Abstract
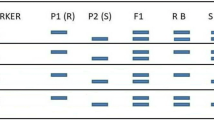
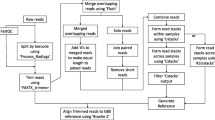
Orphan crops have played a major role in daily diet, health nourishment, economy and livelihood of marginal farmers in under developed and developing world. For various reasons, the majority of these crops including finger millet and tef in cereals; lentil, cowpea and groundnut in legumes; cassava and yam in root crops; have remained neglected and underutilized. With little or no investment these ‘orphan’ crops have lagged far behind in developing genomic resources and are deprived of the application of advanced molecular breeding approaches for their rapid improvement. Single nucleotide polymorphisms, multiple nucleotide polymorphisms, insertions/deletions (indels) and size polymorphisms are important tools for developing rich molecular marker resources. Cataloguing and use of intron based polymorphism have also been demonstrated for applications in molecular breeding. Currently the process of predicting putative introns and designing flanking primers for their amplification requires multiple computer programs and a high level of human intervention. We automated this process by developing intron mapping pipeline (IMP) which allows the generation of large primer sets with minimal human intervention and greater efficiency. Since IMP can take advantage of the highly conserved nature of the introns flanking sequences across a wide range of species, any available model plant genome can be used to predict intron boundaries in related orphan crop species. IMP combined with high resolution melt analysis demonstrated potential for high throughput polymorphism discovery, validation and molecular marker development platform which can generate genomic resources rapidly in orphan species.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Bassam BJ, Caetano-Anollés G, Gresshoff PM (1991) Fast and sensitive silver staining of DNA in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 196:80–83
Cordero D, Peria JB, Saavedra C (2008) Polymorphisms at three introns in the Manila clam (Ruditapes philippinarum) and the grooved carpet-shell clam (R. decussatus). J Shellfish Res 27:301–306
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Feltus FA, Singh HP, Lohithaswa HC, Schulze SR, Silva TD, Paterson AH (2006) A comparative genomics strategy for targeted discovery of single-nucleotide polymorphisms and conserved noncoding sequences in orphan crops. Plant Physiol 140:1183–1191
Florea L, Hartzell G, Zhang Z, Rubin GM, Miller W (1998) A computer program for aligning a cDNA sequence with a genomic DNA sequence. Genome Res 8:967–974
Fredslund J, Madsen LH, Hougaard BK, Sandal N, Stougaard J, Bertioli D, Schauser L (2006) GeMprospector—online design of cross-species genetic marker candidates in legumes and grasses. Nucleic Acids Res 34(Suppl 2):W670–W675. doi:10.1093/nar/gkl201
Galeano CH, Fernandez AC, Gomez M, Blair MW (2009) Single strand conformation polymorphism based SNP and INDEL markers for genetic mapping and synteny analysis of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L). BMC Genom 10:629–643
Gasser RB, Hu M, Chilton NB, Campbell BE, Jex AJ, Otranto D, Cafarchia C, Beveridge I, Zhu X (2007) Single-strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) for genetic variation. Nat Protoc 1:3121–3128
Gepts P, Beavis WD, Brummer EC, Shoemaker RC, Stalker HT, Weeden NF, Young ND (2005) Legumes as a model plant family. Genomics for food and feed report of the cross legume advances through genomics conference. Plant Physiol 137:1228–1235
Hayashi K (1991) PCR-SSCP: a simple and sensitive method for detection of mutations in the genomic DNA. Genome Res 1:34–38
Hsia A-P, Wen T-J, Chen HD, Liu Z, Yandeu-Nelson MD, Wei Y, Guo L, Schnable PS (2005) Temperature gradient capillary electrophoresis (TGCE)—a tool for high throughput discovery and mapping of SNPs and IDPs. Theor Appl Genet 111:218–225
Jayashree B, Jagadeesh VT, Hoisington D (2008) cisPrimerTool: software to implement a comparative genomics strategy for the development of conserved intron scanning markers. Mol Ecol Resour 8:575–577
Kent WJ (2002) BLAT—the BLAST-like alignment tool. Genome Res 4:656–664
Konieczny A, Ansubel F (1993) A procedure for mapping Arabidopsis mutations using co-dominant ecotype-specific markers. Plant J 4:403–410
Krypuy M, Newnham GM, Thomas DM, Conron M, Dobrovic A (2006) High resolution melting analysis for the rapid and sensitive detection of mutations in clinical samples: KRAS codon 12 and 13 mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer 6:295–307
Lee H, An HJ, Yang DC, Kim H, Rhee HG, Harn CH (2012) Development of high resolution melting (HRM) marker linked to genic male sterility in Capsicum annum L. Plant Breed 131:444–448
Mathe C, Sagot M, Schiex T, Rouze P (2002) Current methods of gene predictions, their strengths and weaknesses. Nucleic Acids Res 30:4103–4117
McCallum CM, Comai L, Greene EA, Henikoff S (2000) Targeting induced local lesions in genomes (TILLING) for plant functional genomics. Plant Physiol 123:439–442
Mun JH, Kim DJ, Choi HK, Gish J, Debelle F, Mudge J, Denny R, Endre G, Saurat O, Dudez AM et al (2006) Distribution of microsatellites in the genome of Medicago truncatula: a resource of genetic markers that integrate genetic and physical maps. Genetics 172:2541–2555
Myers RM, Maniatis T, Lerman LS (1987) Detection and localization of single base changes by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol 155:501–527
Naylor RL, Falcon WP, Goodman RM, Jahn MM, Sengooba T, Tefera H, Nelson RJ (2004) Biotechnology in the developing world: a case for increased investments in orphan crops. Food Policy 29:15–44
Nelson RJ, Naylor RL, Jahn MM (2004) The role of genomics research in improvement of “Orphan” crops. Crop Sci 44:1901–1904
Panjabi P, Jagannath A, Bisht NC, Padmaja KL, Sharma S, Gupta V, Pradhan AK, Pental D (2008) Comparative mapping of Brassica juncea and Arabidopsis thaliana using intron polymorphism (IP) markers: homoeologous relationships, diversification and evolution of the A, B and C Brassica genomes. BMC Genom 9:113. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-9-113
RepeatMasker documentation. http://repeatmasker.org/webrepeatmaskerhelp.html
Rice P, Longden I, Bleasby A (2000) EMBOSS: the European molecular biology open software suite. Trends Genet 16:276–277
Rozen S, Skaletsky HJ (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and biologist programmers. In: Misener S, Krawetz SA (eds) Bioinformatics methods and protocols: methods in molecular biology. Humana Press Inc., Totowa, pp 365–386
Till BJ, Zerr T, Comai L, Henikoff S (2006) A protocols for TILLING and EcoTILLING in plants and animals. Nat Protoc 1:2465–2477
Usuka J, Zhu W, Brendel V (2000) Optimal spliced alignment of homologous cDNA to a genomic template. Bioinformatics 16:203–211
Vijayan P, Parkin IAP, Karcz SR, McGown K, Vijayan K, Vandenberg A, Bett KE (2009) Capturing cold stressed related sequence diversity from a wild relative of common bean (Phaseolus angustissimus). Genome 54(8):620–628
White M-B, Carvalho M, Derse D, O’Brien SJ, Dean M (1992) Detecting single base substitution as heteroduplex polymorphism. Genomics 12:301–306
Yang L, Jin G, Zhao X, Zheng Y, Xu Z, Wu W (2007) PIP: a database of potential intron polymorphism. Bioinformatics 23:2174–2177
Young ND, Cannon SB, Sato S, Kim D, Cook DR, Town CD, Roe BA, Tabata S (2005) Sequencing the genespace of Medicago truncatula and Lotus japonicus. Plant Physiol 137:1174–1181
Yu J, Hu S, Wang J, Wong GK, Li S, Liu B, Deng Y, Dai L, Zhou Y, Zhang X et al (2002) A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa spp. indica). Science 296:79–92
Yu JK, La Rota M, Kantety RV, Sorrells ME (2004) EST derived SSR markers for comparative mapping in wheat and rice. Mol Gen Genomics 271:742–751
Acknowledgments
Funded by the Saskatchewan Pulse Growers, Natural Sciences and Engineering Council of Canada (NSERC) and Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada’s ABIP program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sanderson, LA., Sindhu, A., Vijayan, P. et al. IMP-HRM: an automated pipeline for high throughput SNP marker resource development for molecular breeding in orphan crops. Euphytica 200, 197–206 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-014-1144-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-014-1144-y