Abstract
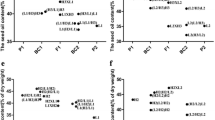
The dynamic expression of genes for oil and protein contents of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) was carried out with time-dependent measures by using the developmental genetic models for quantitative traits in diploid plant. The unconditional and conditional analysis showed that the accumulated genetic effects or net genetic effects from diploid embryo nuclear genes, cytoplasmic genes and diploid maternal plant nuclear genes were all important for the performance of both nutrient quality traits at most developmental times/stages. Results from the conditional analysis further revealed that the activation of quantitative genes was gradually carried through the developmental process with maternal genes playing more active role at most developmental stages. Additive effects from embryo and maternal plant were found more important than the dominant effects at most developmental times/stages for both traits, and especially for protein content of rapeseed. Heritability analysis confirmed that the maternal heritability for protein contents were considerably stronger throughout developmental period except for the developmental time at 22 days, while for oil content the heritability components were dynamic and time dependent. The differences of genetic relationships from various genetic systems were found for oil and protein contents among the developmental times or between the two quality traits.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atchley WR, Zhu J (1997) Developmental quantitative genetics, conditional epigenetic variability and growth in mice. Genetics 147:765–776
Atchley WR, Xu S, Vogl C (1994) Developmental quantitative genetic models of evolutionary change. Dev Genet 15:92–103. doi:10.1002/dvg.1020150110
Brandle JE, McVetty PBE (1988) Effects of inbreeding and estimates of additive genetic variance within seven summer oilseed rape cultivars. Genome 32:115–119
Cowley DE, Atchley WR (1992) Quantitative genetic models for development, epigenetic selection and phenotypic evolution. Evol Int J Org Evol 46:495–518. doi:10.2307/2409867
Gao QY (1994) The relationship of DNA content in corn endosperm nuclei to kernel traits during kernel development. Acta Agron Sin 20(1):46–51
Grami B, Stefansson BR (1977) Paternal and maternal effects on protein and oil content in summer rape. Can J Plant Sci 57:945–949
Han JX (1990) Genetic analysis on oil content in rapeseed (Brassica napus L). Oil Crop China 2:1–6
Henderson CR (1985) Best linear unbiased prediction using numerator relationship matrices derived for selected base populations. J Dairy Sci 68:443–448
Mc Vetty PBE, Pinnisch R (1994) Comparison of the effect of nap and pol cytoplasms on the performance of three summer oilseed rape cultivar-derived isoline pairs. Can J Plant Sci 74:729–731
Mendham NJ, Salisbury PA (1995) Crop development, growth and yield. In: Kimber D, Mc Gregor DI (eds) Brassica oilseeds: production and utilization. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Miller RG (1974) The Jackknife: a review. Biometrika 61:1–15
Pai R, Kumar P (1991) Estimates of gene effects of oil content under normal and late sowing in mustard (Brassica juncea). Indian J Agron Sci 61:918–921
Shi CH, Wu JG, Lou XB, Zhu J, Wu P (2002) Genetic analysis of transparency and chalkiness area at different filling stages of rice (Oryza sative L.). Field Crops Res 76:1–9. doi:10.1016/S0378-4290(02)00011-4
Shi CH, Wu JG, Wu P (2005) Genetic analysis of developmental behavior for amylose content in filling process of rice. J Sci Food Agric 85:791–796. doi:10.1002/jsfa.2027
Shi CH, Ge GK, Wu JG, Ye J, Wu P (2006) The dynamic gene expression from different genetic systems for protein and lysine contents of indica rice. Genetica 128:297–306. doi:10.1007/s10709-006-6276-0
Wang TQ (1992) The heredity of oil content and its heterosis in rapeseed. J Guizhou Agric Sci 6:37–40
Wu JG (2003) NIR spectroscopy model construction and application in the research of crop seed qualities. PhD thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou
Wu JG, Shi CH, Zhang HZ, Fan LJ (2002) Study on analysis of oil content in intact rapeseed with few sample size by near infrared reflectance spectroscopy. Acta Agron Sin 28(3):421–425
Wu JG, Shi CH, Zhang HZ (2005) Genetic analysis of embryo, cytoplasmic, and maternal effects and their environment interactions for protein content in Brassica napus L. Aust J Agric Res 56:69–73. doi:10.1071/AR04089
Wu JG, Shi CH, Zhang HZ (2006) Partioning genetic effects due to embryo, cytoplasm and maternal parent for oil content in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Genet Mol Biol 29:533–538. doi:10.1590/S1415-47572006000300023
Yang TX, Zeng MQ (1984) The changes of isozyme, soluble protein and the dry matter accumulation during endosperm and embryo development in Maize. Acta Phytophysiol Sin 10(1):77–86
Zhu J (1995) Analysis of conditional genetic effects and variance components in development genetics. Genetics 141:1633–1639
Zhu J, Weir BS (1994) Analysis of cytoplasmic and maternal effects. I. A genetic model for diploid plant seeds and animals. Theor Appl Genet 89:153–159
Zhu J, Weir BS (1996) Diallel analysis for sex-linked and maternal effects. Theor Appl Genet 92:1–9. doi:10.1007/BF00222944
Acknowledgments
The project was financially supported from Technology Office of Zhejiang Province (No. 2008C22084), Foundation for University Key Teacher by the Ministry of Education and 151 Foundation for the Talents of Zhejiang Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
M. T. Variath and J. G. Wu are contributed equally to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Variath, M.T., Wu, J.G., Li, Y.X. et al. Genetic analysis for oil and protein contents of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) at different developmental times. Euphytica 166, 145–153 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-008-9851-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-008-9851-x