Abstract
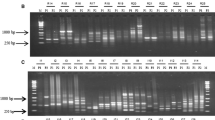
Pea powdery mildew is one of the major constraints in pea production worldwide, causing severe seed yield and quality loss. The resistance is governed by a single recessive gene er1 in majority of resistant cultivars, but er2 and Er3 have also been reported. The objective of the study was to find out tightly linked sequence characterized amplified regions (SCAR) markers to er1 gene using NILs. A total of 620 random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers were screened for length polymorphism between seven sets of NILs. The 880 bp polymorphic band of the tightly linked RAPD marker OPX 04880 was cloned, sequenced and a SCAR marker ScOPX 04880 was developed. In a population of completely classified 208 F2 plants (supported by phenotypic data from 208 F2:3 and 4,390 F3:4 families) ScOPX 04880 was linked at 0.6 cM in coupling phase with er1 gene in the order ScOPX 04880–er1–ScOPD 10650. ScOPX 04880 will correctly differentiate homozygous resistant plants from the susceptible accessions with more than 99 % accuracy. In combination with repulsion phase marker ScOPD 10650, ScOPX 04880 can help in an error free marker-assisted selection.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Superscript indicates the donor parent for powdery mildew susceptible (PMS) or resistant (PMR) trait.
References
Akkurt M, Welter L, Maul E, Töpfer R, Zyprian E (2007) Development of SCAR markers linked to powdery mildew (Uncinula necator) resistance in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L. and Vitis sp.). Mol Breed 19:103–111
Barret P, Delourme R, Foisset N, Renard M (1998) Development of a SCAR (sequence characterized amplified region) marker for molecular tagging of the dwarf BREIZH (Bzh) gene in Brassica napus L. Theor Appl Genet 97:828–833
Braun V (1980) A monograph of Erysiphales (powdery mildews). Nova Hedwigia (Suppl) no. 89. Stuttgart
Cook RTA, Fox RTU (1992) Erysiphe pisi var. pisi of faba bean and other legumes in Britain. Plant Pathol 41:506–512
Cousin R (1965) Resistance to powdery mildew in pea. Ann Amélior Plantes 15:93–97
Dixon GR (1978) Powdery mildew of vegetable and allied crops. In: Spencer DM (ed) The powdery mildews. Academic Press, London, pp 475–524
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Ek M, Eklund M, von Post R, Dayteg C, Henriksson T, Weibull P, Ceplitis A, Isaac P, Tuvesson S (2005) Microsatellite markers for powdery mildew resistance in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Hereditas 142:86–89. doi:10.1111/j.1601-5223.2005.01906.x
Fondevilla S, Moreno MT, Carver TLW, Rubiales D (2006) Macroscopic and histological characterisation of genes er1 and er2 for powdery mildew resistance in pea. Eur J Plant Pathol 115:309–321. doi:10.1007/s10658-006-9015-6
Fondevilla S, Rubiales D, Moreno MT, Torres AM (2008) Identification and validation of RAPD and SCAR markers linked to the gene Er3 conferring resistance to Erysiphe pisi DC in pea. Mol Breed 22:93–200. doi:10.1007/s11032-008-9166-6
Giovanni C-B, Víctor N (2007) SCAR marker for the sex types determination in Colombian genotypes of Carica papaya. Euphytica 153:215–220
Gupta MD (1987) Inheritance of powdery mildew resistance in pea (Pisum sativum L.). PhD Thesis, Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi
Gupta S, Charpe A, Koul S, Haque QMR, Prabhu KV (2006) Development and validation of SCAR markers co-segregating with an Agropyron elongatum derived leaf rust resistance gene Lr24 in wheat. Euphytica 150:233–240
Gutierrez N, Avila CM, Rodriguez-Suarez C, Moreno MT, Torres AM (2007) Development of SCAR markers linked to a gene controlling absence of tannins in faba bean. Mol Breed 19:305–314
Hamdan YAS, Velasco L, Pérez-Vich B (2008) Development of SCAR markers linked to male sterility and very high linoleic acid content in safflower. Mol Breed 22:385–393
Hammarlund C (1925) Zur Genetik, biologic und physiologic einiger Erysiphaeceen. Hereditas 6:1–126
Harland SC (1948) Inheritance of immunity to powdery mildew in Peruvian forms of Pisum sativum. Heredity 2:263–269
Heringa RJ, van Norel A, Tazelaar MF (1969) Resistance to powdery mildew (E. Polygoni D.C.) in peas (Pisum sativum L.). Euphytica 18:163–169
Humphry M, Reinstädler A, Ivanov S, Bisseling T, Panstruga R (2011) Durable broad-spectrum powdery mildew resistance in pea er1 plants is conferred by natural loss-of-function mutations in PsMLO1. Mol Plant Pathol. doi:10.1111/j.1364-3703.2011.00718.x
Janila P, Sharma B (2004) RAPD and SCAR markers for powdery mildew resistance gene er in pea. Plant Breed 123:271–274. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0523.2004.00963.x
Jones N, Ougham H, Thomas H, Pašakinskienė I (2009) Markers and mapping revisited: finding your gene. New Phytol. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.02933.x
Katoch V, Sharma S, Pathania S, Banayal DK, Sharma SK, Rathour R (2010) Molecular mapping of pea powdery mildew resistance gene er2 to pea linkage group III. Mol Breed 25:229–237
Kim GH, Yun HK, Choi C, Park JH, Jung YJ, Park KS, Dane F, Kang KK (2008) Identification of AFLP and RAPD markers linked to anthracnose resistance in grapes and their conversion to SCAR markers. Plant Breed 127:418–423
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map units from recombination values. Ann Eugen Lond 12:172–175
Kraft JM, Pfleger FL (2001) Compendium of pea diseases and pests, 2nd edn. APS Press, Saint Paul
Kumar H, Singh RB (1981) Genetic analysis of adult plant resistance to powdery mildew in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Euphytica 30:147–151. doi:10.1007/BF00033671
Lander E, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newberg LA (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Martin GB, Williams JGK, Tanksley SD (1991) Rapid identification of markers linked to Pseudomonas resistance gene in tomato by using random primers and near-isogenic lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:2336–2340
Marx GA (1971) New linkage relations for chromosome III of Pisum sativum. Pisum Newslett 3:18–19
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9828–9832
Mikolajczyk K, Dabert M, Nowakowska J, Podkowinski J, Poplawska W, Bartkowiak-Broda I (2008) Conversion of the RAPD OPC021150 marker of the Rfo restorer gene into a SCAR marker for rapid selection of oilseed rape. Plant Breed 127:647–649
Mishra SP, Shukla P (1984) Inheritance of powdery mildew resistance in pea. Z Pflanzenzuchtg 93:251–254
Negi MS, Devic M, Delseny M, Lakshmikumaran M (2000) Identification of AFLP fragments linked to seed coat colour in Brassica juncea and conversion to SCAR marker for rapid selection. Theor Appl Genet 101:146–152
Park SO, Steadman JR, Coyne DP, Crosbya KM (2008) Development of a coupling-phase SCAR marker linked to the Ur-7 rust resistance gene and its occurrence in diverse common bean lines. Crop Sci 48:357–363
Pereira G, Marques C, Ribeiro R, Formiga S, Dâmaso M, Sousa TM, Farinhó M, Leitão JM (2010) Identification of DNA markers linked to an induced mutated gene conferring resistance to powdery mildew in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Euphytica 171:327–335
Pierce WH (1948) Resistance to powdery mildew in peas. Phytopathology 38:21
Rakshit S (1997) Biochemical and molecular analysis of powdery mildew resistance in pea (Pisum sativum L.). PhD thesis, I.A.R.I., New Delhi
Rathi AS, Tripathi NN (1994) Assessment of growth reduction and yield losses in peas (Pisum sativum L.) due to powdery mildew disease caused by Erysiphe polygoni D.C. Crop Reis 8(2):372–376
Ray T, Chandra S (2009) Genetic diversity of Amaranthus species from the Indo-Gangetic Plains revealed by RAPD analysis leading to the development of ecotype-specific SCAR marker. J Hered 100:338–347
Reiling TP (1984) Powdery mildews. In: Hagedorn DJ (ed) Compendium of pea diseases. American Phytopathological Society, St. Paul, pp 21–22
Saal B, Struss D (2005) RGA- and RAPD-derived SCAR markers for a Brassica B-genome introgression conferring resistance to blackleg in oilseed rape. Theor Appl Genet 111:281–290
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Sarala K (1993) Linkage studies in pea (Pisum sativum L.) with reference to er gene for powdery mildew resistance and other genes. PhD Thesis, Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi
Saxena JK, Tripathi RM, Srivastava RL (1975) Powdery mildew resistance in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Curr Sci 44:746
Sharma B (1997) Other pulses. In: Paroda RS, Chadha KL (eds) 50 years of crop science research in India. Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi, pp 279–317
Sharma B (2003) The Pisum genus has only one recessive gene for powdery mildew resistance. Pisum Genet 35:22–27
Sharma B, Yadav Y (2003) Pisum fulvum carries a recessive gene for powdery mildew resistance. Pisum Genet 35:30
Singh MP (1984) Genetics of resistance to powdery mildew (E. polygoni DC), combining ability and heterosis in peas (Pisum sativum L.). PhD Thesis, G.B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology, Pantnagar
Singh RB, Singh MN, Singh UP, Singh RM (1983) Inheritance of resistance to powdery mildew in pea and its use in breeding. Indian J Agric Sci 53:855–856
Singh M, Chaudhary K, Boora K (2006) RAPD-based SCAR marker SCA 12 linked to recessive gene conferring resistance to anthracnose in sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]. Theor Appl Genet 114:187–192
Sokhi SS, Jhooty JS, Bains SS (1979) Resistance in pea against powdery mildew. Indian Phytopathol 32:571–574
Srivastava RK, Mishra SK (2004) Inheritance of powdery mildew resistance using near-isogenic lines (NILs) in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Indian J Genet 64(4):303–305
Timmerman GM, Frew TJ, Weeden NF (1994) Linkage analysis of er 1 a recessive Pisum sativum gene for resistance to powdery mildew fungus (Erysiphe pisi D.C.). Theor Appl Genet 88:1050–1055
Tiwari KR, Penner GA, Warkentin TD (1997) Inheritance of powdery mildew resistance in pea. Can J Plant Sci 77:307–310
Tiwari KR, Penner GA, Warkentin TD (1998) Identification of coupling and repulsion phase RAPD markers for powdery mildew resistance gene er-1 in pea. Genome 41:440–444
Vaid A, Tyagi PD (1997) Genetics of powdery mildew resistance in pea. Euphytica 96:203–206
Vinod MS, Raghavan PS, George S, Parida A (2007) Identification of a sex-specific SCAR marker in dioecious Pandanus fascicularis L. (Pandanaceae). Genome 50:834–839
Williams JGK, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucl Acids Res 18:6531–6535
Yarnell SH (1962) Cytogenetics of vegetable crops. III. Legumes. Bot Rev 28:467–537
Young D, Zamin M, Ganae W, Tanksley SD (1988) Use of isogenic lines and simultaneously probing to identify DNA markers tightly linked to the Tm-2a gene in tomato. Genetics 120:579–585
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. N.K. Singh, National Research Centre on Plant Biotechnology (NRCPB), New Delhi, India for his help and valuable suggestions in the course of the study. Rakesh K. Srivastava gratefully acknowledges SRF grant from the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), India; and IARI fellowship from the Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI), New Delhi, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srivastava, R.K., Mishra, S.K., Singh, A.K. et al. Development of a coupling-phase SCAR marker linked to the powdery mildew resistance gene ‘er1’ in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Euphytica 186, 855–866 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-012-0650-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-012-0650-z