Abstract
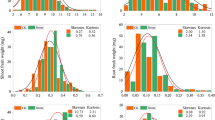
Arsenic phyto-toxicity is a limiting factor affecting rice production in the Indo-Gangetic flood plain. In this study, 98 microsatellite markers were used to map quantitative trait loci (QTL) conferring arsenic phyto-toxicity tolerance (AsT) at seedling stage from a F2 population derived from a cross between an arsenic sensitive indica rice cultivar (BRRI dhan45) and an arsenic tolerant indica rice cultivar (BRRI dhan47) using selective genotyping technique. Arsenic phyto-toxicity tolerance of F2:3 population was assessed with an arsenic stress of 1.25 mg L−1 under hydroponic culture in a climate chamber. AsT indices for shoot length, root length and root-shoot biomass were estimated in terms of comparative growth in treated plants compared to that in control plants. A total of four main effect QTLs with significant LOD comprising two for relative growth in shoot length, one for each of root length and root-shoot biomass under arsenic stress were identified on chromosomes 8 and 12 using composite interval mapping approach. A large effect QTL for arsenic phyto-toxicity tolerance in root length contributing 24.9 % phenotypic variation was identified on chromosome 8 with plausible pleiotropic effect on shoot length and root-shoot biomass.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abedin MJ, Meharg AA (2002) Relative toxicity of arsenite and arsenate on germination and early seedling growth of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Soil 243:57–66
Abedin MJ, Cottep-Howells J, Meharg AA (2002a) Arsenic uptake and accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) irrigated with contaminated water. Plant Soil 240:311–319
Abedin MJ, Cresser MS, Meharg AA, Feldmann J, Cotter-Howells J (2002b) Arsenic accumulation and metabolism in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ Sci Technol 36:962–968
Akter KF, Owens G, Davey DE, Naidu R (2005) Arsenic speciation and toxicity in biological systems. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 184:97–149
Aller A, Bernal JL, Del MJN, Deban L (1990) Effect of selected tree elements on plant growth. J Sci Food Agric 51:447–472
Azad MAK, Islam MN, Alam A, Mahmud H, Islam MA, Karim MR, Rahman M (2009) Arsenic and phytotoxicity of T. Aman rice (Oriza sativa L.) grown in the As-amended soil of Bangladesh. Environ 29:436–440
Bernardo R (2008) Molecular makers and selection for complex traits in plants: learning from the last 20 years. Crop Sci 48:1649–1664
Bhattacharjee Y (2007) A sluggish response to humanity’s biggest mass poisoning. Science 315:1659–1661
Brammer H, Ravenscroft P (2009) Arsenic in groundwater: a threat to sustainable agriculture in South and South–East Asia. Environ Intl 35:647–654
BRRI (Bangladesh Rice Research Institute) (2012) Annual Research Review. Bangladesh Rice Research Institute Gazipur-1701, Bangladesh
Carbonell-Barrachina AA, Burlo-Carbonell F, Mataix-Beneyto J (1995) Arsenic uptake, distribution and accumulation in tomato plants: effect of arsenic on plant growth and yield. J Plant Nutr 18:1237–1250
Carbonell-Barrachina AA, Aarabi MA, Delaune RD, Gambrell RP, Patrick WH Jr (1998) The influence of arsenic chemical form and concentration on Spartina patens and Spartina alterniflora growth and tissue arsenic concentration. Plant Soil 198:33–43
Chatterjee M, Sarkar S, Debnath S, Mukherjee A, Bhattacharya S (2010) Molecular markerlinked with QTLs for arsenic accumulation in rice. In: Abstract: 6th international plant tissue culture and biotechnology conference, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 3–5 February 2010
Churchill GA, Doerge RW (1994) Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138:963–971
Collard BCY, Jahufer MZZ, Brouwer JB, Pang ECK (2005) An introduction to markers, quantitative traits loci (QTL) mapping marker-assisted selection for crop improvement: the basic concept. Euphytica 142:169–196
Dasgupta T, Hossain SA, Meharg AA, Price AH (2004) An arsenate tolerance gene on chromosome 6 of rice. New Phytol 163:45–49
Dittmar J, Voegelin A, Maurer F, Roberts LC, Hug SJ, Saha GC, Ali MA, Badruzzaman ABM, Kretzschmar R (2010) Arsenic accumulation in a paddy field in Bangladesh: seasonal dynamics and trends over a three-year monitoring period. Environ Sci Technol 44:2925–2931
Duxbury JM, Mayer AB, Lauren JG, Hassan N (2003) Food chain aspects of arsenic contamination in Bangladesh: effects on quality and productivity of rice. J Environ Sci Health 38:61–69
Ghandilyan A, Ilk N, Hanhart C, Mbengue M, Barboza L, Schat H, Koornneef M, El-Lithy M, Vreugdenhil D, Reymond M, Aarts MGM (2009) A strong effect of growth medium and organ type on the identification of QTLs for phytate and mineral concentrations in three Arabidopsis thaliana RIL populations. J Exp Bot 60:1409–1425
Hossain MB (2007) Behaviour of arsenic in the soil-plant system. Ph.D. Dissertation, Department of soil science Bangladesh Agricultural University, Mymensingh, Bangladesh, p 126
Hossain K, Delowar M, Yoshida I, Harada M, Sarkar AA, Miah MNH, Razzaque AHM, Uddin MI, Adhana K, Perveen F (2005) Growth and uptake of arsenic by rice irrigated with As-contaminated water. J Food Agric Environ 3:287–291
Islam MR, Jahiruddin M (2010) Effect of arsenic and its interaction with phosphorous on yield and arsenic accumulation in rice. In: 19th world congress of soil science, soil solutions for changing world, Brisbane, Australia, pp 91–94, 1–6 August 2010
Islam MR, Islam S, Jahiruddin M, Islam MA (2004) Effects of irrigation water arsenic in the rice cropping system. J Biol Sci 4:542–546
Jahiruddin M, Islam MA, Islam MR, Islam S (2004) Effects of arsenic contamination on rice crop. Environtropica 1:204–210
Joehanes R, Nelson JC (2008) QGene 4.0, an extensible Java QTL-analysis platform. Bioinformatics 24:2788–2789
Kang LJ, Li XD, Liu JH, Zhang XY (1996) The effect of arsenic on the growth of rice and residues in a loam paddy soil. J Jilin Agric Univ 18:58–61
Khan MA, Islam MR, Panaullah GM, Duxbury JM, Jahiruddin M, Loeppart RH (2010) Accumulation of arsenic in soil and rice under wetland condition in Bangladesh. Plant Soil 333:263–274
Knauer K, Behra R, Hemond H (1999) Toxicity of inorganic and methylated arsenic to algal communities from lakes along an arsenic contamination gradient. Aquat Toxicol 46:221–230
Kuramata M, Abe T, Kawasaki A, Ebana K, Shibaya T, Yano M, Ishikawa S (2013) Genetic diversity of arsenic accumulation in rice and QTL analysis of methylated arsenic in rice grains. Rice 6:1–10
Lander ES, Botstein D (1989) Mapping Mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics 121:185–199
Liu XL, Zhang SZ, Shan XQ, Zhu YG (2005) Toxicity of arsenate and arsenite on germination, seedling growth and amylolytic activity of wheat. Chemosphere 61:93–301
Marin AR, Masscheleya PH, Patrick WH Jr (1992) The influence of chemicals form and concentration of arsenic on rice growth and tissue arsenic concentration. Plant Soil 139:175–183
Marin AR, Masscheleyn PH, Patrick WH (1993) Soil redox-pH stability of arsenic species and its influence on arsenic uptake by rice. Plant Soil 152:245–253
McCouch SR, CGSNL (Committee on Gene Symbolization, Nomenclature and Linkage, Rice Genetics Cooperative) (2008) Gene nomenclature system for rice. Rice 1:72–84
McCouch SR, Chen X, Panaud O, Temnykh S, Xu Y, Cho YG, Huang N, Ishii T, Blair M (1997) Microsatellite marker development, mapping and applications in rice genetics and breeding. Plant Mol Biol 35:88–99
Meharg AA, Hartley-Whitaker J (2002) Arsenic uptake and metabolism in arsenic resistant and nonresistant plant species. New Phytol 154:29–43
Meharg AA, Jardine L (2003) Arsenite transport into paddy rice (Oryza sativa L.) roots. New Phytol 157:39–44
Meharg AA, Rahman MM (2003) Arsenic contamination of Bangladesh paddy soils: implications for rice contribution to arsenic consumption. Environ Sci Technol 37:229–234
Mohammadi R, Mendioro M, Diaz GQ, Gregorio GB, Singh RK (2013) Mapping quantitative trait loci associated with yield and yield components under reproductive stage salinity stress in rice (Oryza sativa L). J Genet 92:433–443
Mondal D, Polya DA (2008) Rice is a major exposure route for arsenic in Chakdaha block, Nadia district, West Bengal, India: a probabilistic risk assessment. Appl Geochem 23:2987–2998
Norton GJ, Deacon CM, Xiong L, Huang S, Meharg AA, Price AH (2010) Genetic mapping of the rice ionome in leaves and grain: identification of QTLs for 17 elements including arsenic, cadmium, iron and selenium. Plant Soil 329:139–153
Odanaka Y, Tsuchiya N, Matano O, Goto S (1987) Absorption, translocation and metabolism of the arsenical fungicides, iron methanearsonate and ammonium iron methanearsonate, in rice plants. J Pestic Sci 12:199–208
Panaullah GM, Alam T, Hossain MB, Loeppert RH, Lauren JG, Meisner CA, Ahmed ZU, Duxbury JM (2009) Arsenic toxicity to rice (Oryza sativa L.) in Bangladesh. Plant Soil 317:31–39
Peng S, Cassman KG, Virmani SS, Sheehy J, Khush GS (1999) Yield potential trends of tropical rice since the release of IR8 and the challenge of increasing rice yield potential. Crop Sci 39:1552–1559
Rahman MA, Rahman MM, Miah MAM, Khaled HM (2004) Influence of soil arsenic concentrations in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Sub-trop Agric Res Dev 2:24–31
Rahman A, Rabbi SMF, Islam S, Kibria KQ, Dowling K, Huq SMI (2005) Arsenic uptake by rice plants in relation to salinity and calcareousness in some soils of Bangladesh. In: Book of abstracts, University of Ballarat, Australia. Annual research conference, held in Ballarat, Victoria, Australia, 9 November 2005
Rahman MA, Hasegawa H, Rahman MM, Islam MN, Miah MAM et al (2007) Effect of arsenic on photosynthesis, growth and yield of five widely cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties in Bangladesh. Chemosphere 67:1072–1079
Rahman MA, Hasegawa H, Rahman MM, Miah MAM, Tasmin A (2008) Straighthead disease of rice (Oryza sativa L.) induced by arsenic toxicity. Environ Exp Bot 62:54–59
Rahman MM, Rahman MA, Maki T, Hasegawa H (2012) Phytotoxicity of arsenate and salinity on early seedling growth of rice (Oryza sativa L.): a threat to sustainable rice cultivation in South and South–East Asia. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 88:695–702
Rauf MA (2009) Influence of soil arsenic on yield and arsenic accumulation in rice and wheat. Ph.D. Dissertation, Department of Soil Science, Bangabandhu Sheik Mujibur Rahman Agricultural University, Gazipur, Bangladesh, pp 124–125
Shri M, Kumar S, Chakrabarty D, Trivedi PK, Mallick S, Misra P, Shukla D, Mishra S, Srivastava S, Tripathi RD, Tuli R (2009) Effect of arsenic on growth, oxidative stress, and antioxidant system in rice seedlings. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:1102–1110
Veldboom LR, Lee M, Woodman WL (1994) Molecular marker facilitated studies in an elite maize population I. Linkage analysis and determination of QTLs for morphological traits. Theor Appl Genet 88:7–16
Virk PS, Ford-Lioyd BV, Jackson MT, Newbury HJ (1995) Use of RAPD for the study of diversity within plant germplasm collections. Heredity 74:170–179
Williams PN, Islam MR, Hussain SA et al (2005) Arsenic absorption by rice. In: Behavior of arsenic in aquifers, soils and plants (Conference Proceedings), Dhaka
Xiao J, Li J, Yuan L, Tanksley SD (1996) Identification of QTLs affecting traits of agronomic importance in a recombinant inbred population derived from a specific rice cross. Theor Appl Genet 92:230–244
Xie ZM, Huang CY (1998) Control of arsenic toxicity in rice plants grown on arsenic polluted paddy soil. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 29:2471–2477
Xue D, Chen M, Zhang C (2009) Mapping of QTLs associated with cadmium tolerance and accumulation during seedling stage in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 165:587–596
Yan FP, Lestari P, Lee KJ, Kim MY, Lee SH, Lee BW (2013) Identification of quantitative trait loci for cadmium accumulation and distribution in rice (Oryza sativa). Genome 56:227–232
Zhang J, Zhu YG, Zeng DL, Cheng WD, Qian Q, Duan GL (2008) Mapping quantitative trait loci associated with arsenic accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa). New Phytol 177:355
Zhi HL, Li QY, Lan CG, Yuan ZY, Ping AY, Doo YJ, Jong KH (2004) QTL analysis of cold tolerance during early growth period of rice. Rice Sci 11:245–250
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support for this research from the United States Dept. of Agriculture Food for Progress Program at Cornell University (FCC-388-2009) and administrative assistance from Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman Agricultural University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Syed, M.A., Iftekharuddaula, K.M., Mian, M.A.K. et al. Main effect QTLs associated with arsenic phyto-toxicity tolerance at seedling stage in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 209, 805–814 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-016-1683-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-016-1683-5