Abstract
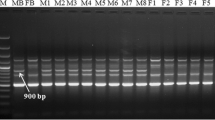
Garden asparagus (Asparagus officinalis L.) is an economically important plant. This species is dioecious, and male plants are considered to be more desirable than females due to their higher yields. To reduce the time required for asparagus breeding, molecular marker techniques have been employed to identify sex-linked DNA markers. In the present study, we converted the male-specific random amplified polymorphic DNA marker T35R54-1600 into a sequence tagged site marker. We cloned a male-specific DNA fragment amplified with the T35R54 primer and determined the sequence of the fragment. The size of T35R54-1600 is 1,586 bp, and this fragment is not homologous to known sex-linked BAC sequences, indicating that this fragment is a new sex-linked region. Within this fragment, we designed the primer pair ‘MSSTS710’ to amplify a 710 bp region. This marker could be used to identify the sex of eight cultivars of A. officinalis: ‘Mary Washington 500W’, ‘UC157’, ‘Harumachi Green’, ‘Super Welcome’, ‘F4’, ‘Pacific 2000’, ‘F2’ and ‘Backlim’. We also analyzed the applicability of this marker to two dioecious Asparagus species, A. schoberioides and A. kiusianus, which are cross-compatible with A. officinalis. Although male-specific DNA fragments of two dioecious Asparagus species, A. schoberioides and A. kiusianus, were generated using the existing male-specific marker Asp1T7sp, no amplicon was obtained using the MSSTS710 marker. Since MSSTS710 can be employed for sex identification only in A. officinalis and not in closely related Asparagus species, the DNA region around the MSSTS710 marker must be variable among Asparagus species.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ellison JH (1986) Asparagus breeding. In: Bassett MJ (ed) Breeding vegetables crops. AVI Publishing Company, Westport, pp 521–569
Falavigna A, Alberti P, Casali PE, Toppino L, Huaisong W, Mennella G (2008) Interspecific hybridization for asparagus breeding in Italy. Acta Hort 776:291–297
Flory WS (1932) Genetic and cytological investigations on Asparagus officinalis L. Genet Princet 17:432–467
Franken AA (1970) Sex characteristics and inheritance of sex in asparagus (Asparagus officinalis L.). Euphytica 19:277–287
Fukuda T, Ashizawa H, Suzuki R, Nakamura T, Ochiai T, Kanno A, Kameya T, Yokoyama J (2005) Molecular phylogeny of the genus Asparagus (Asparagaceae) inferred from plastid petB intron and petD-rpoA intergenic spacer sequences. Plant Species Biol 20:121–132
Honda H, Hirai A (1990) A simple and efficient method for identification of hybrids using nonradioactive rDNA as probe. Jpn J Breed 40:339–348
Ii Y, Uno Y, Kanechi M, Inagaki N (2012a) Screening of sex in asparagus at early growth stages. HortTechnology 22:77–82
Ii Y, Uragami A, Uno Y, Kanechi M, Inagaki N (2012b) RAPD-based analysis of differences between male and female genotypes of Asparagus officinalis. Hort Sci (Prague) 39:33–37
Ito T, Ochiai T, Aizawa H, Shimodate T, Sonoda T, Fukuda T, Yokoyama J, Kameya T, Kanno A (2007) Production and analysis of reciprocal hybrids between Asparagus officinalis L. and A. schoberioides Kunth. Genet Resour Crop Evol 54:1063–1071
Ito T, Konno I, Kubota S, Ochiai T, Sonoda T, Hayashi Y, Fukuda T, Yokoyama J, Nakayama H, Kameya T, Kanno A (2011) Production and characterization of interspecific hybrids between Asparagus kiusianus Makino and A. officinalis L. Euphytica 182:285–294
Jamsari A, Nitz I, Reamon-Büttner SM, Jung C (2004) BAC-derived diagnostic markers for sex determination in asparagus. Theor Appl Genet 108:1140–1146
Jiang C, Sink KC (1997) RAPD and SCAR markers linked to the sex expression locus M in asparagus. Euphytica 94:329–333
Jiang C, Lewis ME, Sink KC (1997) Combined RAPD and RFLP molecular linkage map of asparagus. Genome 40:69–76
Kanno A, Yokoyama J (2011) Asparagus. In: Kole C (ed) Wild crop relatives: genomic and breeding resources, vegetables. Springer, Berlin, pp 23–42
Kubota S, Konno I, Kanno A (2012) Molecular phylogeny of the genus Asparagus (Asparagaceae) explains interspecific crossability between the garden asparagus (A. officinalis) and other Asparagus species. Theor Appl Genet 124:345–354
Lewis ME, Sink KC (1996) RFLP linkage map of asparagus. Genome 39:622–627
Löptien H (1979) Identification of the sex chromosome pair in asparagus (Asparagus offcinalis L.). Z Pflanzensüchtg 82:162–173
Nakayama H, Ito T, Hayashi Y, Sonoda T, Fukuda T, Ochiai T, Kameya T, Kanno A (2006) Development of sex-linked primers in garden asparagus (Asparagus officinalis L.). Breed Sci 56:327–330
Ochiai T, Sonoda T, Kanno A, Kameya T (2002) Interspecific hybrids between Asparagus schoberioides Kunth and A. officinalis L. Acta Hort 589:225–229
Penner GA, Bush A, Wise R, Kim W, Domier L, Kasha K, Laroche A, Scoles G, Molnar SJ, Fedak G (1993) Reproducibility of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis among laboratories. Genome Res 2:341–345
Reamon-Büttner SM, Jung C (2000) AFLP-derived STS markers for the identification of sex in Asparagus officinalis L. Theor Appl Genet 100:432–438
Reamon-Büttner SM, Schondelmaier J, Jung C (1998) AFLP markers tightly linked to the sex locus in Asparagus officinalis L. Mol Breed 4:91–98
Restivo FM, Tassi F, Biffi R, Falavigna A, Caporali E, Carboni A, Doldi ML, Spada A, Marziani GP (1995) Linkage arrangement of RFLP loci in progenies from crosses between double haploid Asparagus officinalis L. clones. Theor Appl Genet 90:124–128
Shiobara Y, Yoshino M, Uragami A, Widiastuti A, Omori A, Kuba K, Saito H, Hirata Y, Sonoda T, Koizumi T, Sato T (2011) Sex distinction of asparagus by loop-mediated isothermal amplification and observation of seedling phenotypes. Euphytica 177:91–97
Sinton SM, Wilson DR (1999) Comparative performance of male and female plants during the annual growth cycle of a dioecious asparagus cultivar. Acta Hort 479:347–353
Sneep J (1953a) The significance of andromonoecy for the breeding of Asparagus officinalis L. Euphytica 2:89–172
Sneep J (1953b) The significance of andromonoecy for the breeding of Asparagus officinalis L. II. Euphytica 2:224–228
Stajner N, Bohanec B, Javornik B (2002) Genetic variability of economically important Asparagus species as revealed by genome size analysis and rDNA ITS polymorphisms. Plant Sci 162:931–937
Stewart CN Jr, Via LE (1993) A rapid CTAB DNA isolation technique useful for RAPD fingerprinting and other PCR amplifications. Biotechniques 14:748–750
Telgmann-Rauber A, Jamsari A, Kinney MS, Pires JC, Jung C (2007) Genetic and physical maps around the sex-determining M-locus of the dioecious plant asparagus. Mol Genet Genomics 278:221–234
Zhou JS, Zhan FX, Tang YP, Luo SC, Sheng WT, Chen GY (2009) Interspecific hybridization between A. officinalis L. and Asparagus dauricus Fisch.ex link. In: XIIth international asparagus symposium, Lima
Acknowledgments
We gratefully thank Drs. Takahiro Sonoda (Rakuno Gakuen University, Japan) and Yuichi Uno (Kobe University, Japan) for helpful discussion. This work was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant Number 23380015 and a Grant-in-Aid for JSPS Fellows (to S.K.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanno, A., Kubota, S. & Ishino, K. Conversion of a male-specific RAPD marker into an STS marker in Asparagus officinalis L.. Euphytica 197, 39–46 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-013-1048-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-013-1048-2