wilson EW, Rowntree SC, Suhre JJ, Weidenbenner NH, Conley SP, Davis VM, Diers BW, Naeve SL, Esker PD, Specht J, Casteel SN (2014) Genetic gain × management interactions in soybean: II. Nitrogen utilization. Crop Sci 54(1):340–348
Wortman SE, Francis CA, Galusha TD, Hoagland C, VanWart J, Baenziger PS, Johnson M et al (2013) Evaluating cultivars for organic farming: maize, soybean, and wheat genotype by system interactions in Eastern Nebraska. Agroecol Sust Food Syst 37(8):915–932
Wu T, Sun S, Wang C, Lu W, Sun B, Song X, Han T (2015) Characterizing changes from a century of genetic improvement of soybean cultivars in Northeast China. Crop Sci 55(5):2056–2067
Xavier A, Xu S, Muir WM, Rainey KM (2015) NAM: association studies in multiple populations. Bioinformatics 31:3862–3864
Xavier A, Muir WM, Rainey KM (2016) Impact of imputation methods on the amount of genetic variation captured by a single-nucleotide polymorphism panel in soybeans. BMC Bioinform 17(1):17–55
Xavier A, Hall B, Hearst A, Cherkauer KA, Rainey KM (2017) Genetic architecture of phenomic-enabled canopy coverage in glycine max. Genetics 206(2):1081–1089
Yan W, Rajcan I (2003) Prediction of cultivar performance based on single-versus multiple-year tests in soybean. Crop Sci 43(2):549–555
Zera AJ, Harshman LG (2001) The physiology of life history trade-offs in animals. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 32:95–126
Zhang WK, Wang YJ, Luo GZ, Zhang JS, He CY, Wu XL, Chen SY et al (2004) QTL mapping of ten agronomic traits on the soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.) genetic map and their association with EST markers. Theor Appl Genet 108(6):1131–1139
Zhang D, Cheng H, Wang H, Zhang H, Liu C, Yu D (2010) Identification of genomic regions determining flower and pod numbers development in soybean (Glycine max L.). J Genet Genom 37(8):545–556
Zhao T, Liu H, Roeder K, Lafferty J, Wasserman L (2012) The huge package for high-dimensional undirected graph estimation in R. J Mach Learn Res 13(1):1059–1062
Funding
United Soybean Board funded the SoyNAM experiment from 2012 to 2013. Dow AgroScience funded the SoyNAM experiment from 2014 to 2015 in Indiana, and the data collection of yield component data from 2013 to 2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xavier, A., Hall, B., Casteel, S. et al. Using unsupervised learning techniques to assess interactions among complex traits in soybeans. Euphytica 213, 200 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-017-1975-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-017-1975-4