Abstract
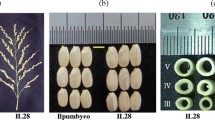
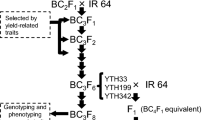
Total spikelet number per panicle (TSN) is thought to be one of the most important agronomic traits associated with grain production in rice (Oryza sativa L.). We previously reported the development of 334 introgression lines (ILs) with variations in agronomic traits in the genetic background of indica rice variety IR64. Among these, an IL derived from high-yielding rice variety Hoshiaoba showed significantly higher TSN than IR64. We therefore have conducted a quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis for TSN in an F2 population of IL × IR64 to ascertain the genetic basis for the high TSN of the IL. The analysis revealed the presence of a QTL for TSN on chromosome 7, where several QTLs for grain number have been previously reported. We developed a near-isogenic line (NIL) for this QTL by using DNA marker-assisted selection and characterized its effect. The NIL showed significantly higher TSN than IR64. These results suggest that the QTL and the NIL will be useful materials in breeding programs aimed at increasing TSN.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allard RW (1956) Formulas and tables to facilitate the calculation of recombination values in heredity. Hilgardia 24:235–278
Ashikari M, Sakakibara H, Lin S et al (2005) Cytokinin oxidase regulates rice grain production. Science 309:741–745
Bai X, Luo L, Yan W et al (2010) Genetic dissection of rice grain shape using a recombinant inbred line population derived from two contrasting parents and fine mapping a pleiotropic quantitative trait locus qGL7. BMC Genet 11:16
Fujita D, Santos RE, Ebron LA et al (2009) Development of introgression lines of an Indica-type rice variety, IR64, for unique agronomic traits and detection of the responsible chromosomal regions. Field Crops Res 114:244–254
Fujita D, Santos RE, Ebron LA et al (2010a) Development and characterization of introgression lines of an Indica-type rice variety, IR64, for unique agronomic traits. Jpn Int Res Cent Agric Sci Work Rep 66:1–95
Fujita D, Santos RE, Ebron LA et al (2010b) Characterization of introgression lines for yield-related traits with Indica-type rice variety IR64 genetic background. JARQ 44:277–290
Fujita D, Rizza SE, Ebron LA et al (2011) Characterization of quantitative trait locus for days to heading in near-isogenic lines with genetic background of Indica-type rice variety IR64 (Oryza sativa). Plant Breed 130:526–532
Guiderdoni E, Galinato E, Luistro J et al (1992) Anther culture of tropical japonica × indica hybrids of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 62:219–224
Huang X, Qian Q, Liu Z et al (2009) Natural variation at the DEP1 locus enhances grain yield in rice. Nature Genet 41:494–497
Ikeda K, Ito M, Nagasawa N et al (2007) Rice ABERRANT PANICLE ORGANIZATION 1, encoding an F-box protein, regulates meristem fate. Plant J 51:1030–1040
Ikeda-Kawakatsu K, Yasuno N, Oikawa T et al (2009) Expression level of ABERRANT PANICLE ORGANIZATION1 determines rice inflorescence form through control of cell proliferation in the meristem. Plant Physiol 150:736–747
Jiang GH, Xu CG, Li XH et al (2004) Characterization of the genetic basis for yield and its component traits of rice revealed by doubled haploid population. Acta Genetica Sinica 31:63–72
Jiao Y, Wang Y, Xue D et al (2010) Regulation of OsSPL14 by OsmiR156 defines ideal plant architecture in rice. Nature Genet 42:541–544
Khush GS (1987) Rice breeding: past, present and future. J Genet 66:195–216
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distance from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Liu GF, Li M, Wen J et al (2010) Functional mapping of quantitative trait loci associated with rice tillering. Mol Genet Genomics 284:263–271
Maeda H, Sunohara Y, Iida S et al (2003) A new rice cultivar for whole crop silage, ‘Hoshiaoba’ (in Japanese, with English summary). Bull Natl Agric Res Cent West Reg, Fukuyama 2:83–98
McCouch SR, Teytelman L, Xu Y et al (2002) Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L.). DNA Res 9:199–207
Mei HW, Xu JL, Li ZK et al (2006) QTLs influencing panicle size detected in two reciprocal introgressive line (IL) populations in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 112:648–656
Miura K, Ikeda M, Matsubara A et al (2010) OsSPL14 promotes panicle branching and higher grain productivity in rice. Nat Genet 42:545–549
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high-molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Obara M, Kajiura M, Fukuta Y et al (2001) Mapping of QTLs associated with cytosolic glutamine synthetase and NADH-glutamate synthase in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Exp Bot 52:1209–1217
Ookawa T, Hobo T, Yano M et al (2010) New approach for rice improvement using a pleiotropic QTL gene for lodging resistance and yield. Nat Commun 1:132
Song XJ, Huang W, Shi M et al (2007) A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nat Genet 39:623–630
Uga Y, Okuno K, Yano M (2008) QTLs underlying natural variation in stele and xylem structures of rice root. Breed Sci 58:7–14
Wang S, Basten CJ, Zeng ZB (2011) Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh. Available at: http://statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm
Wu JL, Wu C, Lei C et al (2005) Chemical- and irradiation-induced mutants of indica rice IR64 for forward and reverse genetics. Plant Mol Biol 59:85–97
Xue W, Xing Y, Weng X et al (2008) Natural variation in Ghd7 is an important regulator of heading date and yield potential in rice. Nature Genet 40:761–767
Acknowledgments
This paper reports the results obtained in the IRRI–Japan Collaborative Research Project (phases III, IV, V, and VI), which was funded by the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries through the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan. This work was partially supported by Research Fellowships from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science for Young Scientists (22-6429 for Y.K. and 23-7274 for D.F.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koide, Y., Fujita, D., Tagle, A.G. et al. QTL for spikelet number from a high-yielding rice variety, Hoshiaoba, detected in an introgression line with the genetic background of an indica rice variety, IR64. Euphytica 192, 97–106 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-013-0882-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-013-0882-6