Abstract
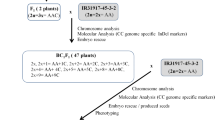
Oryza brachyantha, the African wild rice which is resistant to yellow stem borer (YSB), was exploited as a source for introgression of YSB resistance trait into cultivated rice (O. sativa), through development of monosomic alien addition lines (MAALs). BC2F1 backcross hybrids (O. sativa cv Savitri/O. brachyantha//O. sativa cv Savitri///O. sativa cv Savitri) were produced employing embryo rescue, with a crossability of 0.12 %. Hybrid embryos that were collected at 10 and 12 days after pollination showed highest percentage of survival in culture with a germination percentage of 35.8 %. Cytological analysis of pollen mother cells (PMCs) of the BC2F1 hybrids revealed 15 hybrids with 2n + 1(2n = 25) chromosome number that exhibited typical trisomic chromosomal configurations. These aneuploids were putatively designated as MAALs and characterized morphologically and cytologically. Based on their morphological similarity to primary trisomics of the cultivated rice (O. sativa), 8 MAALs viz., MAALs-4 (Sterile), 5 (Twisted leaf), 7 (Narrow leaf), 8 (Rolled leaf), 9 (Stout), 10 (Short grain), 11 (Pseudonormal) and 12 (Tall) were isolated, each of which exhibited several distinct morphological features. Among the 505 PMCs analysed, 79.80 % had 12II, 5.45 % had 11II and 1.78 % PMCs had 1III configurations. The size of the extra chromosome was found to be smaller than those of O. sativa chromosomes and in 97.25 % of PMCs it remained unpaired and at a distance from the rest of the chromosomes. Of the 8 MAALs screened for YSB resistance, MAAL 11 was found to be moderately resistant. Undesirable morphological traits of O. brachyantha were found to be eliminated in the MAALs.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi FM, Shah AH, Perveen F, Afzal M, Sajid M, Masood R, Nawaz F (2010) Genomic affinity between Oryza sativa and Oryza brachyantha as revealed by in situ hybridization and chromosome pairing. Afr J Biotechnol 9(21):3068–3072
Aggarwal RK, Brar DS, Huang N, Khush GS (1996) Molecular analysis of introgression in Oryza sativa/O. brachyantha and O. sativa/O. granulata derivatives. Int Rice Res Notes 21:2–3
Amante AD, Sitch LA, Nelson R, Dalmacio RD, Oliva NP, Aswidinoor H, Leung H (1992) Transfer of bacterial blight and blast resistance from the tetraploid wild rice Oryza minuta to cultivated rice, Oryza sativa. Theor Appl Genet 84:345–354
Behura N, Sen P, Kar MK (2011) Introgression of yellow stem borer (Scirpophaga incertulas) resistance genes into cultivated rice (Oryza sp.) from wild species. Indian J Agri Sci 81(4):359–362
Brar DS, Khush GS (2002) Transferring genes from wild species into rice. In: Kang MS (ed) Quantitative genetics, genomics and plant breeding. CABI, Wallingford, pp 197–217
Brar DS, Elloran R, Khush GS (1991) Interspecific hybrids produced through embryo rescue between cultivated and eight wild species of rice. Rice Genet News 8:91–93
Brar DS, Dalmacio R, Elloran R, Aggarwal R, Angeles R, Khush GS (1996) Gene transfer and molecular characterization of introgression from wild Oryza species into rice. In: Rice genetics III. IRRI, pp 477–486
Dalmacio R, Brar DS, Ishii T, Sitch LA, Virmani SS, Khush GS (1995) Identification and transfer of a new cytoplasmic male sterility source from Oryza perennis into indica rice (O. sativa). Euphytica 82:221–225
Heinrichs EA, Medranof G, Rapusash R (1985) Genetic evaluation for insect resistance in rice. IRRI, Manila, pp 199–213
Hu CH (1961) Comparative karyological studies of wild and cultivated species of Oryza. Taiwan Prov Coll Agr Mineo, p 104
Hue NTN, Ram T, Barrion AA, Brar DS (2003) Characterization of monosomic alien addition lines of Oryza ridleyi through genomic in situ hybridization using meiotic chromosomes. Rice Genet Newsl 20:110–111
IRRI (2002) Standard evaluation system for rice (SES). International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos
Iyer RD, Govila OP (1964) Embryo culture of interspecific hybrids in the genus Oryza. Indian J Genet Plant Breed 24(2):116–121
Jena KK, Khush GS (1989) Monosomic alien addition lines of rice: production, morphology, cytology, and breeding behavior. Genome 32:449–455
Jena KK, Khush GS (1990) Introgression of genes from Oryza officinalis Well ex Watt to cultivated rice O. sativa L. Theor Appl Genet 80:737–745
Khush GS (2010) Trisomics and alien addition lines in rice. Breed Sci 60:469–474
Khush GS, Ling KC, Aquino RC, Aguiero VM (1977) Breeding for resistance to grassy stunt in rice In: Plant breeding papers: I (46), Proceeding of the 3rd international congress society breeding res Asia Oceania (SABRAO), vol 6, Canberra, pp 3–9
Khush GS, Bacalangco E, Ogawa T (1990) A new gene for resistance to bacterial blight from O. longistaminata. Rice Genet News 7:121–122
Ko SW, Wong CK, Woo SC (1983) A simplified method of embryo rescue in rice of Oryza sativa L. Bot. Bull Acad Sin 24:94–101
Kumari HMPS, Abayarathne WM, Abeysiriwardana DS, De Z (2005) Development of a protocol for embryo rescue in wide hybridization in rice. Ann Sri Lanka Dep Agric 7:157–164
Lu BR, Naredo MEB, Juliano AB, Jackson MT (1998) Taxonomic status of Oryza glumaepatula Steud. III. Assessment of genomic affinity among AA genome species from the new world, Asia, and Australia. Genet Resour Crop Evol 45:215–223
Maqbool SB, Husnain T, Riazuddin S, Masson L, Christou P (1998) Effective control of yellow stem borer and rice leaf folder in transgenic rice indica varieties Basmati 370 and M 7 using the novel δ endotoxin cry2A Bacillus thuringiensis gene. Mol Breed 4(6):501–507
Mohankumar S, Thiruvengadam V, Samiayyan K, Shanmugasundaram P (2003) Generation and screening of recombinant inbred lines of rice for yellow stemborer resistance. Indian J Exp Biol 41:346–351
Multani DS, Jena KK, Brar DS, de Los Reyes BG, Angeles ER, Khush GS (1994) Development of monosomic alien addition lines and introgression of genes from Oryza australiensis. Domin. to cultivated rice O. sativa L. Theor Appl Genet 88:102–109
Multani DS, Khush GS, de Los Reyes BG, Brar DS (2003) Alien genes introgression and development of monosomic alien additional lines from Oryza latifolia Desv. to rice. Theor Appl Genet 107:395–405
Niroula RK, Subedi LP, Sharma RC, Upadhyay MP (2004) Embryo culture for interspecific hybridization in the genus Oryza: a simplified technique of hardening improves the field plant establishment. In: Joshi B K, Joshi SL, Paudyal KP (eds) Agricultural research for enhancing livelihood of nepalese people. Proceedings of 2nd SAS-N Convention, 30 July 2003, Kathmandu, pp 147–152
Padhi G, Sen P (2002) Evaluation of wild rice species against yellow stem borer (Scirpophaga incertulas Walk). J Appl Zoo Res 13(2 & 3):147–148
Pathak MD (1964) Varietal resistance to rice stem borers at IRRI. In: Symposium on the major insect pests of the rice plant, The Johns Hopkins Press, Baltimore, pp 405–408
Pathak MD, Khan ZR (1994) Insect pests of rice. IRRI, Philippines, pp 5–17
Sanchez PL, Wing RA, Brar DS (2013) The wild relative of rice: genomes and genomics. In: Zhang Q, Wing RA (eds) Genetics and genomics of rice, plant genetics and genomics: crops and models 5. Springer Science, New York, pp 9–25
Sarwar M (2013) Valuation of some aromatic rice (Oryza sativa L.) genetic materials to achieve tolerant resources for rice stem borers (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Indian J Sci Res Environ Sci 1(10):285–290
Sastri DC, Mallikarjuna M (1985) Overcoming incompatibility in wide crosses. In: Proceedings of the inter-centre seminar on international agricultural research centres (IARCs) and biotechnology. IRRI, Manila, pp 209–217
Sitch LA, Romero GO, Dalmacio RD (1989) Prefertilization incompatibility barriers in interspecific and intergeneric crosses involving Oryza sativa. Int Rice Res Newsl 14:5–6
Swaminathan MS (1986) Plant research and world agriculture. Plant Mol Biol Rep 4:1–17
Virmani SS, Virktamath BC, Casal CL, Toledo RS, Lopez MT, Monalo JO (1997) Hybrid rice breeding manual. Los Banos, IRRI, p 40
Wuu KD, Jui Y, Lu KCL, Chou C, Li HW (1963) Cytogenetic studies of Oryza sativa L. and its related species. 3. Two intersectional hybrids, O. sativa Linn x O. brachyantha A. Chev et Roehr and O. minuta Presl x O. brachyantha A. Chev et Roehr. Bot Bull Acad Sin 4:51–59
Xiong ZY, Tan GX, He GY, He GC, Song YC (2006) Cytogenetic comparisons between A and G genomes in Oryza using genomic in situ hybridization. Cell Res 16:260–266
Yan H, Xiong Z, Min S, Hu H, Zhang Z, Tian S, Tang S (1997) The transfer of brown planthopper resistance from Oryza eichingeri to O. sativa. Acta Genet Sin 24(5):424–431
Yasui H, Iwata N (1991) Production of monosomic alien addition lines of Oryza sativa having a single O. punctata chromosome In: Rice genetics II: IRRI, Manila, pp 147–155
Acknowledgments
The research work was carried out at the Central Rice Research Institute. It was supported and funded by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Narain, A., Kar, M.K., Kaliaperumal, V. et al. Development of monosomic alien addition lines from the wild rice (Oryza brachyantha A. Chev. et Roehr.) for introgression of yellow stem borer (Scirpophaga incertulas Walker.) resistance into cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 209, 603–613 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-016-1633-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-016-1633-2